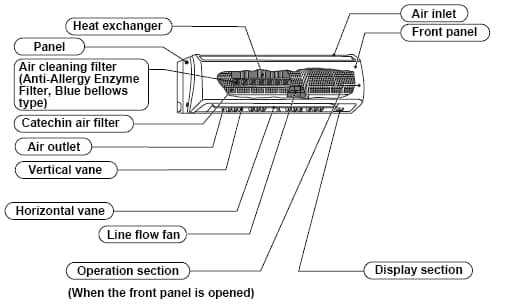
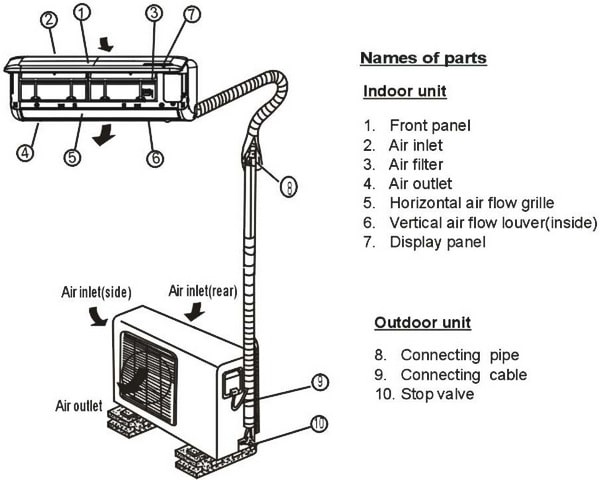
Ac Parts Name List With Picture
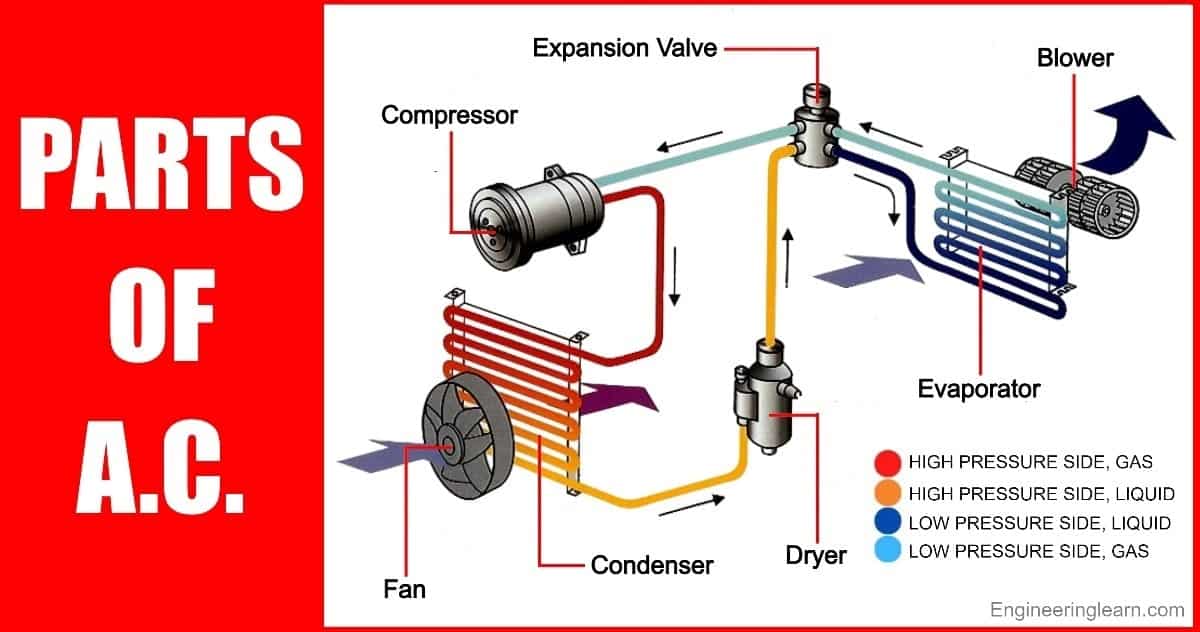
Understanding the components of your Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) system is essential for homeowners, technicians, and facility managers alike. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common HVAC parts, complete with pictures and explanations, covering everything from basic residential units to more complex commercial systems.
The Outdoor Unit: The Condenser
Often referred to as the condenser, the outdoor unit is a critical part of a split HVAC system. Its primary function is to release heat from the refrigerant. Let's break down its components:
Major Components of the Condenser Unit:
- Compressor: The heart of the system, the compressor circulates refrigerant and increases its pressure and temperature. Different types of compressors exist, including scroll, reciprocating, and rotary, each with varying efficiency levels and lifespans. A scroll compressor, for example, is generally quieter and more efficient than a reciprocating compressor.
- Condenser Coil: This coil is where the hot refrigerant releases its heat to the outside air. It's a series of copper or aluminum tubes with fins to increase surface area and promote heat transfer. Regular cleaning of the condenser coil is vital for maintaining efficiency. Dirt and debris buildup significantly reduce heat transfer, causing the system to work harder and consume more energy.
- Condenser Fan: The fan pulls air across the condenser coil, facilitating heat dissipation. A failing fan can cause the system to overheat, potentially damaging the compressor. Variable-speed fans are becoming increasingly common, offering improved efficiency and quieter operation.
- Reversing Valve (Heat Pumps Only): In a heat pump system, the reversing valve controls the direction of refrigerant flow, allowing the system to switch between heating and cooling modes. Its failure can result in the system being stuck in one mode.
- Accumulator (Heat Pumps Only): Protects the compressor from liquid refrigerant, which can cause damage.
- Filter Drier: Removes moisture and contaminants from the refrigerant. Replacing the filter drier during refrigerant line repairs is crucial to prevent future problems.
- Electrical Components: Include capacitors, contactors, and wiring. Capacitors provide the initial surge of power to start the compressor and fan motors. Contactors act as switches, controlling the flow of electricity to different components.
The Indoor Unit: The Air Handler or Furnace
The indoor unit, whether it's an air handler or a furnace, circulates air throughout the building and either cools or heats it. The type of indoor unit depends on whether you have a forced-air system using ductwork, or a ductless system like mini-splits.
Air Handler Components:
- Evaporator Coil: The evaporator coil absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it down. Like the condenser coil, it's constructed of copper or aluminum tubing with fins. A dirty evaporator coil reduces cooling efficiency and can contribute to mold growth.
- Blower Motor and Fan: The blower motor drives the fan, which circulates air across the evaporator coil and through the ductwork. Variable-speed blower motors offer improved comfort and energy efficiency by maintaining a more consistent airflow.
- Air Filter: The air filter removes dust, pollen, and other particles from the air. Regular filter replacement is essential for maintaining air quality and protecting the HVAC system components. MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) ratings indicate the filter's effectiveness. Higher MERV ratings capture smaller particles, but they can also restrict airflow.
- Expansion Valve or Metering Device: Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. A TXV (Thermostatic Expansion Valve) offers more precise control than a fixed orifice, resulting in improved efficiency.
- Drain Pan and Drain Line: Collects condensate (water) produced during the cooling process and directs it outside. A clogged drain line can lead to water damage and mold growth.
- Electric Resistance Heaters (Optional): Used as a supplemental heat source in some heat pump systems. These heaters consume a significant amount of electricity and are typically used only when the heat pump cannot meet the heating demand.
Furnace Components (Gas or Oil):
- Burner Assembly: Mixes fuel (natural gas, propane, or oil) with air and ignites the mixture to produce heat. Regular burner cleaning and maintenance are crucial for safe and efficient operation.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the combustion gases to the air that is circulated through the ductwork. A cracked heat exchanger is a serious safety hazard, as it can allow carbon monoxide to leak into the living space.
- Blower Motor and Fan: Similar to the air handler, the blower motor drives the fan that circulates heated air through the ductwork.
- Flue: Vents combustion gases safely to the outside. Proper venting is essential to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Gas Valve or Oil Pump: Controls the flow of fuel to the burner assembly.
- Ignition System: Ignites the fuel mixture. Common ignition systems include spark ignition and hot surface ignition.
- Safety Controls: Including flame sensors, high-limit switches, and pressure switches, ensure safe operation and prevent overheating or other malfunctions.
Ductwork
Ductwork is the network of channels that distributes heated or cooled air throughout a building. Properly designed and sealed ductwork is essential for efficient HVAC operation. Leaky ducts can result in significant energy losses, as conditioned air escapes into unconditioned spaces.
Key Considerations for Ductwork:
- Material: Ductwork is typically made of sheet metal or fiberglass duct board. Flexible duct is often used in short runs to connect registers to the main ductwork.
- Insulation: Insulating ductwork, especially in unconditioned spaces, reduces heat loss or gain, improving energy efficiency.
- Sealing: Sealing ductwork with mastic or foil tape prevents air leaks. Professional duct sealing can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Design: Proper ductwork design ensures adequate airflow to all areas of the building. Undersized or poorly designed ductwork can result in uneven temperatures and increased energy bills.
Refrigerant Lines
Refrigerant lines carry refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units. These lines are typically made of copper and are insulated to prevent heat loss or gain.
Important Notes about Refrigerant Lines:
- Refrigerant Leaks: Refrigerant leaks can reduce system efficiency and damage the compressor. Regular inspections and repairs are essential.
- Refrigerant Type: Different refrigerants have different environmental impacts and performance characteristics. Older systems may use R-22, which is being phased out due to its ozone-depleting potential. Newer systems typically use R-410A or other more environmentally friendly refrigerants.
- Line Sizing: Proper line sizing is crucial for optimal system performance. Undersized lines can restrict refrigerant flow, while oversized lines can reduce efficiency.
Thermostat
The thermostat controls the operation of the HVAC system, allowing you to set the desired temperature and schedule. Modern thermostats offer a variety of features, including programmable schedules, remote access, and energy monitoring.
Types of Thermostats:
- Programmable Thermostats: Allow you to set different temperatures for different times of the day, reducing energy consumption when you're away or asleep.
- Smart Thermostats: Learn your preferences and automatically adjust the temperature to maximize comfort and energy savings. They can also be controlled remotely via a smartphone app.
- Non-Programmable Thermostats: Simple and easy to use, but they don't offer the energy-saving benefits of programmable or smart thermostats.
Other Important HVAC Components
- Dampers: Control airflow within the ductwork, allowing you to adjust the temperature in different zones of the building.
- Diffusers and Registers: Distribute air evenly throughout the rooms.
- Zone Controllers: Used in zoned HVAC systems to control dampers and thermostats in different zones.
- Humidifiers and Dehumidifiers: Control humidity levels in the air.
- UV Lights: Installed in the ductwork to kill mold, bacteria, and other microorganisms.
Understanding these basic HVAC parts and their functions can empower homeowners, technicians, and facility managers to make informed decisions about system maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Regular maintenance, including filter replacement, coil cleaning, and ductwork inspection, can significantly extend the lifespan of your HVAC system and reduce energy costs. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional is always recommended for complex repairs or installations.