Aircon Troubleshooting Chart
Air conditioning systems, while marvels of modern technology, aren't immune to issues. Understanding common problems and how to troubleshoot them can save you a significant amount of money on energy bills and prevent costly repairs. This article provides a comprehensive aircon troubleshooting chart and guide, designed for homeowners, businesses, and HVAC professionals alike, with a focus on energy efficiency and cost savings.
Understanding Your Air Conditioning System: A Prerequisite to Troubleshooting
Before diving into specific problems, it's crucial to understand the basic components of your air conditioning system. A typical system consists of an outdoor unit (condenser) and an indoor unit (evaporator). The refrigerant circulates between these units, absorbing heat from inside your home and releasing it outside. Knowing these core components helps in pinpointing the source of the problem.
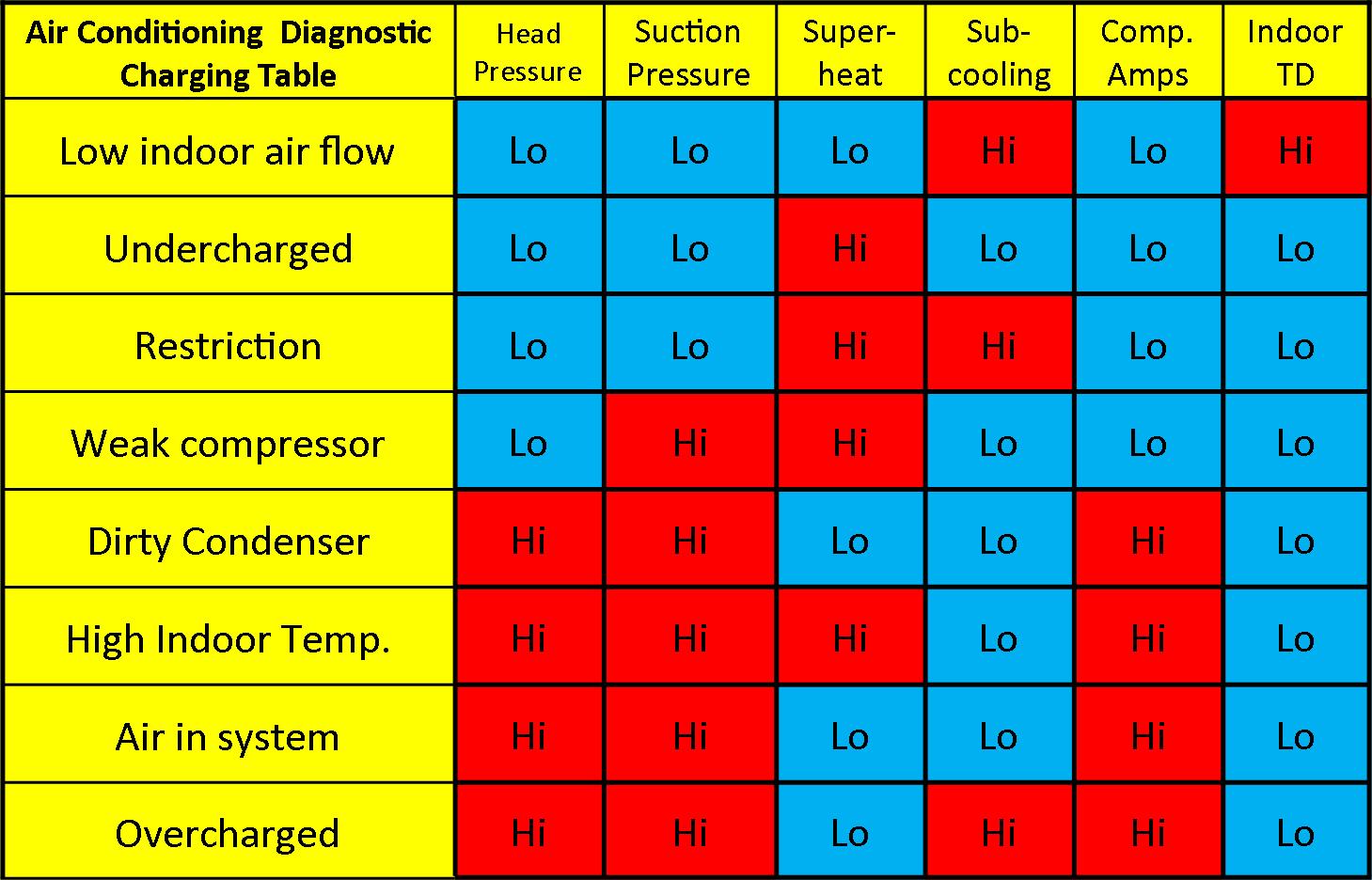
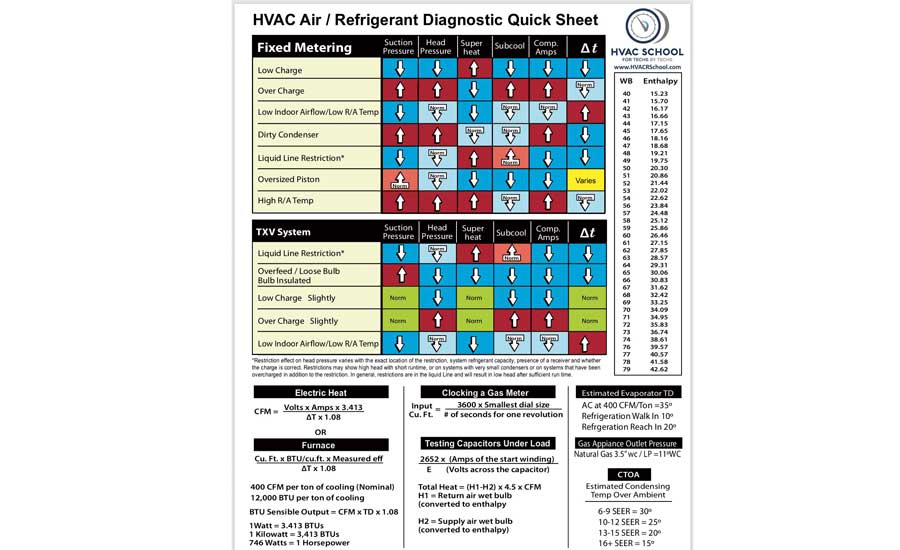
Common Air Conditioning Problems and Their Solutions: The Troubleshooting Chart
Here's a comprehensive chart outlining common air conditioning issues, their potential causes, and practical solutions. We'll also discuss the energy-saving implications of addressing these problems promptly.
| Problem | Possible Cause(s) | Solution(s) | Energy Savings Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
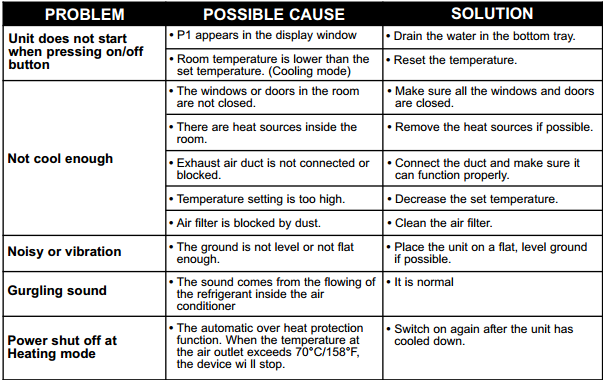
| Air Conditioner Not Turning On |
|
|
Minimal (primarily prevents further damage) |
| Air Conditioner Blowing Warm Air |
|
|
Significant (up to 20% improvement in efficiency) |
| Air Conditioner Running Constantly |
|
|
High (up to 30% reduction in energy consumption) |
| Air Conditioner Making Unusual Noises |
|
|
Moderate (prevents further damage and improves efficiency) |
| Water Leaking from Air Conditioner |
|
|
Minimal (prevents water damage and potential mold growth) |
| Thermostat Not Working Properly |
|
|
Moderate (ensures accurate temperature control and prevents unnecessary energy usage) |
Important Note: Many of these solutions, especially those involving refrigerant or electrical components, require the expertise of a licensed HVAC technician. Attempting these repairs yourself can be dangerous and may void your warranty.
The Role of Regular Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding many of the problems listed above. Regular servicing by a qualified HVAC technician can identify potential issues early on, preventing costly breakdowns and ensuring optimal energy efficiency. A well-maintained system can operate more efficiently and last longer, maximizing your return on investment.
Here's a checklist of essential maintenance tasks:
- Change air filters regularly (every 1-3 months): Dirty filters restrict airflow, forcing your system to work harder and consume more energy.
- Clean condenser coils annually: Dirt and debris on the coils reduce their ability to dissipate heat, reducing efficiency.
- Inspect ductwork for leaks: Leaky ducts can waste up to 30% of your heating and cooling energy.
- Schedule professional servicing annually: A technician can inspect and clean components, check refrigerant levels, and identify potential problems.
Smart HVAC Systems and Energy Savings
Integrating your air conditioning system with smart home technology can further enhance energy efficiency and comfort. Smart thermostats learn your heating and cooling preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly, saving energy without sacrificing comfort. Some models even offer zone control, allowing you to heat or cool only the rooms you're using.
Furthermore, smart sensors can monitor temperature and humidity levels in different areas of your home, providing valuable data for optimizing your HVAC system's performance. Some systems can even detect potential problems, such as refrigerant leaks, and alert you before they become major issues.
According to Energy Star, a smart thermostat can save you up to 8% on your heating and cooling costs.
Energy Efficiency Incentives and Rebates
Many utility companies and government agencies offer incentives and rebates for upgrading to energy-efficient HVAC systems and implementing energy-saving measures. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of upgrading to a more efficient system or installing smart home technology. Check with your local utility company and state energy office for available programs. The Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) is a great resource to find rebates and incentives in your area.
Look for Energy Star certified products, which meet stringent energy efficiency standards. These products are independently certified to save energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Replacing Your Air Conditioner: When is it Time?
Even with proper maintenance, air conditioning systems eventually reach the end of their lifespan. If your system is more than 10-15 years old, experiences frequent breakdowns, or has become significantly less efficient, it may be time to consider replacing it. Modern air conditioners are significantly more energy-efficient than older models, and the energy savings can quickly offset the cost of replacement.
When choosing a new air conditioner, consider the following factors:
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating: A higher SEER rating indicates greater energy efficiency. Look for models with a SEER rating of 15 or higher.
- Size: An appropriately sized unit is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. Have a qualified HVAC technician perform a load calculation to determine the correct size for your home.
- Features: Consider features such as variable-speed compressors, smart controls, and zoning capabilities.
Conclusion: Investing in Efficiency Pays Off
By understanding common air conditioning problems, implementing regular maintenance, and embracing smart home technology, you can significantly improve the energy efficiency of your HVAC system and save money on your energy bills. Remember to consult with qualified HVAC professionals for repairs and upgrades, and take advantage of available incentives and rebates to maximize your return on investment. Addressing even seemingly minor issues promptly can prevent larger problems and ensure your system runs efficiently for years to come.