Average Cost To Replace An Air Conditioner

Replacing an air conditioner is a significant investment, and understanding the associated costs is crucial for homeowners, facility managers, and even HVAC technicians. This comprehensive guide breaks down the average cost to replace an air conditioner, exploring the factors that influence pricing, different system types, efficiency ratings, and lifespan considerations.
Understanding the Baseline Costs
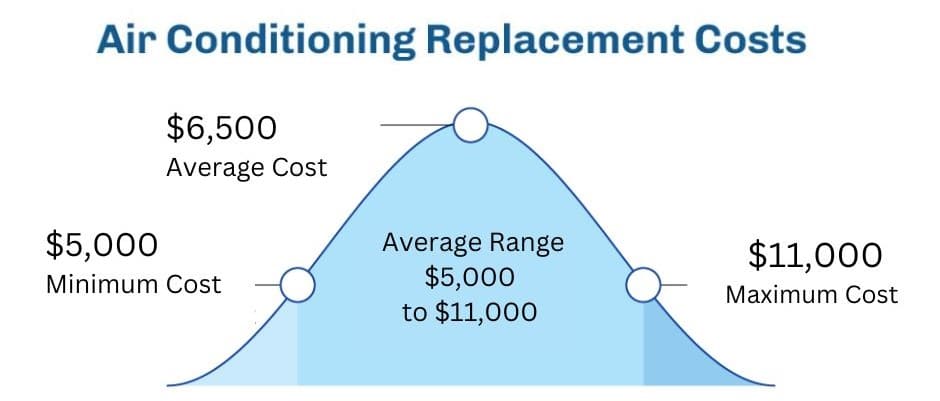
The average cost to replace an air conditioner typically ranges from $5,000 to $12,000, including the unit itself and professional installation. However, this is a broad estimate. Several key elements determine the final price:
- Unit Size (BTU): The cooling capacity of an air conditioner is measured in British Thermal Units (BTU). Larger homes or buildings require higher BTU ratings, resulting in more expensive units. A small apartment might need a 1.5-ton (18,000 BTU) AC, while a large house could require a 5-ton (60,000 BTU) system.
- SEER Rating: The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measures an AC unit's cooling efficiency. Higher SEER ratings translate to lower energy bills but also come with a higher upfront cost. Current minimum SEER ratings are mandated by federal regulations, but premium units can reach SEER 20 or higher.
- Type of System: Central AC systems, ductless mini-splits, and window units all have different price points. Central AC is generally the most expensive to install but provides whole-house cooling.
- Installation Complexity: Existing ductwork, the location of the outdoor condenser, and any necessary modifications to the electrical system can impact installation costs.
- Brand Reputation: Well-known and trusted HVAC brands often command higher prices due to their reliability, performance, and warranty offerings.
- Labor Costs: HVAC technician labor rates vary depending on location and experience.
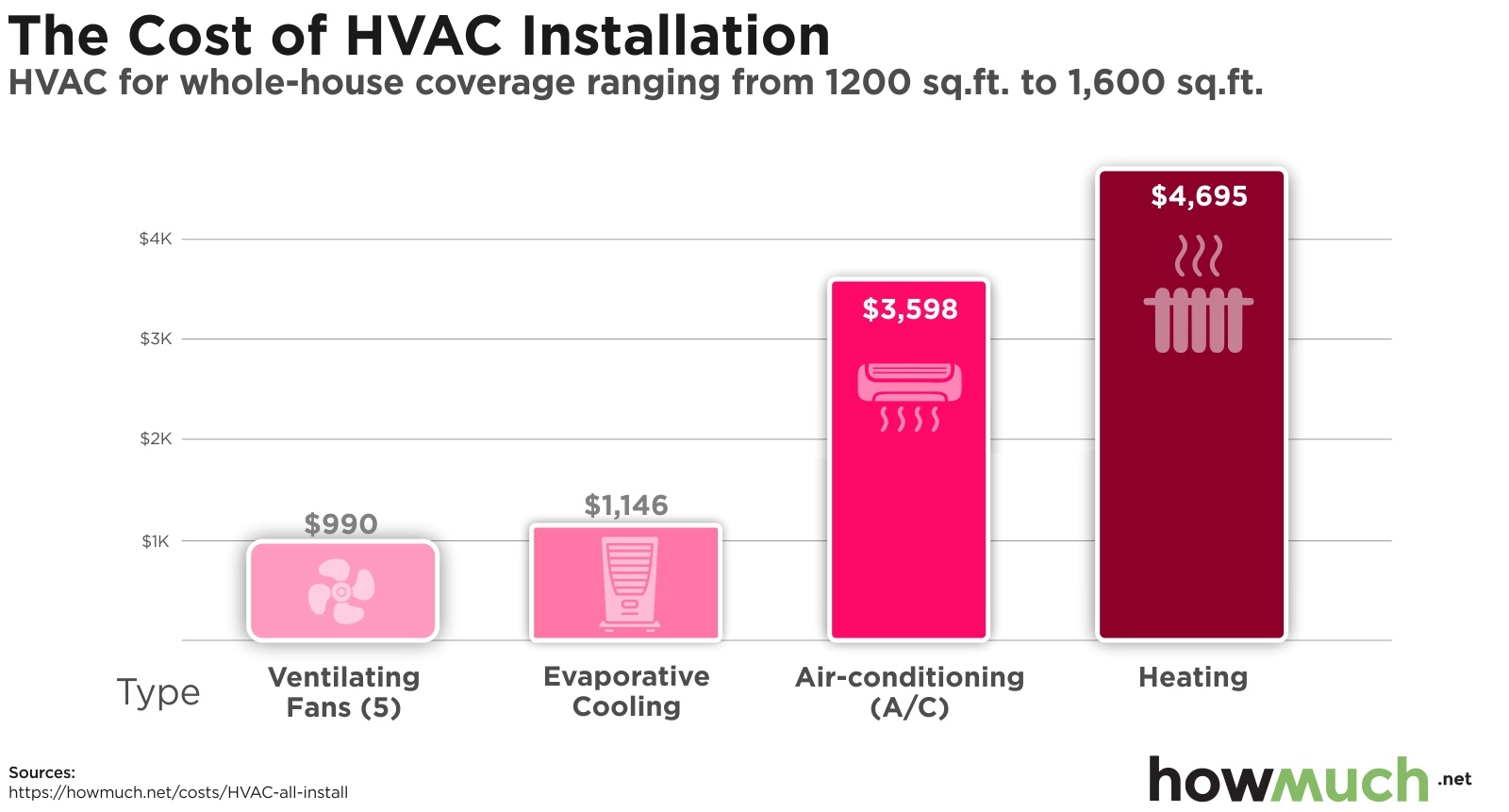
Central Air Conditioner Replacement Costs
Central air conditioning systems are the most common type in many homes. Replacing a central AC unit involves removing the old unit, installing the new condenser unit outside, connecting it to the existing ductwork, and ensuring proper refrigerant levels.
Cost Breakdown for Central AC Replacement:
- Unit Price: $3,500 - $8,000 (depending on size and SEER rating)
- Installation Costs: $1,500 - $4,000 (including labor, materials, and disposal of the old unit)
- Total Estimated Cost: $5,000 - $12,000
Example: Replacing a 3-ton central AC unit with a 16 SEER rating might cost around $6,500, while upgrading to a 18 SEER unit of the same size could increase the cost to $8,000 or more.
Ductless Mini-Split System Costs
Ductless mini-split systems are a popular choice for homes without existing ductwork or for zoning specific areas. These systems consist of an outdoor condenser connected to one or more indoor air handlers.
Cost Breakdown for Ductless Mini-Split Replacement:
- Unit Price (Single Zone): $1,500 - $4,000
- Unit Price (Multi-Zone): $4,000 - $10,000+
- Installation Costs (Single Zone): $500 - $1,500
- Installation Costs (Multi-Zone): $1,500 - $4,000+
- Total Estimated Cost (Single Zone): $2,000 - $5,500
- Total Estimated Cost (Multi-Zone): $5,500 - $14,000+
Note: Multi-zone systems, which can cool multiple rooms with individual air handlers, will be significantly more expensive than single-zone systems.
Window Air Conditioner Costs
Window AC units are the most affordable cooling option, suitable for small spaces like bedrooms or offices. They are relatively easy to install and require minimal professional assistance.
Cost Breakdown for Window AC Replacement:
- Unit Price: $150 - $800 (depending on size and features)
- Installation Costs: $0 - $100 (typically DIY installation)
- Total Estimated Cost: $150 - $900
While the upfront cost is low, window AC units are generally less energy-efficient than central AC or mini-split systems, leading to higher operating costs over time.
Factors Influencing Replacement Costs in Detail
Beyond the basic cost categories, several other factors can significantly impact the final price of an air conditioner replacement:
- SEER Rating and Energy Efficiency: As mentioned earlier, SEER rating is a key factor. Higher SEER units cost more upfront but save money on energy bills in the long run. For example, upgrading from a 14 SEER to a 18 SEER unit could save you hundreds of dollars per year in electricity costs, but the initial investment will be higher. Consider the long-term cost savings when choosing a SEER rating.
- System Size (Tonnage): Correctly sizing an air conditioner is crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. An oversized unit will cycle on and off frequently, leading to wasted energy and poor dehumidification. An undersized unit will struggle to cool the space adequately. A professional HVAC technician will perform a Manual J load calculation to determine the appropriate tonnage for your home or building.
- Ductwork Condition: If your existing ductwork is damaged, leaky, or poorly designed, it can significantly reduce the efficiency of your new air conditioner. Repairing or replacing ductwork can add to the overall cost of the project. Duct sealing is a relatively inexpensive way to improve efficiency and reduce energy waste.
- Refrigerant Type: Older AC units used R-22 refrigerant, which is being phased out due to its environmental impact. Newer units use R-410A, a more environmentally friendly refrigerant. If you are replacing an older unit that uses R-22, you will need to replace the entire system.
- Smart Thermostats and Zoning: Adding a smart thermostat can give you precise temperature control and remote access via your smartphone, which may add to the initial cost. Zoning systems allow you to control the temperature in different areas of your home independently, improving comfort and saving energy.
- Permits and Inspections: Depending on your location, you may need to obtain permits and inspections before and after installing a new air conditioner. These costs can vary but are typically a small percentage of the overall project cost.
- Warranty: A good warranty can protect you from unexpected repair costs. Look for units with a comprehensive warranty on both parts and labor. Many manufacturers offer extended warranties for added peace of mind.
Choosing the Right HVAC Contractor
Selecting a qualified and reputable HVAC contractor is essential for a successful air conditioner replacement. Here are some tips for choosing the right contractor:
- Get Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from at least three different contractors to compare pricing and services.
- Check Licenses and Insurance: Ensure the contractor is properly licensed and insured to protect yourself from liability.
- Read Reviews and Testimonials: Check online reviews and ask for references from previous customers.
- Ask About Experience: Choose a contractor with experience installing the type of system you are considering.
- Verify Certifications: Look for contractors with certifications from organizations such as NATE (North American Technician Excellence).
- Detailed Proposal: A reputable contractor should provide a detailed proposal outlining the scope of work, equipment specifications, and total cost.
Extending the Lifespan of Your New Air Conditioner
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your new air conditioner and prevent costly repairs. Here are some tips for maintaining your AC unit:
- Regular Filter Changes: Change your air filter every 1-3 months, or as recommended by the manufacturer. A dirty air filter restricts airflow and reduces efficiency.
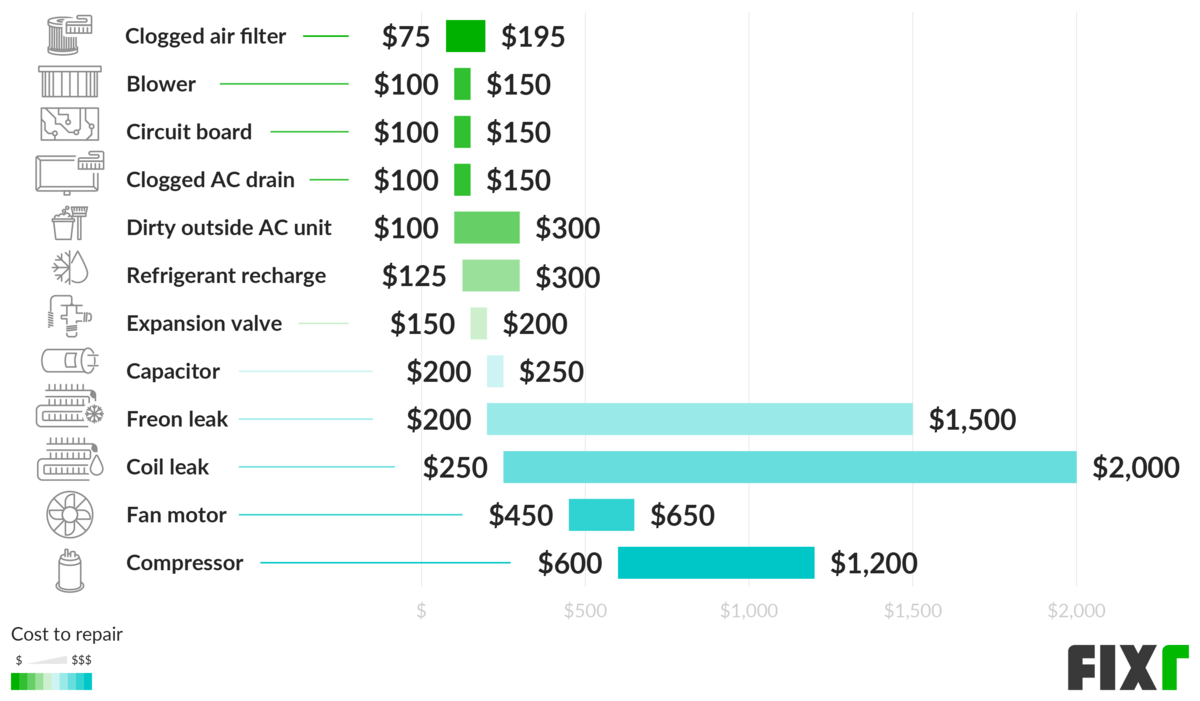
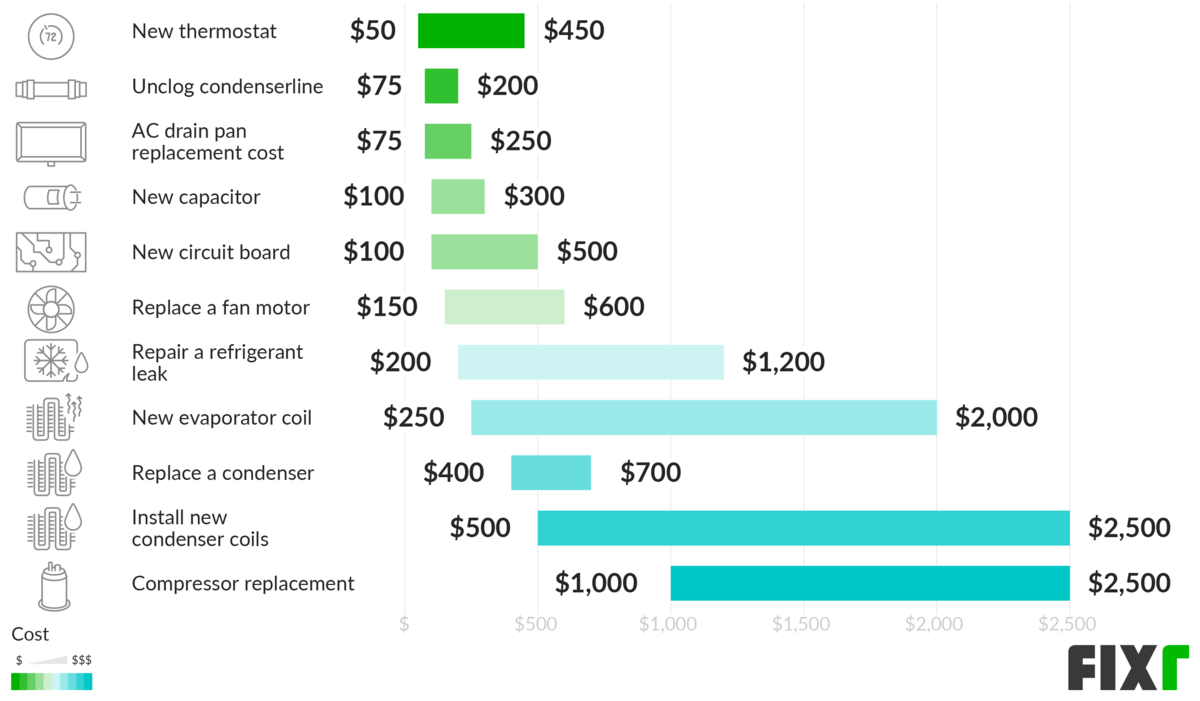
- Professional Maintenance: Schedule annual maintenance with a qualified HVAC technician. During maintenance, the technician will clean the coils, check refrigerant levels, and inspect other components.
- Keep the Outdoor Unit Clean: Remove leaves, debris, and vegetation from around the outdoor condenser unit.
- Inspect Ductwork: Periodically inspect your ductwork for leaks and damage.
- Use a Programmable Thermostat: A programmable thermostat can help you save energy by automatically adjusting the temperature when you are away from home.
Financial Assistance and Rebates
Several financial assistance programs and rebates can help offset the cost of replacing an air conditioner. Check with your local utility company, state energy office, and federal government for available programs. The Energy Star website is also a valuable resource for finding rebates and incentives.
Conclusion
Replacing an air conditioner is a significant investment, but with careful planning and research, you can choose the right system for your needs and budget. Understanding the factors that influence replacement costs, selecting a reputable contractor, and performing regular maintenance will ensure that your new AC unit provides years of reliable and efficient cooling. Remember to consider long-term energy savings and potential rebates when making your decision. Properly maintaining your new system ensures years of comfort and minimizes the need for future replacements.