Best Height For Carbon Monoxide Detector

Optimizing Safety: The Ideal Height for Carbon Monoxide Detectors in HVAC Systems
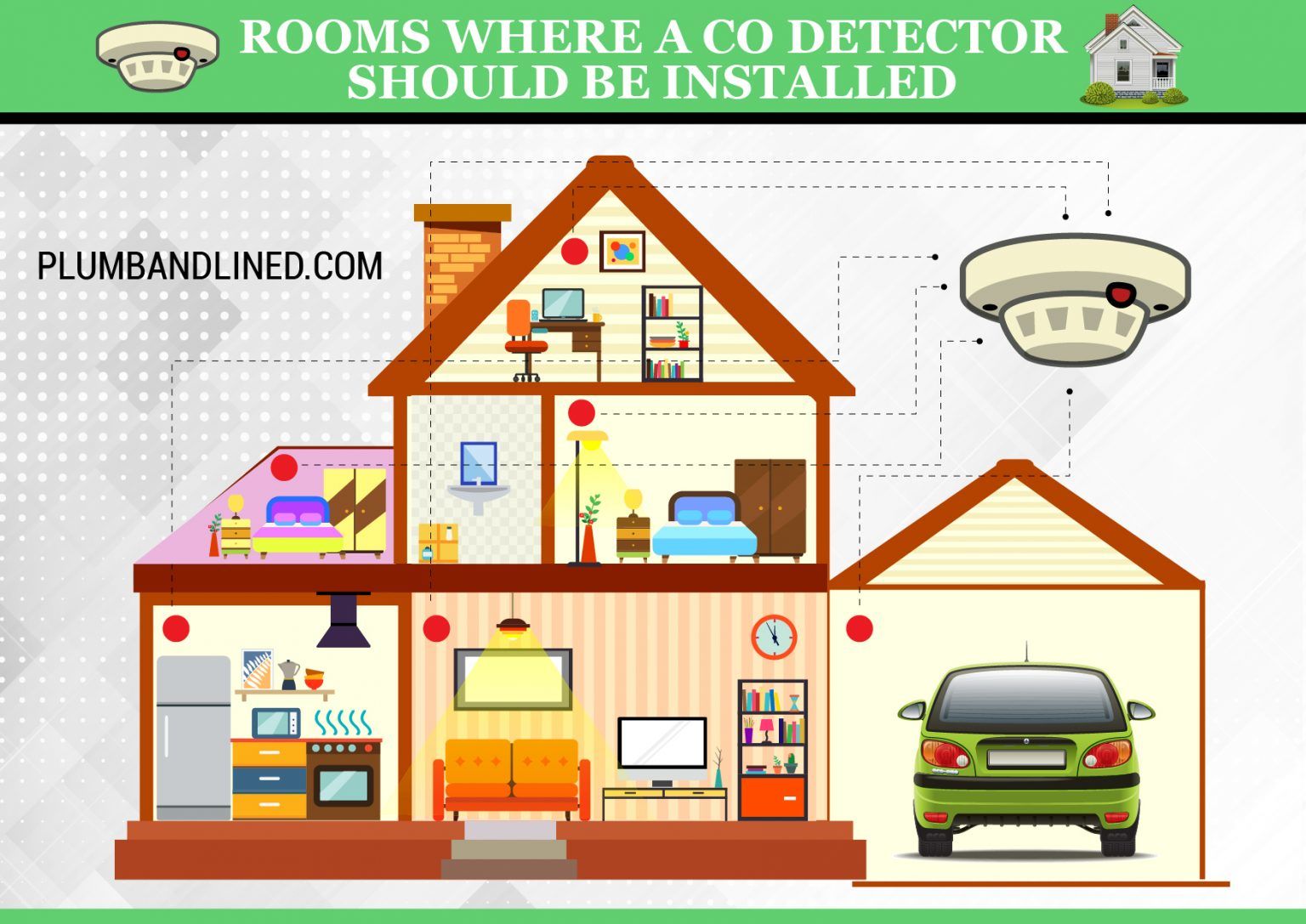
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an invisible, odorless, and deadly gas produced by incomplete combustion of fuels such as natural gas, propane, oil, and wood. Because it is virtually undetectable without specialized equipment, carbon monoxide detectors are critical safety devices in homes and buildings. For HVAC professionals, understanding the optimal placement of these detectors is not just best practice, it's a life-saving responsibility. This article dives into the science behind CO detector placement, industry standards, and how proper installation can impact your career and business.
The Science Behind CO Detection and Air Density
The debate around high versus low placement for CO detectors stems from the gas's density relative to air. While older beliefs suggested CO rises with warm air, modern understanding acknowledges that at room temperature, carbon monoxide has a density very similar to air. Therefore, it tends to disperse evenly throughout a room. This means detector placement should prioritize proximity to potential sources and breathing zones.
However, stratification – the formation of layers of air at different temperatures – can influence CO distribution. In some scenarios, slightly warmer air (and any CO within it) may tend to accumulate near the ceiling. This makes high placement potentially advantageous in certain situations, especially if the primary source of CO is a poorly ventilated appliance located high in the room, such as a furnace in an attic.
Industry Standards and Recommendations
While specific regulations vary by jurisdiction, most building codes and safety organizations align on general guidelines for CO detector placement. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), via NFPA 720: Standard for the Installation of Carbon Monoxide Detection and Alarm Equipment, provides comprehensive recommendations. A key takeaway from NFPA 720 is the emphasis on placing detectors:
- On each level of a dwelling unit, including basements.
- Outside each separate sleeping area in the immediate vicinity of the bedrooms.
- Within 10 feet of every sleeping area.
In terms of height, both the NFPA and other organizations like the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) generally recommend installing CO detectors at a height where they can be easily heard and maintained. This often translates to:
- Wall-mounted: Approximately 5 feet (at eye level) from the floor.
- Ceiling-mounted: At least 4 inches from the wall.
These height recommendations balance the need for effective CO detection with practical considerations like accessibility for testing and battery replacement. They also account for the potential for CO to disperse throughout the room, regardless of whether it initially rises or settles.
Impact on HVAC Professionals: Career Paths and Certification
Understanding CO detector placement is a fundamental skill for HVAC technicians, installers, and contractors. It directly relates to ensuring the safety and well-being of clients and adhering to industry best practices. Mastering this knowledge opens doors to various career opportunities, including:
- HVAC Technician/Installer: Responsible for installing and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, including ensuring proper CO detector placement during installations.
- Home Inspector: Evaluates residential properties for safety and code compliance, including verifying the presence and proper installation of CO detectors.
- Energy Auditor: Assesses a building's energy efficiency and safety, identifying potential CO hazards and recommending solutions.
- HVAC Contractor: Oversees HVAC projects, ensuring that all installations, including CO detectors, meet safety standards and building codes.
Advancing your career in HVAC often involves obtaining relevant certifications. Several certifications demonstrate expertise and commitment to professional standards:
- NATE (North American Technician Excellence): This is the leading certification organization for HVAC technicians. Achieving NATE certification signifies a high level of competence and knowledge in specific areas of HVAC, including combustion analysis and safety.
- EPA 608 Certification: Required for technicians who handle refrigerants. While not directly related to CO detection, it demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility and professional development.
- HVAC Excellence: Offers a range of certifications covering various HVAC disciplines, including safety and troubleshooting.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for HVAC mechanics and installers was $59,620 in May 2023. The job outlook is projected to grow 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations. The demand for skilled technicians who understand safety protocols and can properly install and maintain CO detectors is expected to remain strong.
Real-World Examples and Practical Considerations
Consider a scenario where a homeowner complains of frequent CO detector alarms. An HVAC technician who understands proper placement will investigate several factors:
- Detector Age: CO detectors have a limited lifespan (typically 5-7 years) and should be replaced periodically.
- Detector Location: Is the detector placed near a potential CO source (e.g., furnace, water heater) and within the recommended distance of sleeping areas?
- Appliance Ventilation: Are appliances properly vented to the outside?
- Combustion Efficiency: Is the furnace operating efficiently, or is it producing excessive CO due to a malfunction?
By systematically addressing these factors, the technician can identify the root cause of the problem and ensure the homeowner's safety.
Another crucial consideration is the type of CO detector. There are two main types:
- Biomimetic Sensor: These detectors use a gel that changes color when exposed to CO, triggering the alarm.
- Electrochemical Sensor: These detectors use an electrode that reacts with CO, generating an electrical current that triggers the alarm.
Electrochemical sensors are generally considered more accurate and reliable than biomimetic sensors, and are the most common type used today. Be aware of the differences and lifespan when choosing a detector.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can compromise the effectiveness of CO detectors:
- Placing detectors too close to cooking appliances: This can trigger false alarms.
- Placing detectors in dusty or humid environments: This can damage the sensor.
- Ignoring manufacturer's instructions: Always follow the manufacturer's recommendations for installation and maintenance.
- Painting or covering detectors: This can block the sensor and prevent it from detecting CO.
- Removing the battery: Ensure the detector has a working battery and test it regularly.
In summary, while the ideal height may slightly vary based on specific circumstances and local codes, a general rule of thumb is to install CO detectors at eye level (approximately 5 feet) on the wall and outside of sleeping areas. Prioritizing proximity to potential CO sources and adherence to manufacturer's instructions are also essential. HVAC professionals who prioritize safety and stay informed about best practices will not only protect their clients but also enhance their career prospects in a growing and vital industry.
Investing in ongoing training and certifications demonstrates a commitment to excellence and positions you for success in the HVAC field. The skills and knowledge you gain will enable you to provide valuable services and ensure the safety and well-being of your community.


/fig 1.png?width=1275&name=fig 1.png)