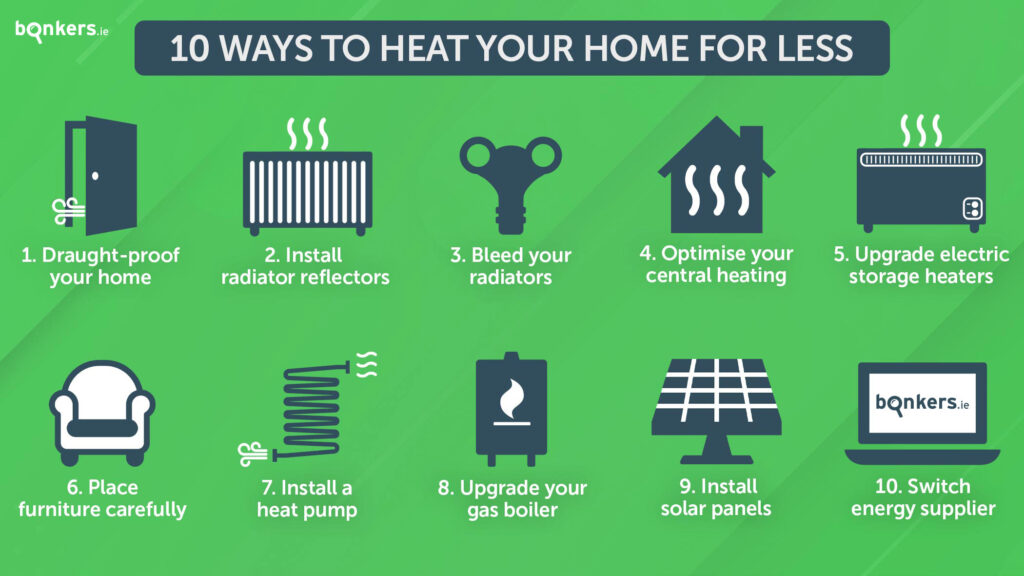
Best Way To Heat A Home With Electricity
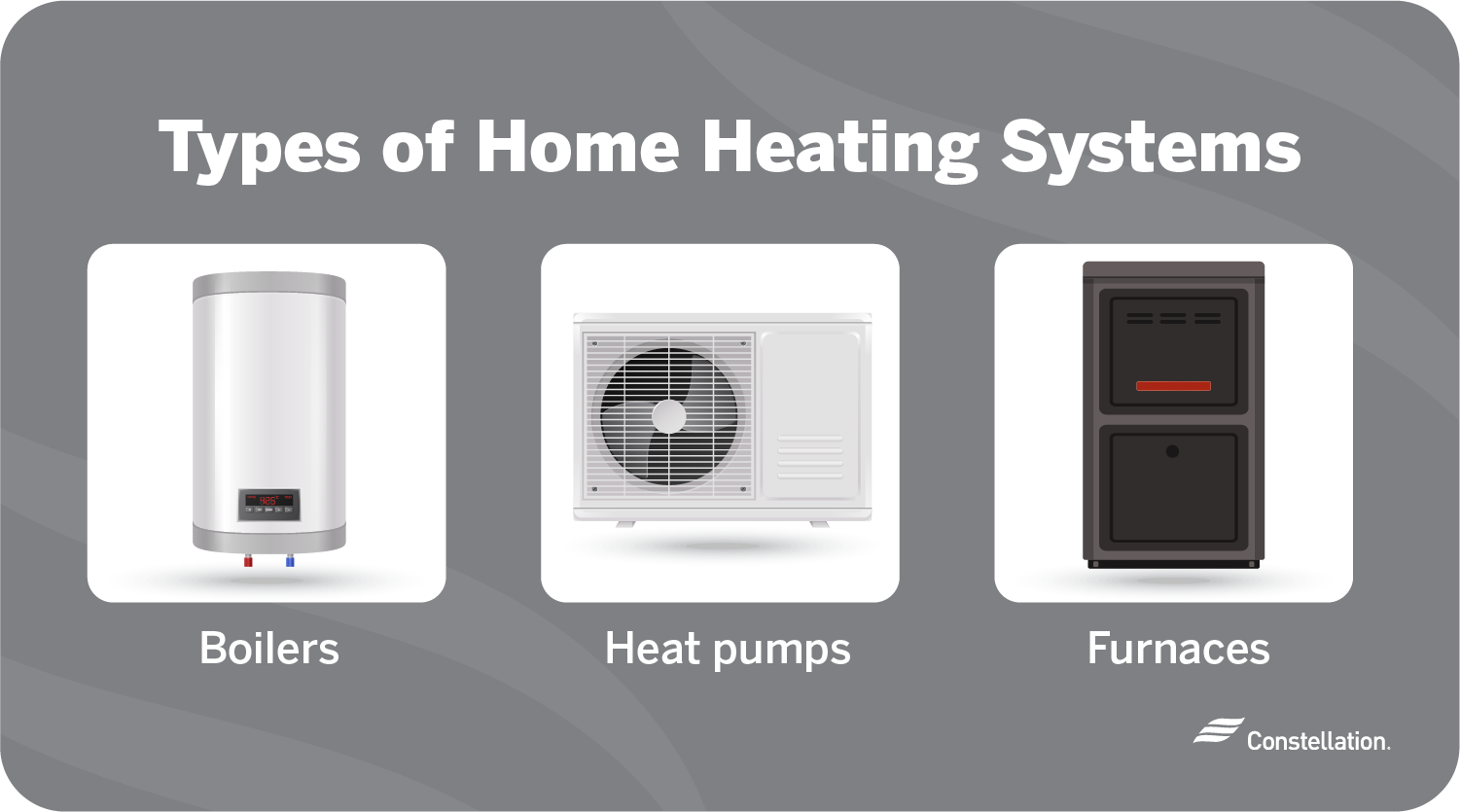
The Ultimate Guide to Electric Home Heating: Finding the Best System for Your Needs
Electric heating offers a clean, efficient, and increasingly popular alternative to traditional gas or oil-based systems. With advancements in technology and rising fossil fuel costs, many homeowners are exploring the best ways to heat their homes using electricity. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the various electric heating options available, comparing their pros, cons, costs, and key features, empowering you to make an informed decision for your specific needs.
Understanding Electric Heating Options
Several types of electric heating systems exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s delve into the most common options:
Electric Resistance Heaters
Baseboard Heaters: These are perhaps the simplest and most affordable electric heating option. They work by passing electricity through a resistor, which heats up and radiates warmth into the room.
Pros: Low initial cost, easy installation, individual room control. Cons: Can be expensive to operate (low efficiency), uneven heating, potential safety concerns with hot surfaces, visually unappealing for some.Pricing: Typically range from $50 to $200 per unit, depending on length and wattage.
Space Heaters: Portable units that offer on-demand heating for small areas. They come in various types, including radiant, convection, and fan-forced models.
Pros: Highly portable, inexpensive, immediate heat. Cons: High operating cost per BTU, can be a fire hazard if not used properly, only suitable for small spaces.Pricing: $20 to $100 or more, depending on features and type.
Electric Furnaces: These central heating systems use electric resistance coils to heat air, which is then distributed throughout the house via ductwork.
Pros: Lower upfront cost than heat pumps, relatively simple to install. Cons: Lower efficiency compared to heat pumps (close to 1:1 energy ratio), higher operating costs than heat pumps.
Heat Pumps: The Efficiency Champions
Heat pumps don't generate heat; instead, they transfer it from one place to another. In winter, they extract heat from the outside air (even cold air contains some heat) and pump it inside. In summer, they reverse the process, removing heat from the inside and transferring it outdoors.
Heat pumps are significantly more energy-efficient than electric resistance heaters.
Air Source Heat Pumps (ASHP): These are the most common type of heat pump. They use the outside air as the heat source/sink.
Pros: High efficiency (SEER and HSPF ratings), can provide both heating and cooling, environmentally friendly. Cons: Efficiency decreases in very cold temperatures, can be more expensive to install than electric resistance heaters.SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures cooling efficiency, while HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) measures heating efficiency. Look for higher ratings for better energy savings. A good ASHP will have a SEER rating above 15 and an HSPF rating above 8.
Geothermal Heat Pumps (GSHP): Also known as ground-source heat pumps, these systems use the earth's stable temperature as the heat source/sink. They are significantly more efficient than ASHPs but also more expensive to install.
Pros: Highest efficiency among heat pumps, stable performance regardless of outside temperature, long lifespan. Cons: High installation cost, requires significant land area for ground loop installation.
Other Electric Heating Options
Radiant Floor Heating: Electric radiant floor heating uses electric cables or mats embedded in the floor to provide even, comfortable heat.
Pros: Comfortable, even heating, energy-efficient when properly insulated, silent operation. Cons: High installation cost, slow response time, can be difficult to install in existing homes.
Electric Fireplaces: These units provide supplemental heat and a visual ambiance. They typically use electric resistance heating.
Pros: Easy to install, relatively inexpensive, aesthetically pleasing. Cons: Low heating capacity, primarily for supplemental heat only.
Comparing Popular HVAC Brands and Models
When choosing an electric heating system, selecting a reputable brand is crucial. Here are some popular brands and models known for their quality and performance:
- Carrier: Known for their high-efficiency heat pumps and furnaces. Their Infinity series heat pumps offer excellent SEER and HSPF ratings.
- Trane: A reliable brand with a wide range of heat pumps and electric furnaces. Their XV20i heat pump is a top performer.
- Lennox: Offers innovative and energy-efficient electric heating solutions, including heat pumps and radiant floor heating systems.
- Mitsubishi Electric: A leader in ductless mini-split heat pump technology, ideal for zone heating and cooling.
- Daikin: Known for their inverter technology and energy-efficient heat pumps.
When comparing models, pay attention to the following factors:
- Efficiency Ratings (SEER, HSPF, AFUE): Higher ratings translate to lower operating costs. AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) is typically associated with gas furnaces, but it can sometimes be used to describe the energy efficiency of electric furnaces as well (though SEER/HSPF is more common).
- Features: Look for features like variable-speed blowers, smart thermostats compatibility, and advanced filtration systems.
- Warranty: A longer warranty provides peace of mind and protects your investment.
- Noise Level: Consider the noise level of the unit, especially for heat pumps.
Cost Considerations: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
The initial cost of an electric heating system can vary significantly depending on the type of system and the size of your home. However, it's essential to consider the long-term operating costs as well. While electric resistance heaters may have a lower upfront cost, their higher operating costs can quickly offset any initial savings. Heat pumps, despite a higher initial investment, offer significantly lower operating costs due to their superior efficiency.
Factors affecting operating costs:
- Electricity Rates: The cost of electricity in your area will directly impact your heating bills.
- Insulation: Proper insulation is crucial for minimizing heat loss and reducing heating costs.
- Climate: Colder climates will require more heating, increasing energy consumption.
- Thermostat Settings: Setting your thermostat to a lower temperature when you're away or asleep can save energy.
Warranties and Maintenance Needs
Most electric heating systems come with a manufacturer's warranty, which typically covers parts and labor for a specific period. It's essential to understand the terms of the warranty and keep records of all maintenance and repairs.
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your electric heating system. Recommended maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning or replacing air filters regularly: Dirty filters can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
- Inspecting and cleaning coils: Dirty coils can reduce heat transfer efficiency.
- Checking electrical connections: Loose connections can be a safety hazard.
- Scheduling annual professional maintenance: A qualified HVAC technician can inspect and tune up your system to ensure optimal performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
Choosing the best way to heat your home with electricity requires careful consideration of your individual needs and circumstances. Consider the following factors:
- Your Budget: Determine how much you can afford to spend on both the initial investment and ongoing operating costs.
- Your Climate: Colder climates may benefit more from geothermal heat pumps or high-efficiency air source heat pumps.
- Your Home's Size and Layout: Consider the size and layout of your home when choosing a heating system. Ductless mini-split systems are ideal for zone heating and cooling in homes without ductwork.
- Your Energy Efficiency Goals: If energy efficiency is a top priority, a heat pump is the best choice.
- Your Comfort Preferences: Consider your comfort preferences when choosing a heating system. Radiant floor heating provides even, comfortable heat.
By carefully evaluating these factors and comparing the different electric heating options, you can choose the best system for your home and enjoy comfortable, efficient, and cost-effective heating for years to come.