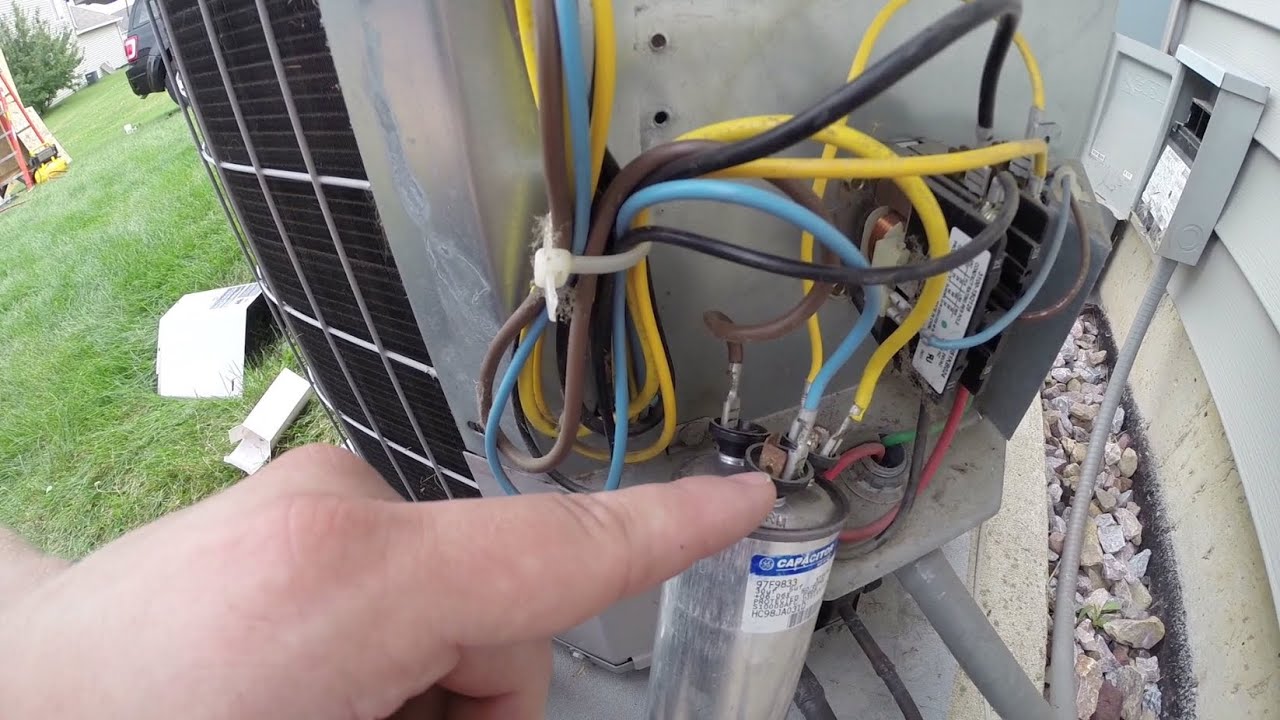
Capacitor For 5 Ton Ac Unit

Understanding the role of a capacitor in your 5-ton AC unit is crucial for maintaining its efficiency and longevity. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of capacitors, specifically as they relate to larger air conditioning systems. We'll break down the technical aspects into easily digestible information to help you make informed decisions regarding maintenance or replacement.
What is a Capacitor and Why is it Important?
A capacitor is an electrical component that stores energy in an electric field. Think of it like a small battery, but instead of providing a continuous flow of power, it releases stored energy quickly to start or run motors. In an AC unit, capacitors are primarily responsible for starting and running the compressor motor and the fan motors (both inside and outside the house). These motors require a surge of energy to overcome inertia and begin operating, which the capacitor provides.
Without a functioning capacitor, your AC unit may struggle to start, run inefficiently, or fail completely. A failing capacitor is one of the most common causes of AC system breakdowns, and replacing it is often a relatively inexpensive fix compared to replacing an entire motor or the entire AC unit.
Capacitors in a 5-Ton AC Unit
A 5-ton AC unit, being a larger system, requires more powerful capacitors than smaller units. A 5-ton AC unit, or 60,000 BTU/hour unit, typically uses two types of capacitors:
- Start Capacitor: This capacitor provides the initial surge of power needed to start the compressor motor. It's only in the circuit for a very short period, typically a fraction of a second, during startup.
- Run Capacitor: This capacitor assists the compressor motor and fan motors in maintaining consistent operation while the AC unit is running. It's continuously in the circuit.
The size and specifications of the capacitors used in a 5-ton AC unit are crucial for its performance. Using the wrong capacitor can lead to motor damage, inefficient operation, and premature failure.
Understanding Capacitor Specifications
When dealing with capacitors, you'll encounter specific terms and ratings. Understanding these is important for identifying the correct replacement.
- Capacitance (Microfarads - µF): This indicates the capacitor's ability to store an electrical charge. It's measured in microfarads (µF). The correct µF rating is critical. A slight deviation may be acceptable (typically +/- 5% to 10%), but it's best to match the original capacitor's rating as closely as possible.
- Voltage (VAC - Volts Alternating Current): This indicates the maximum voltage the capacitor can safely handle. It's crucial to choose a capacitor with a voltage rating equal to or higher than the original. Using a capacitor with a lower voltage rating is dangerous and can lead to failure.
- Hertz (Hz): This is the frequency of the alternating current, typically 50 or 60 Hz. In most cases, this is not a primary concern when selecting a replacement capacitor for a 5-ton AC unit, as capacitors are generally designed to operate at standard frequencies.
- Terminal Type: Capacitors have terminals (usually two or three) for connecting wires. Ensure the replacement capacitor has the same number and type of terminals as the original.
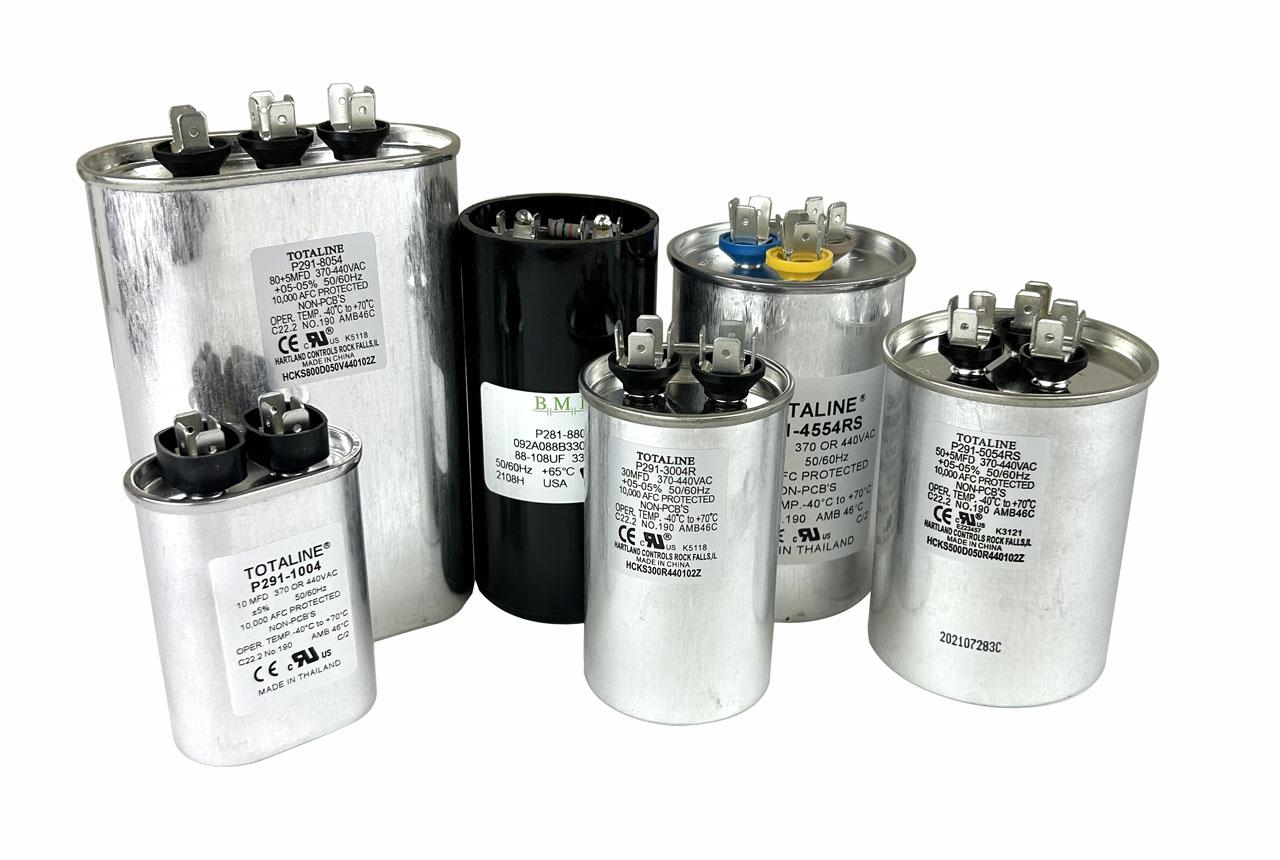
Example: A capacitor might be labeled "45/5 µF 370 VAC." This means it's a dual-run capacitor with 45 µF for the compressor and 5 µF for the fan motor, and it can handle up to 370 volts of alternating current.
Identifying a Failing Capacitor
Several signs can indicate a failing capacitor. Recognizing these symptoms early can prevent more significant damage to your AC unit.
- Humming Noise: The AC unit may hum but fail to start. This is a common sign of a weak start capacitor.
- Slow Starting: The compressor or fan motor may start slowly or intermittently.
- Increased Energy Bills: An inefficient AC unit due to a failing capacitor will consume more energy, leading to higher electricity bills.
- Overheating: The compressor or fan motor may overheat due to the capacitor not providing the necessary power for efficient operation.
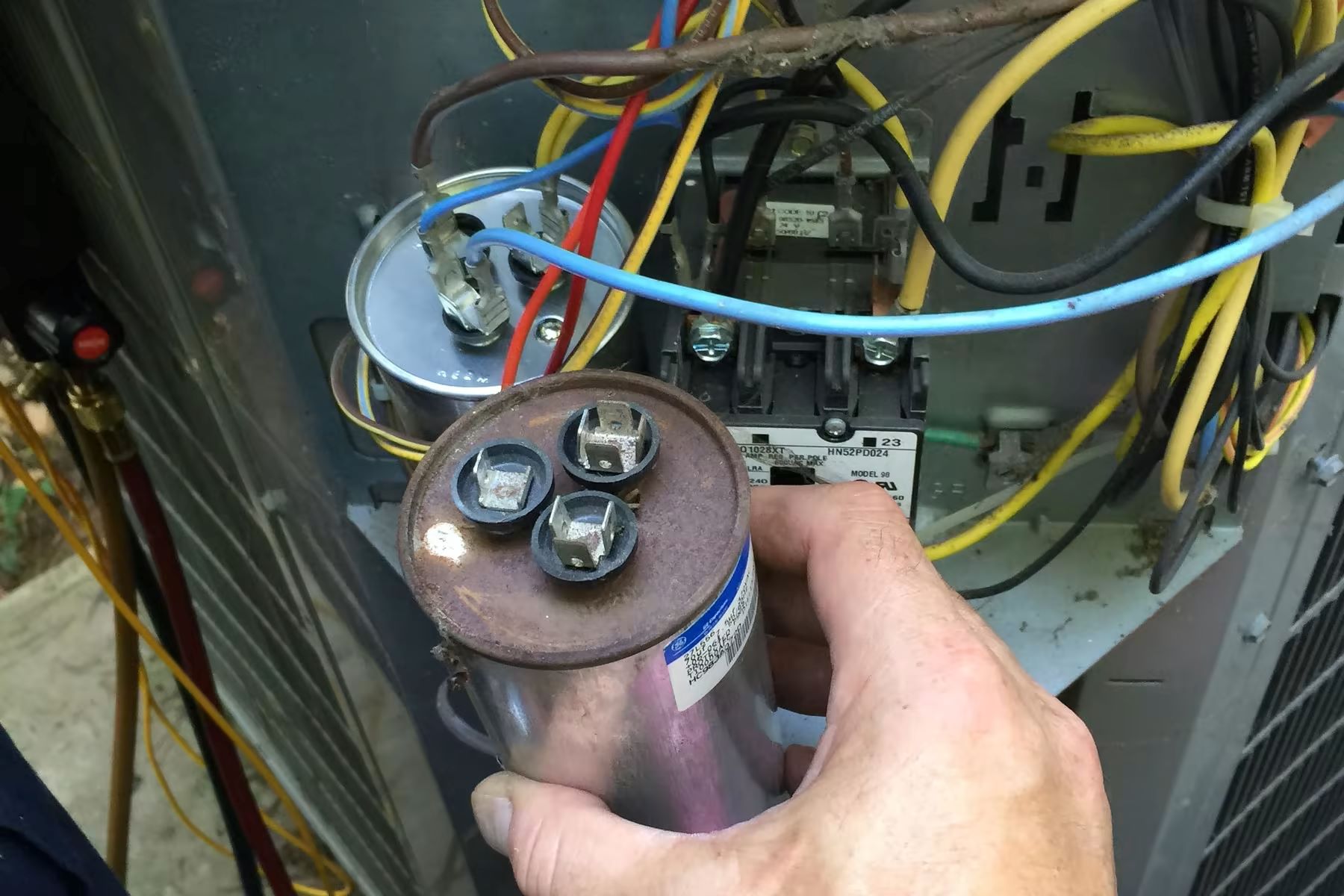
- Physical Signs: A bulging, leaking, or cracked capacitor is a clear indication of failure. Never touch a capacitor that shows signs of damage, as it may still hold a charge.
If you observe any of these signs, it's essential to have a qualified HVAC technician inspect your AC unit. They can accurately diagnose the issue and replace the capacitor if necessary.
Replacing a Capacitor: DIY vs. Professional
Replacing a capacitor can be a relatively straightforward task for someone with electrical experience and a good understanding of AC systems. However, it involves working with electricity and potentially dangerous voltages. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, it's always best to hire a qualified HVAC technician.
DIY Replacement (Proceed with Caution):
Disclaimer: Attempting to replace a capacitor yourself involves risks. Ensure you understand the dangers and take necessary safety precautions. If you're unsure, consult a professional.
Steps:
- Safety First: Turn off the power to the AC unit at the breaker box. Double-check that the power is off using a non-contact voltage tester.
- Discharge the Capacitor: Even with the power off, the capacitor may still hold a charge. Use a properly insulated screwdriver with an insulated handle to carefully discharge the capacitor by shorting the terminals. Be extremely cautious!
- Take Pictures: Before disconnecting any wires, take clear pictures of the capacitor and the wiring connections. This will serve as a reference when reconnecting the new capacitor.
- Disconnect Wires: Carefully disconnect the wires from the capacitor terminals. Use needle-nose pliers to avoid damaging the terminals.
- Remove the Old Capacitor: Remove the old capacitor from its mounting bracket.
- Install the New Capacitor: Install the new capacitor in the mounting bracket.
- Reconnect Wires: Reconnect the wires to the correct terminals, using your pictures as a guide. Ensure the wires are securely connected.
- Restore Power: Turn the power back on at the breaker box.
- Test the AC Unit: Observe the AC unit to ensure it starts and runs properly.
Important Safety Considerations:
- Always turn off the power before working on any electrical components.
- Discharge the capacitor before handling it.
- Use insulated tools.
- Wear safety glasses.
- If you're unsure about any step, stop and consult a qualified HVAC technician.
Professional Replacement:
Hiring a qualified HVAC technician offers several benefits:
- Expertise: Technicians have the knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose the problem and replace the capacitor correctly.
- Safety: Technicians are trained to work safely with electricity and refrigerants.
- Warranty: Reputable HVAC companies typically offer warranties on their work.
- Proper Disposal: Technicians will properly dispose of the old capacitor.
While professional replacement costs more than DIY, it provides peace of mind and ensures the job is done correctly and safely.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your 5-Ton AC Unit
Selecting the correct replacement capacitor is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of your AC unit. Always refer to the original capacitor's specifications (µF and VAC) when selecting a replacement.
- Match the µF Rating: The microfarad (µF) rating should match the original capacitor as closely as possible. A slight deviation (typically +/- 5% to 10%) may be acceptable, but it's best to stick with the original rating.
- Match or Exceed the Voltage Rating: The voltage (VAC) rating should be equal to or higher than the original capacitor. Never use a capacitor with a lower voltage rating.
- Choose a Reputable Brand: Opt for capacitors from reputable manufacturers known for quality and reliability.
- Consider a Dual-Run Capacitor: If your AC unit uses a dual-run capacitor (one capacitor for both the compressor and fan motor), ensure the replacement is also a dual-run capacitor with the correct µF ratings for both components.
Your HVAC technician can help you select the correct capacitor for your specific AC unit model.
Extending Capacitor Lifespan
Several factors can affect the lifespan of a capacitor. By taking proactive measures, you can potentially extend its life and prevent premature failure.
- Regular AC Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks with a qualified HVAC technician. They can inspect the capacitor and other components for signs of wear or damage.
- Keep the AC Unit Clean: A dirty AC unit can cause components to overheat, which can shorten the lifespan of the capacitor. Clean the outdoor unit regularly to remove debris.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure the AC unit has adequate ventilation. Restricted airflow can cause overheating.
- Avoid Overloading the System: Avoid setting the thermostat too low, as this can overwork the AC unit and put stress on the capacitor.
- Consider a Surge Protector: Power surges can damage electrical components, including capacitors. A surge protector can help protect your AC unit from power surges.
By following these tips, you can help ensure your AC unit operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.
Cost of Capacitor Replacement
The cost of replacing a capacitor in a 5-ton AC unit can vary depending on several factors:
- Type of Capacitor: Dual-run capacitors are generally more expensive than single-run capacitors.
- Brand of Capacitor: Capacitors from reputable brands tend to cost more.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs vary depending on the HVAC technician's hourly rate and the complexity of the job.
- Location: Prices may vary depending on your geographic location.
Generally, you can expect to pay anywhere from $100 to $300 for a professional capacitor replacement, including parts and labor. It's always a good idea to get quotes from multiple HVAC technicians to ensure you're getting a fair price.
Conclusion
The capacitor is a small but vital component of your 5-ton AC unit. Understanding its function, recognizing the signs of failure, and knowing how to choose the right replacement are essential for maintaining a comfortable and efficient home. While DIY replacement is possible, it's crucial to prioritize safety and consult a qualified HVAC technician if you're unsure about any step. Regular maintenance and proactive measures can help extend the lifespan of your capacitor and prevent costly repairs.