Carrier Diagnostic Codes

Understanding Carrier diagnostic codes is crucial for homeowners, real estate investors, and HVAC contractors alike. These codes, displayed on your thermostat or control panel, are your system's way of communicating potential problems, allowing for quicker diagnosis and repairs. Ignoring them can lead to escalating issues, costly repairs, and even premature system failure. This guide will break down what you need to know about Carrier diagnostic codes, helping you understand their meaning and how to respond effectively.
Decoding Carrier Diagnostic Codes: A Homeowner's Guide
Carrier, a leading manufacturer of HVAC systems, utilizes a sophisticated system of diagnostic codes to indicate specific issues within their equipment. These codes can range from simple problems like a dirty air filter to more complex malfunctions requiring professional attention. While the specific codes may vary slightly depending on the model and age of your Carrier system, a general understanding can empower you to troubleshoot basic issues and communicate effectively with your HVAC technician.
Common Categories of Carrier Diagnostic Codes
Carrier diagnostic codes often fall into several broad categories:
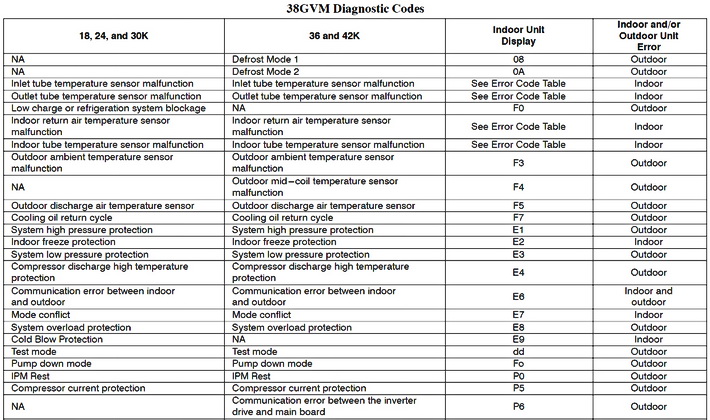
- Sensor Errors: These codes indicate problems with temperature sensors, pressure sensors, or other critical components that monitor system performance. For example, a code related to the outdoor temperature sensor might trigger if the sensor is faulty or disconnected.
- Communication Errors: Modern HVAC systems rely on communication between different components, such as the thermostat, indoor unit, and outdoor unit. Communication error codes suggest a disruption in this communication pathway.
- Compressor Issues: The compressor is the heart of your air conditioner. Codes related to compressor overheating, pressure imbalances, or electrical faults are serious and require immediate attention.
- Fan Motor Problems: Issues with the indoor or outdoor fan motor can significantly impact system performance. Codes might indicate a motor malfunction, wiring problem, or obstruction preventing proper airflow.
- Refrigerant Issues: Low refrigerant levels or leaks are common problems. Diagnostic codes can point to these issues, allowing for timely repairs and preventing further damage to the system.
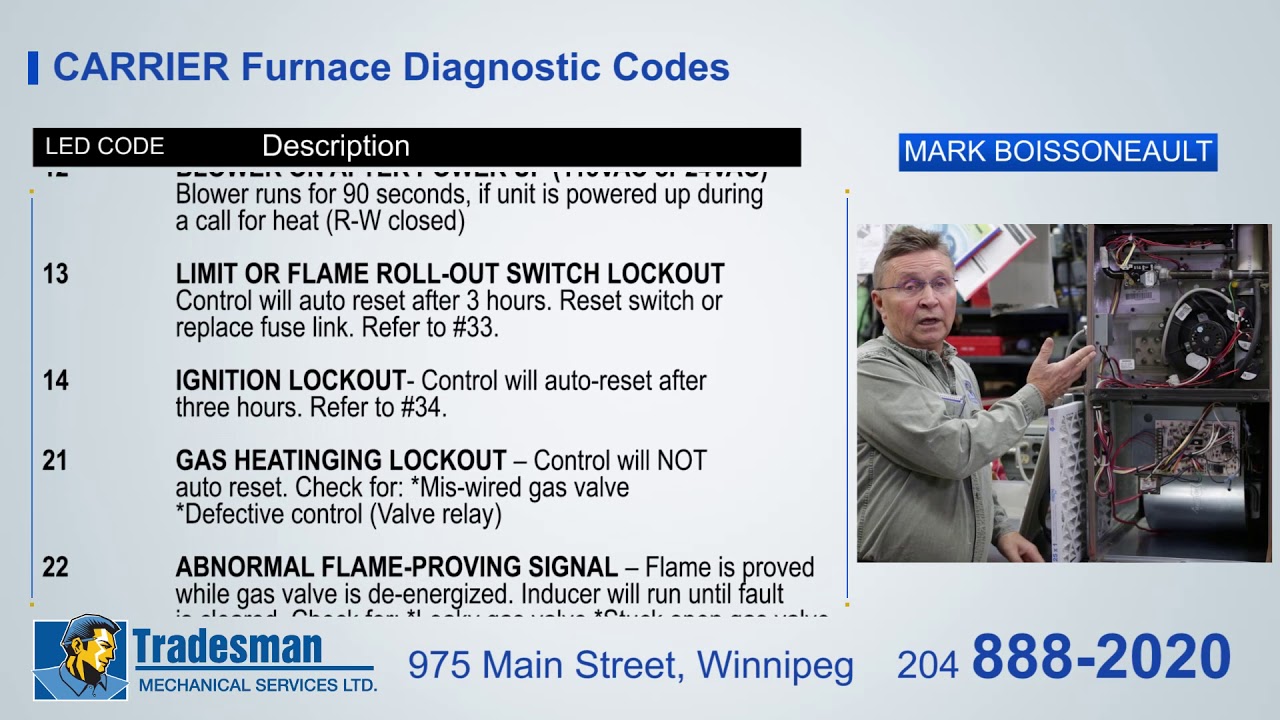
- Ignition Problems (Furnaces): For gas furnaces, codes related to ignition failure, flame sensor issues, or gas valve malfunctions are common. These codes require immediate attention due to safety concerns.
Examples of Specific Carrier Diagnostic Codes and Their Meanings
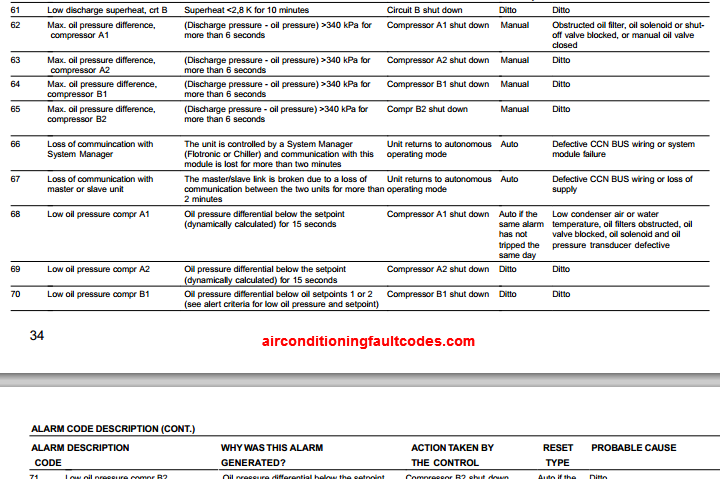
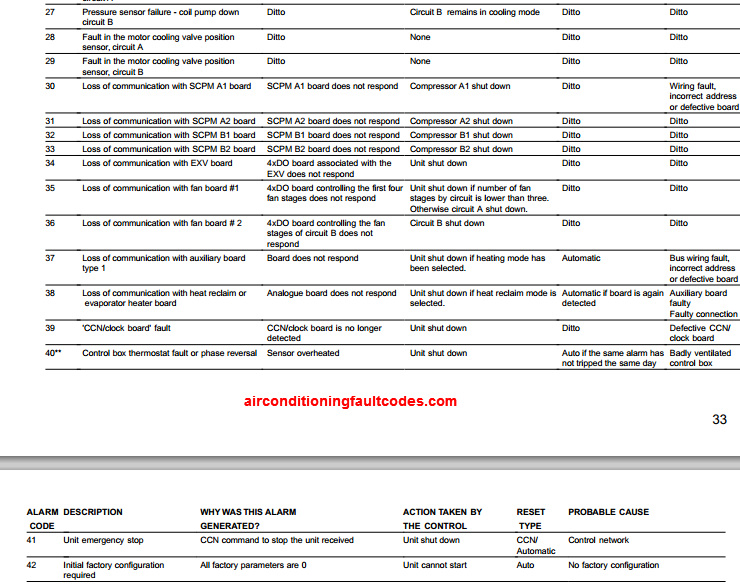
While a complete list of all Carrier diagnostic codes would be extensive, here are some common examples to illustrate how to interpret them:
- Code 13: This code often indicates a reversed line voltage polarity. This is a safety concern and requires immediate attention from a qualified technician.
- Code 21: This code typically signifies an outdoor fan motor problem. The motor might be failing, or there could be an obstruction preventing it from spinning freely.
- Code 31: This code usually points to a low-pressure switch fault, potentially indicating a refrigerant leak or low refrigerant levels.
- Code 41: This code can indicate a high-pressure switch fault, which might be caused by a blocked condenser coil, overcharged refrigerant, or a failing compressor.
- Code 54: This code frequently indicates a compressor lockout, often triggered by multiple failed start attempts or an overheating condition.
Important Note: Always consult your Carrier system's owner's manual or contact a qualified HVAC technician for a definitive interpretation of any diagnostic code. Misinterpreting a code can lead to incorrect troubleshooting and potentially worsen the problem.
Troubleshooting Common Carrier Diagnostic Codes: When to DIY and When to Call a Pro
Some diagnostic codes can be addressed with simple troubleshooting steps, while others require professional expertise. Here's a breakdown of when to attempt a DIY fix and when to call a qualified HVAC technician:
DIY Troubleshooting (with caution):
- Dirty Air Filter: A clogged air filter can trigger various error codes related to airflow restrictions. Replacing the filter is a simple and common maintenance task that can often resolve these issues.
- Thermostat Settings: Ensure your thermostat is properly configured and set to the correct mode (heating or cooling). Incorrect settings can sometimes trigger false error codes.
- Power Cycle: Sometimes, simply turning off the HVAC system and then turning it back on can reset the control board and clear minor error codes. However, if the code reappears, it indicates a more serious problem.
When to Call a Professional HVAC Technician:
- Any Code Related to Refrigerant: Refrigerant handling requires specialized equipment and training. Attempting to handle refrigerant yourself is illegal and dangerous.
- Compressor or Motor Issues: These components are complex and require specialized diagnostic tools and repair techniques.
- Electrical Issues: Working with electrical components can be hazardous. Always call a qualified electrician or HVAC technician for any electrical troubleshooting or repairs.
- Gas Furnace Issues: Gas furnaces involve flammable fuels and potentially dangerous combustion processes. Never attempt to repair a gas furnace yourself.
- Persistent or Recurring Codes: If a diagnostic code continues to reappear after attempting basic troubleshooting, it indicates a more serious underlying problem that requires professional attention.
Choosing the Right Carrier HVAC System: Features, AFUE, SEER, and HSPF Ratings
If your existing Carrier HVAC system is nearing the end of its lifespan or experiencing frequent problems, it may be time to consider a replacement. When choosing a new system, consider these key factors:
Energy Efficiency Ratings:
- AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): This rating applies to furnaces and measures how efficiently the furnace converts fuel into heat. Higher AFUE ratings indicate greater energy savings. Look for models with AFUE ratings of 90% or higher for optimal efficiency.
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): This rating applies to air conditioners and measures cooling efficiency. Higher SEER ratings indicate greater energy savings. Consider models with SEER ratings of 16 or higher.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): This rating applies to heat pumps and measures heating efficiency. Higher HSPF ratings indicate greater energy savings. Look for models with HSPF ratings of 8.2 or higher.
Popular Carrier HVAC Models:
Carrier offers a wide range of HVAC systems to suit various needs and budgets. Some popular models include:
- Carrier Infinity Series: These are Carrier's premium models, offering the highest levels of efficiency, comfort, and features, including smart home integration and advanced zoning capabilities.
- Carrier Performance Series: These models offer a balance of performance, efficiency, and affordability, making them a popular choice for many homeowners.
- Carrier Comfort Series: These are Carrier's entry-level models, providing reliable performance at a more budget-friendly price point.
Warranty Information:
Carrier offers a range of warranties on their HVAC systems, typically including a limited parts warranty and potentially an extended warranty option. Be sure to understand the terms and conditions of the warranty before purchasing a new system. Proper installation and regular maintenance are often required to maintain warranty coverage.
Comparing Carrier to Other Top HVAC Brands
While Carrier is a leading brand, it's important to compare it to other top contenders in the HVAC market. Here's a brief comparison:
- Carrier vs. Trane: Both brands are known for their quality and durability. Trane often focuses on robust construction and industrial-grade components, while Carrier emphasizes innovation and advanced features.
- Carrier vs. Lennox: Lennox is known for its quiet operation and energy-efficient models. Carrier offers a broader range of options, including more budget-friendly models.
- Carrier vs. Rheem: Rheem provides a good balance of affordability and reliability. Carrier offers more premium features and higher efficiency options.
Ultimately, the best HVAC brand and model for you will depend on your specific needs, budget, and preferences. Consulting with a qualified HVAC contractor can help you make the right choice.
The Importance of Regular HVAC Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your Carrier HVAC system. Scheduling annual maintenance appointments with a qualified HVAC technician can help identify potential problems early, prevent costly repairs, and maintain optimal system performance. Maintenance tasks typically include:
- Cleaning or replacing air filters
- Inspecting and cleaning coils
- Checking refrigerant levels
- Inspecting and lubricating moving parts
- Testing electrical components
- Calibrating the thermostat
By understanding Carrier diagnostic codes, choosing the right system, and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure your HVAC system provides reliable and efficient comfort for years to come.