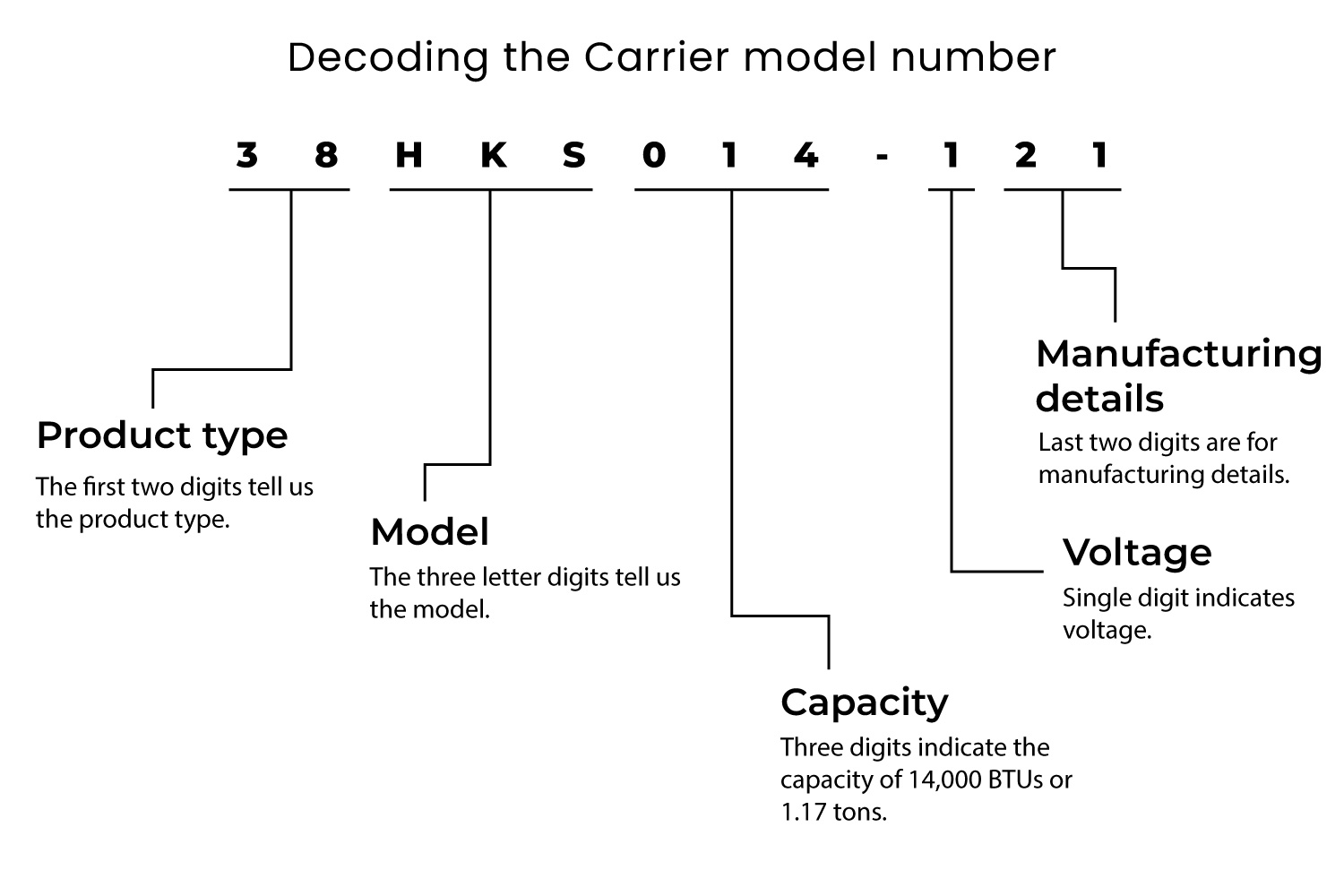
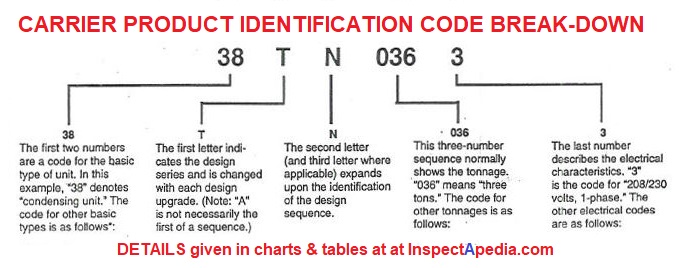
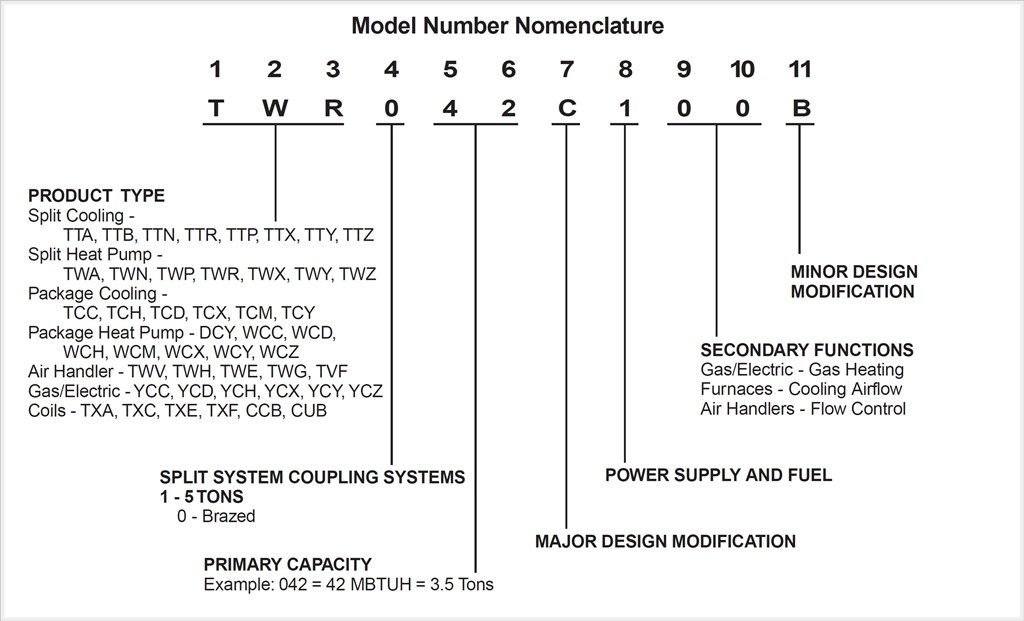
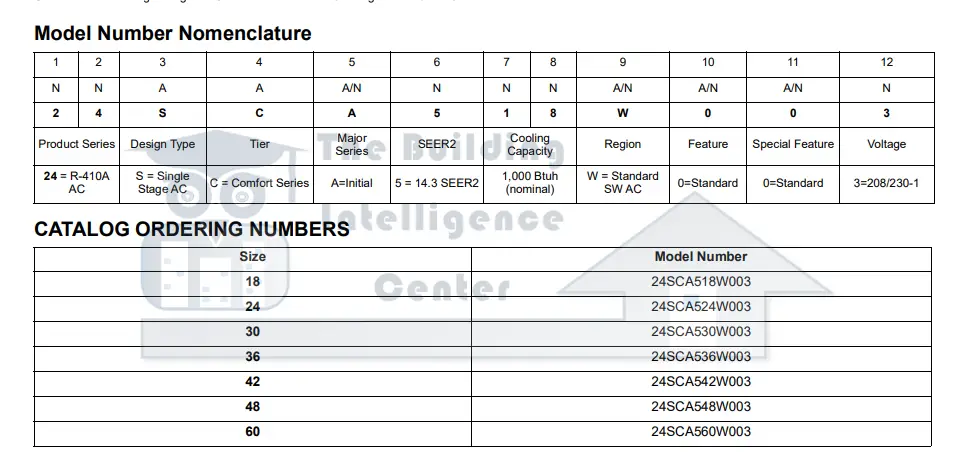
Carrier Model Number Decoder
Understanding your HVAC system is the first step to optimizing its performance and reducing your energy bills. Carrier, a leading manufacturer in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, uses a model number system that, once deciphered, unlocks valuable information about your unit’s capabilities and efficiency. This guide breaks down the Carrier model number decoder, empowering you to make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, and smart home integration for maximum energy savings.
Why Decode Your Carrier Model Number?
Your Carrier model number isn't just a random string of characters; it's a blueprint of your HVAC system. Decoding it provides crucial insights, including:
- Unit Type: Identifies whether you have an air conditioner, heat pump, furnace, or packaged unit.
- Efficiency Rating (SEER, HSPF, AFUE): Tells you how efficiently the unit converts energy into heating or cooling, directly impacting your energy bills.
- Features and Technology: Reveals specific technologies like variable-speed compressors, inverter technology, and smart controls.
- Manufacturing Date: Helps determine the age of the unit, which is critical for assessing its remaining lifespan and eligibility for warranties.
- Capacity (BTU): Indicates the unit’s heating or cooling power, ensuring it’s appropriately sized for your space.
- Compatibility: Determines compatibility with smart thermostats and other energy-saving accessories.
Armed with this knowledge, you can optimize your HVAC system for peak performance, lower energy consumption, and potentially qualify for rebates and incentives.
The Anatomy of a Carrier Model Number
While the exact format can vary slightly depending on the unit type and age, Carrier model numbers generally follow a consistent structure. Let's break down a typical Carrier air conditioner model number: 24ABC360A30
Prefix (Unit Type)
The first one or two characters usually indicate the type of unit:
- 24: Typically denotes an air conditioner.
- 38: Often represents a heat pump.
- 58: Usually indicates a gas furnace.
- 48: Could represent a packaged unit (heating and cooling combined).
Series (Efficiency and Features)
The next set of characters (usually two or three letters) specifies the series, providing clues about the unit's efficiency level and included features. These letters require cross-referencing with Carrier's product literature or online resources. However, some common indicators exist:
- ABC: This section can contain letters which can indicate the tier. The higher quality models can be indicated with an X or a V.
Capacity (BTU)
This section usually consists of three numbers and signifies the cooling or heating capacity of the unit in BTU/h (British Thermal Units per hour). Divide this number by 1,000 to get the BTU/h. In our example, "360" indicates a 36,000 BTU/h (3-ton) unit. Larger numbers indicate greater capacity.
Voltage and Phase
This part varies. In our example "A30" is a representation of the model number, but it may be representative of the voltage and phase requirements.
Decoding Key Efficiency Metrics
Understanding efficiency ratings is crucial for comparing different HVAC systems and estimating potential energy savings. Here's a quick overview of the key metrics:
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): Measures the cooling efficiency of air conditioners and heat pumps. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit. Energy Star certified air conditioners generally have a SEER rating of 15 or higher. Look for units with SEER ratings of 16 or higher to maximize energy savings. A jump from SEER 13 (the minimum standard for many older units) to SEER 16 can result in a 20% reduction in cooling costs.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): Measures the heating efficiency of heat pumps. A higher HSPF rating indicates better heating efficiency. Energy Star certified heat pumps typically have an HSPF of 8.5 or higher.
- AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): Measures the heating efficiency of furnaces. A higher AFUE rating means more of the fuel is converted into usable heat. Modern high-efficiency furnaces can achieve AFUE ratings of 95% or higher, significantly reducing fuel consumption compared to older furnaces with AFUE ratings in the 70-80% range.
When comparing HVAC systems, always consider these efficiency ratings to estimate the long-term cost savings associated with a more efficient unit.
Locating Your Carrier Model Number
The location of your Carrier model number varies depending on the type of unit:
- Air Conditioners and Heat Pumps (Outdoor Unit): Typically found on a nameplate located on the exterior of the unit, often behind a removable panel or on the side.
- Furnaces (Indoor Unit): Usually located on a nameplate inside the furnace cabinet, often near the burner or blower compartment. You may need to remove a panel to access it.
- Packaged Units: The nameplate is typically located on the exterior of the unit.
Always disconnect power to the unit before attempting to remove any panels. If you're uncomfortable locating or accessing the model number, contact a qualified HVAC technician.
Beyond the Model Number: Maximizing Energy Savings
Decoding your Carrier model number is just the beginning. To truly optimize your HVAC system for energy efficiency, consider the following:
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule annual maintenance checks by a qualified HVAC technician. Regular cleaning, filter replacements, and system tune-ups can significantly improve efficiency and extend the lifespan of your unit. Dirty air filters can reduce airflow and decrease efficiency by as much as 15%.
- Smart Thermostat Integration: Upgrade to a smart thermostat that allows you to remotely control your HVAC system, schedule temperature settings, and monitor energy usage. Some smart thermostats even learn your preferences and automatically adjust settings to optimize energy savings. Many smart thermostats are Energy Star certified.
- Proper Insulation and Sealing: Ensure your home is properly insulated and sealed to minimize heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings. According to the EPA, proper insulation and sealing can reduce energy bills by up to 15%.
- Ductwork Inspection: Inspect your ductwork for leaks and damage. Leaky ducts can waste a significant amount of energy, reducing the efficiency of your HVAC system. Seal any leaks with duct tape or mastic sealant.
- Consider Zoning: If you have a large home, consider zoning your HVAC system to control the temperature in different areas independently. This can help you avoid heating or cooling unoccupied rooms, saving energy and money.
- Utilize Government Rebates and Incentives: Check for federal, state, and local rebates and incentives for energy-efficient HVAC upgrades. The Energy Star website is a valuable resource for finding available rebates.
Leveraging Smart Home Integration for Enhanced Efficiency
Integrating your Carrier HVAC system with a smart home ecosystem can unlock even greater energy savings. Smart thermostats, sensors, and automation routines can work together to optimize your home's climate control based on your occupancy patterns, weather conditions, and energy prices.
- Occupancy Sensors: These sensors detect when rooms are occupied and automatically adjust the temperature accordingly.
- Window and Door Sensors: These sensors detect when windows or doors are open and automatically turn off the HVAC system to prevent energy waste.
- Weather Integration: Smart thermostats can access real-time weather data and adjust temperature settings to anticipate changes in outdoor conditions.
- Energy Monitoring: Smart home systems can provide detailed energy usage reports, allowing you to identify areas where you can further reduce consumption.
By leveraging the power of smart home technology, you can create a more comfortable and energy-efficient living environment.
Working with an HVAC Professional
While decoding your Carrier model number provides valuable information, it's essential to consult with a qualified HVAC professional for accurate assessments, repairs, and installations. A professional can:
- Perform a comprehensive system inspection to identify potential problems and inefficiencies.
- Recommend the most appropriate HVAC system for your home based on your specific needs and budget.
- Properly install and maintain your HVAC system to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Provide expert advice on energy-saving strategies and smart home integration.
Investing in professional HVAC services is an investment in the long-term health and efficiency of your home.
Conclusion
Decoding your Carrier model number is a powerful tool for understanding your HVAC system and identifying opportunities for energy savings. By combining this knowledge with regular maintenance, smart home integration, and professional assistance, you can create a more comfortable, efficient, and sustainable home.
Embrace the power of information and take control of your energy consumption. Your wallet – and the planet – will thank you for it. Don't forget to check for available government rebates and incentives to further reduce the cost of upgrading to a more efficient HVAC system. By understanding the technology in your home, you can begin to harness its power to lower your energy costs and lessen the impact on the planet.