Checking A Capacitor With Ohm Meter

Understanding Capacitors and HVAC Systems
Capacitors are essential components in many HVAC systems, playing a crucial role in starting and running motors. They provide the initial surge of energy needed to get a motor spinning and help maintain efficient operation. If your air conditioner, heat pump, or furnace isn't functioning correctly, a faulty capacitor could be the culprit. This article will guide you through the process of checking a capacitor using an ohm meter (also known as a multimeter in its resistance mode), empowering you to troubleshoot common HVAC issues.
What is a Capacitor and Why Does it Fail?
A capacitor is essentially a temporary energy storage device. In HVAC systems, they are primarily used with motors that power fans, compressors, and blowers. There are two main types: start capacitors (used for initial motor startup) and run capacitors (used for continuous motor operation).
Capacitors fail for various reasons, including:
- Overheating: Excessive heat can damage the internal components.
- Age: Capacitors have a limited lifespan, typically 5-10 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
- Voltage Surges: Fluctuations in voltage can stress the capacitor beyond its rated capacity.
- Physical Damage: Cracks, bulges, or leaks are clear signs of capacitor failure.
Safety First: Disconnecting Power
Safety is paramount when working with electrical components. Before you begin any testing or repair, always disconnect the power supply to your HVAC unit. This typically involves turning off the breaker at the electrical panel that serves the unit. Double-check with a voltage tester to ensure the power is completely off.
Important: Capacitors can store a dangerous electrical charge even after the power is disconnected. You must discharge the capacitor before handling it. Use an insulated screwdriver to short the terminals. Touch the screwdriver blade across both terminals simultaneously. The blade and terminals should be fully insulated. This step is vital to prevent electric shock.
Gathering Your Tools
You'll need the following tools and equipment:
- Ohm Meter (Multimeter): Set to resistance mode (Ohms - Ω). An auto-ranging meter is preferred.
- Insulated Screwdriver: For discharging the capacitor.
- Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from potential hazards.
- Work Gloves: To provide electrical and physical protection.
- Camera or Phone: To take pictures of the wiring connections before disconnecting anything (for easy reassembly).
The Testing Process: Checking with an Ohm Meter
Follow these steps to check a capacitor using an ohm meter:
- Disconnect Power: As described above, disconnect power to the HVAC unit and discharge the capacitor.
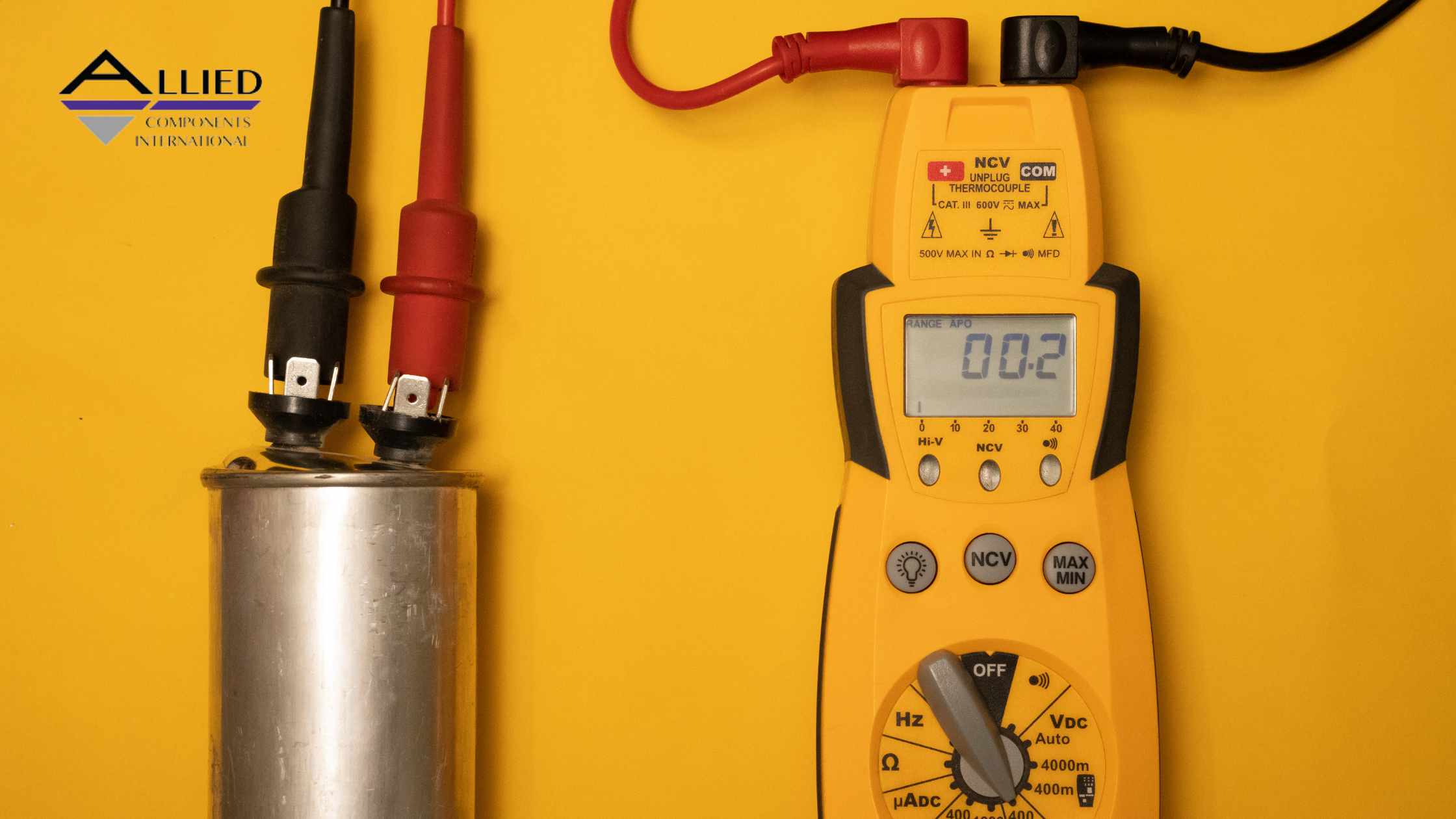
- Locate the Capacitor: Capacitors are typically cylindrical components found inside the HVAC unit's control panel. They are usually silver or gray in color.
- Disconnect Wires: Carefully disconnect the wires attached to the capacitor terminals. Take a picture or draw a diagram of the wiring configuration *before* disconnecting anything to ensure you can reconnect everything correctly. Use needle-nose pliers to remove the wires if necessary.
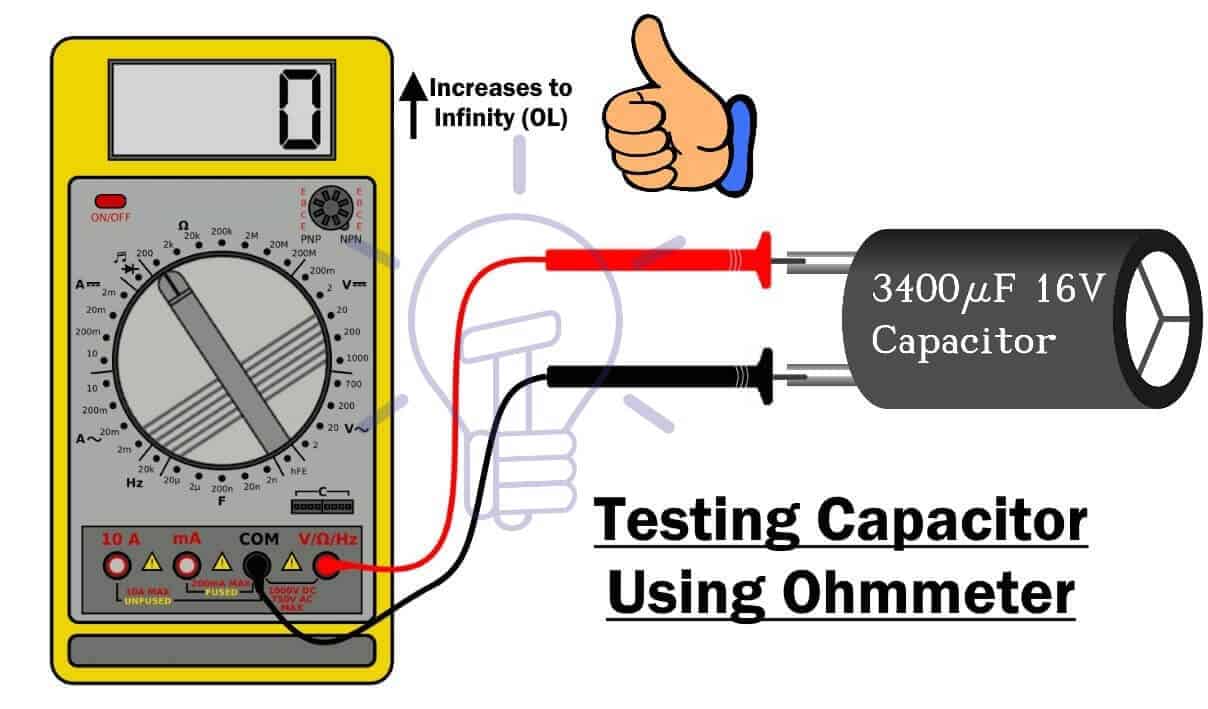
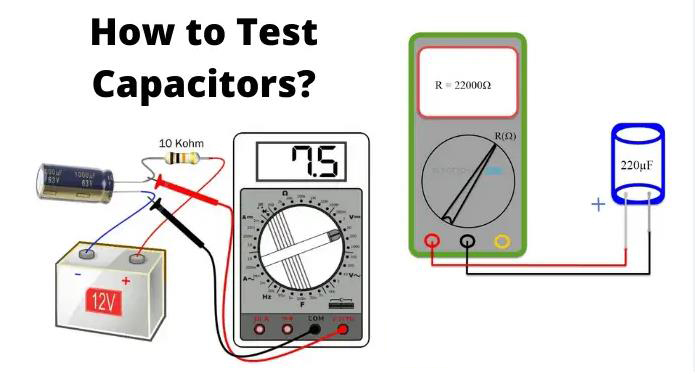
- Set the Meter: Turn on your ohm meter and set it to the highest resistance range (usually in megaohms – MΩ). If you have an auto-ranging meter, simply set it to resistance mode (Ω).
- Connect the Probes: Connect the meter probes to the capacitor terminals. Polarity doesn't matter for most HVAC capacitors.
- Observe the Reading:
- Charging Capacitor: A good capacitor will initially show a low resistance reading, which will then gradually increase towards infinity (or overload - OL on some meters) as the capacitor charges. This indicates the capacitor is storing energy.
- Open Capacitor: If the meter reads infinity (OL) immediately and doesn't change, the capacitor is likely open, meaning it's not storing any charge. It's faulty and needs replacing.
- Shorted Capacitor: If the meter reads a very low resistance (close to zero) and stays there, the capacitor is likely shorted. It's faulty and needs replacing.
- Leaky Capacitor: If the meter reading starts low and increases slowly but stops at a low resistance value (e.g., a few ohms or kilohms), the capacitor may be leaky. This indicates a weakening capacitor. While it might still function somewhat, it's nearing failure and should be replaced.
- Reverse the Probes: Reverse the meter probes on the capacitor terminals and repeat the observation. The reading should behave similarly to the initial test.
Understanding Microfarads (µF) and Voltage Ratings
Capacitors are rated in microfarads (µF), which indicates their capacitance (energy storage capacity), and voltage. The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the capacitor can safely handle. It's crucial to replace a capacitor with one that has the same microfarad rating and equal or higher voltage rating. Using a capacitor with a lower voltage rating can result in failure and potential safety hazards. The microfarad and voltage ratings are printed on the capacitor's label.
Testing Microfarad (µF) Capacity
For the most accurate assessment, a capacitance meter is preferable. Some multimeters include a capacitance testing function. If your meter has this, set it to the appropriate microfarad (µF) range and connect the probes to the capacitor terminals. The reading should be close to the value printed on the capacitor label. A significant deviation (e.g., more than 10%) indicates a failing capacitor.
Replacing the Capacitor
If your capacitor fails any of the tests, it needs to be replaced. Here's a simplified overview of the replacement process:
- Purchase a Replacement: Buy a new capacitor with the exact same microfarad (µF) rating and equal or higher voltage rating.
- Disconnect Power: Ensure the power is disconnected and the old capacitor is discharged.
- Remove the Old Capacitor: Disconnect the wires from the old capacitor.
- Install the New Capacitor: Connect the wires to the terminals of the new capacitor, following the wiring diagram or photo you took earlier.
- Secure the Capacitor: Make sure the capacitor is securely mounted in its original position.
- Restore Power: Turn the breaker back on at the electrical panel.
- Test the System: Turn on the HVAC unit and observe its operation. It should now function correctly.
Note: If you're uncomfortable working with electrical components, it's always best to hire a qualified HVAC technician to perform the replacement.
Popular HVAC Brands and Models
When choosing a new HVAC system, several brands and models stand out for their efficiency and reliability. Here are a few popular options, along with key specifications:
- Carrier Infinity Series: Known for high efficiency and advanced features.
- AFUE (Furnaces): Up to 98.5%
- SEER (Air Conditioners): Up to 26
- HSPF (Heat Pumps): Up to 13
- Trane XV Series: Offers excellent performance and durability.
- AFUE (Furnaces): Up to 97%
- SEER (Air Conditioners): Up to 22
- HSPF (Heat Pumps): Up to 10
- Lennox Signature Series: Innovative technology and energy efficiency.
- AFUE (Furnaces): Up to 99%
- SEER (Air Conditioners): Up to 28
- HSPF (Heat Pumps): Up to 10
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) measures the efficiency of furnaces. SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) measures the cooling efficiency of air conditioners. HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) measures the heating efficiency of heat pumps. Higher ratings indicate greater energy efficiency and lower operating costs.
Warranties and Maintenance
HVAC systems typically come with warranties covering parts and labor. It's essential to understand the terms and conditions of the warranty. Register your system with the manufacturer to ensure coverage. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning coils and changing air filters, can extend the lifespan of your system and maintain its efficiency. Consider a service agreement with a qualified HVAC contractor for routine inspections and maintenance.
Conclusion
Checking a capacitor with an ohm meter is a valuable skill for troubleshooting HVAC issues. By following the safety precautions and testing procedures outlined in this guide, you can identify a faulty capacitor and determine if replacement is necessary. Remember to prioritize safety and consult a qualified HVAC technician if you're unsure about any aspect of the process. Choosing a reputable HVAC brand and model, coupled with proper maintenance, will ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency for years to come.