Concrete Slab Radiant Floor Heating Systems

Radiant floor heating, particularly when embedded in a concrete slab, offers a compelling alternative to traditional forced-air HVAC systems. This method provides consistent, comfortable heat, often with significantly lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint. This article delves into the intricacies of concrete slab radiant floor heating, exploring its advantages, installation considerations, cost-effectiveness, and integration with smart home technologies.
Understanding Concrete Slab Radiant Floor Heating
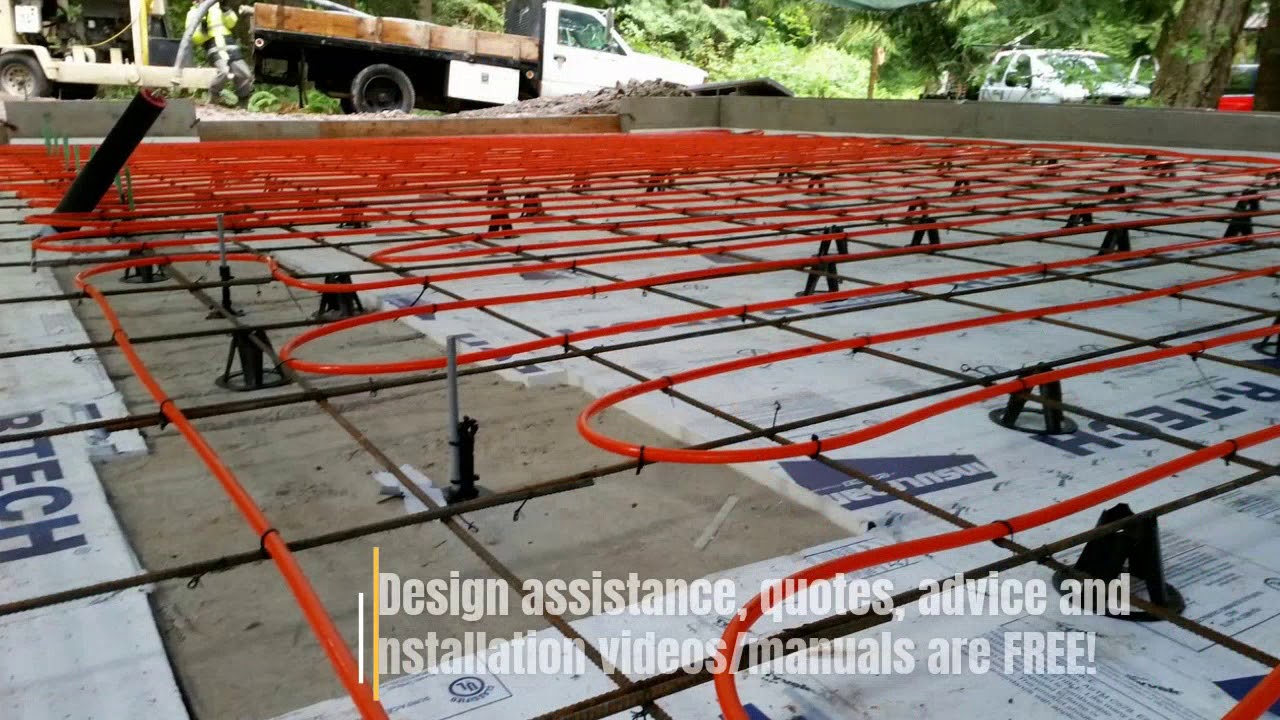
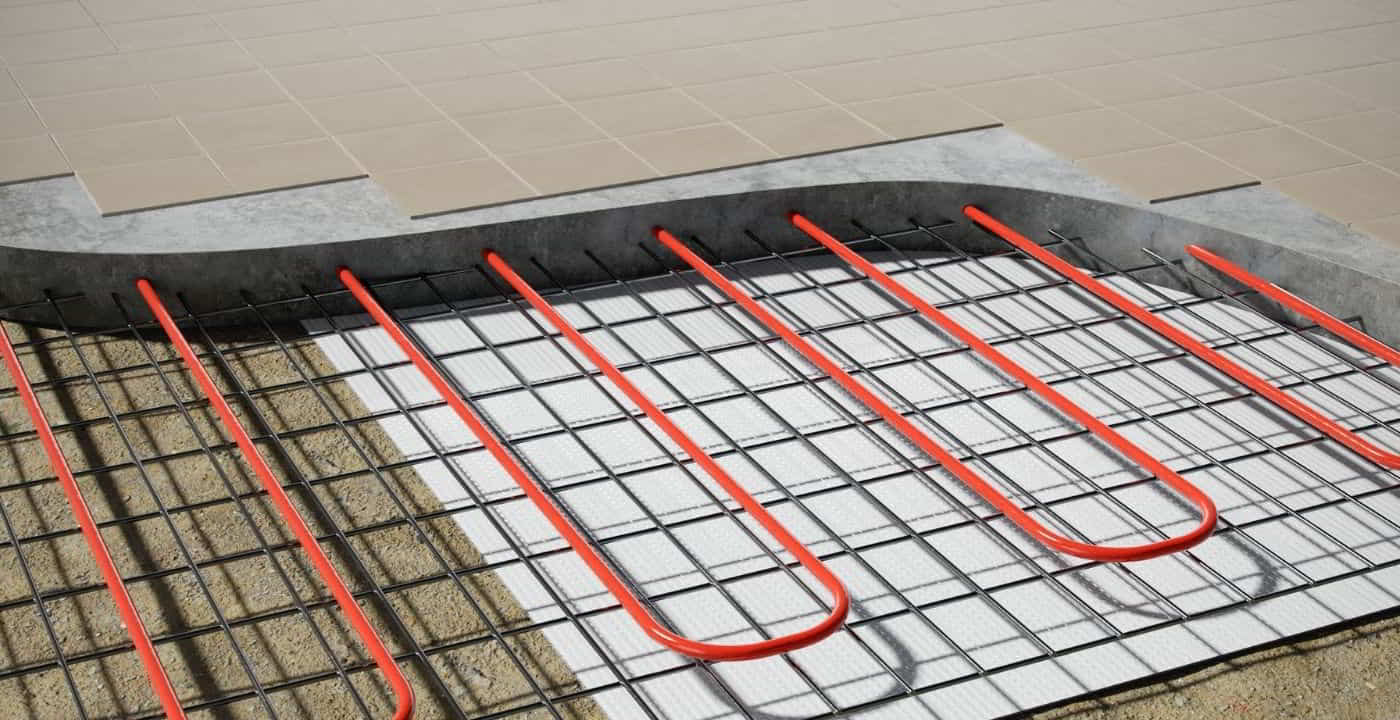
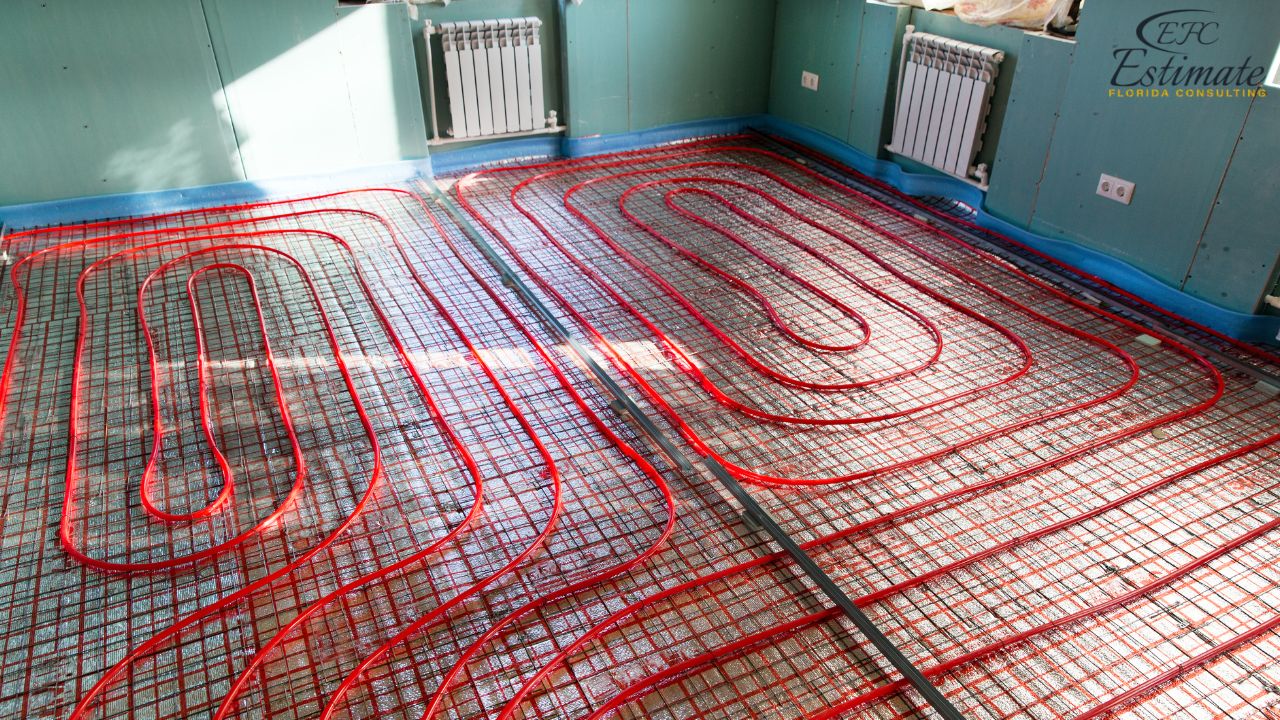
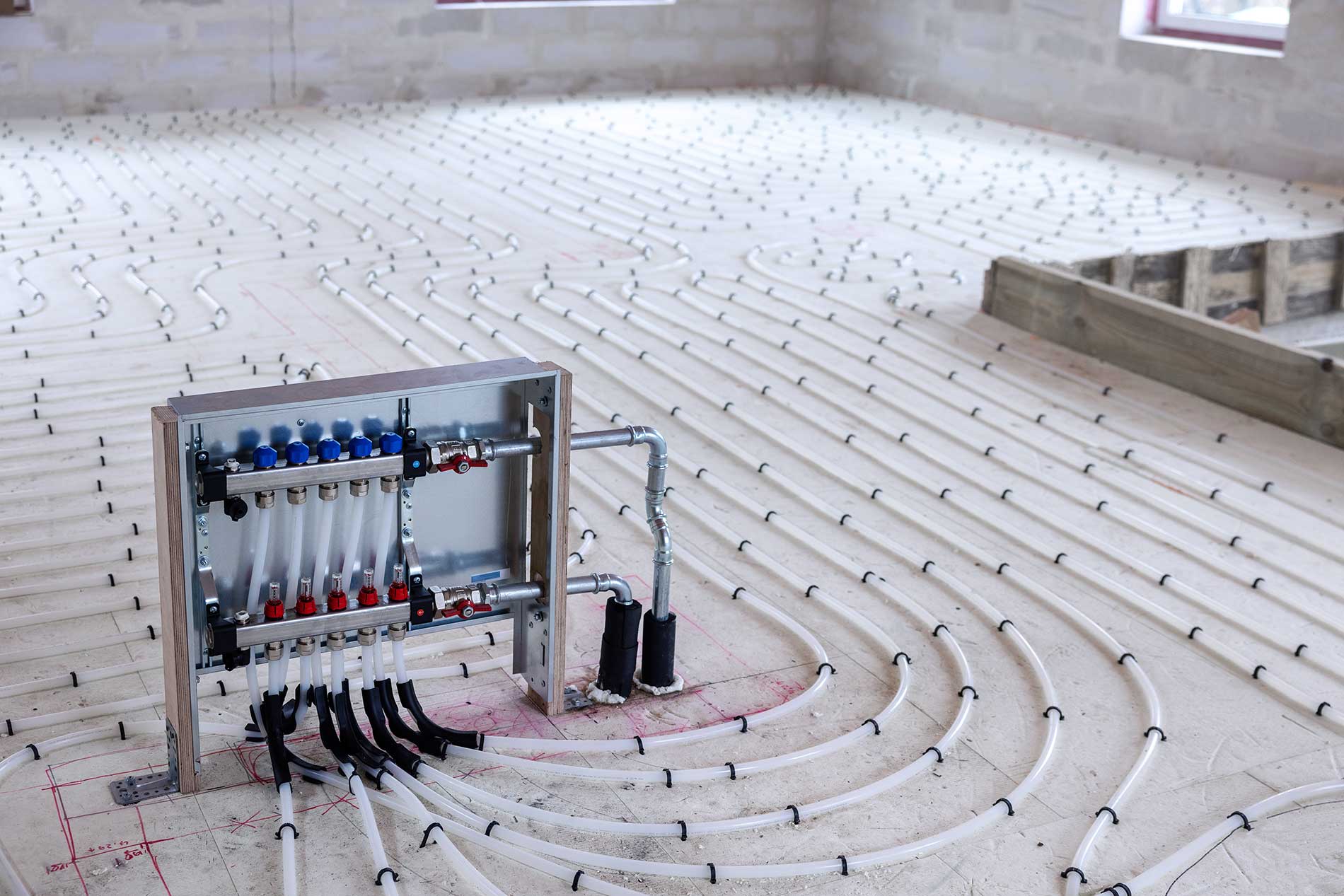
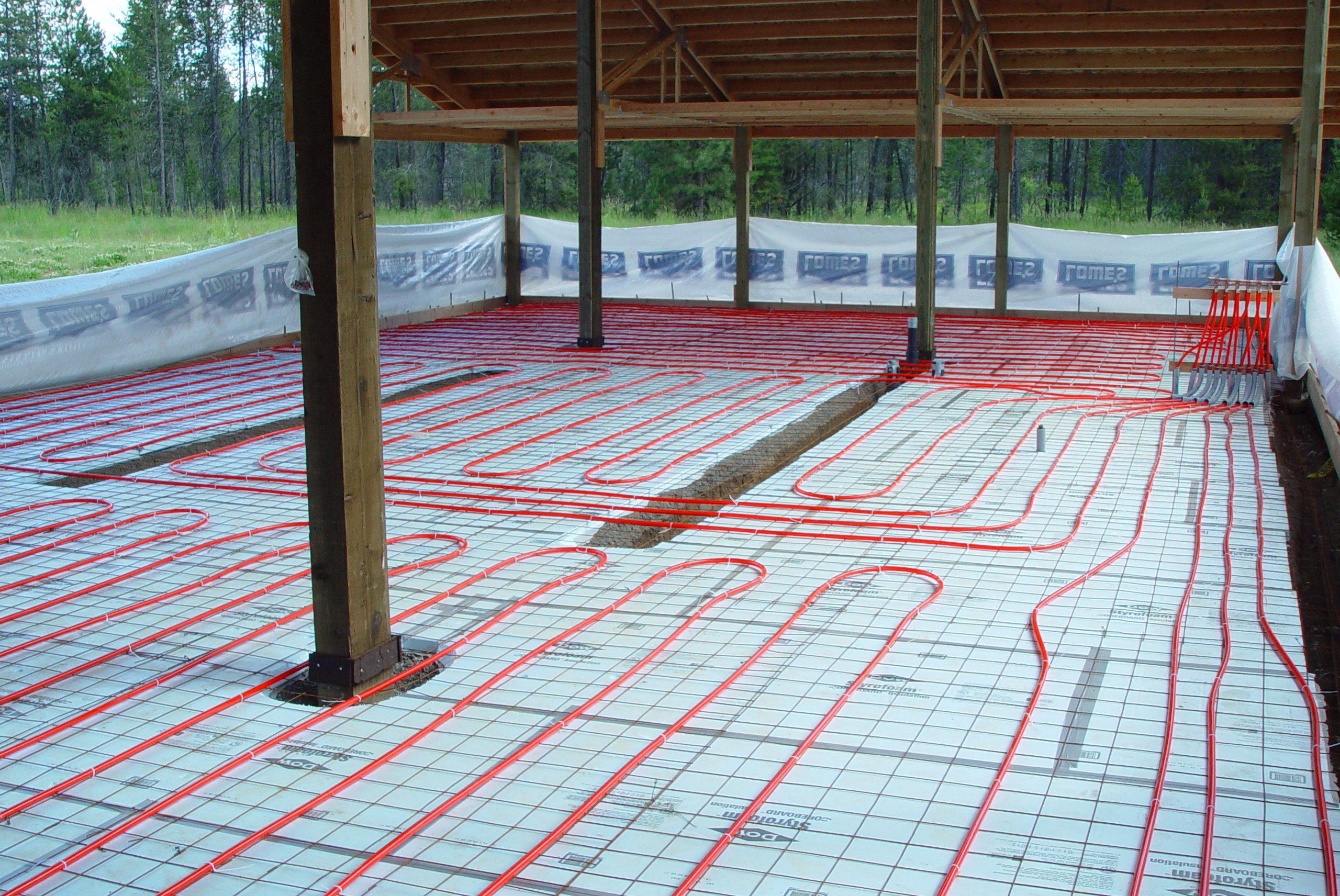
At its core, a concrete slab radiant floor heating system utilizes the thermal mass of a concrete slab to store and radiate heat. PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) tubing is embedded within the concrete, through which heated water circulates. This warm water transfers its heat to the concrete, which then radiates that heat upwards into the room. This radiant heat warms objects and people directly, rather than just heating the air, leading to a more comfortable and efficient heating experience. Unlike forced-air systems that can create drafts and uneven temperatures, radiant floor heating provides consistent warmth from the ground up.
There are two primary installation methods: wet installations and dry installations. Wet installations involve encasing the PEX tubing directly within the concrete slab during construction. Dry installations, on the other hand, involve placing the tubing in pre-grooved panels or between sleepers on top of the existing subfloor before pouring a thin concrete topping or installing other flooring materials. Wet installations generally offer better thermal performance due to the direct contact between the tubing and the concrete mass. Dry installations are more suitable for retrofit projects where the existing slab is already in place.
Benefits of Concrete Slab Radiant Floor Heating
The advantages of concrete slab radiant floor heating are numerous and contribute to its growing popularity:
- Energy Efficiency: Radiant floor heating operates at lower water temperatures (typically 80-120°F) compared to baseboard heaters (140-180°F) or forced-air systems (120-140°F). This lower temperature differential reduces heat loss and allows for more efficient operation, especially when paired with high-efficiency boilers, heat pumps, or solar thermal systems. Studies have shown potential energy savings of 20-40% compared to conventional heating systems.
- Consistent Comfort: The radiant heat provides even temperatures throughout the room, eliminating cold spots and drafts. The thermal mass of the concrete slab ensures that the heat is retained and released gradually, maintaining a comfortable environment even when the heating system isn't actively running.
- Improved Air Quality: Unlike forced-air systems, radiant floor heating doesn't circulate dust, allergens, and other airborne particles, leading to improved indoor air quality. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with allergies or respiratory sensitivities.
- Quiet Operation: Radiant floor heating systems operate silently, eliminating the noise associated with fans and ductwork.
- Design Flexibility: Radiant floor heating allows for greater design flexibility, as it eliminates the need for bulky radiators or unsightly vents. It's compatible with a wide range of flooring materials, including tile, stone, wood, and carpet (although carpet can slightly reduce efficiency).
- Increased Home Value: Installing a modern, energy-efficient heating system like radiant floor heating can increase the resale value of your home.
Cost Considerations and ROI
The initial cost of installing a concrete slab radiant floor heating system can be higher than that of traditional forced-air systems. However, the long-term cost savings associated with reduced energy consumption can often offset this initial investment. Factors influencing the cost include:
- Size of the area to be heated.
- Type of flooring material.
- Complexity of the installation.
- Choice of heat source (boiler, heat pump, solar thermal).
- Installation method (wet vs. dry).
While costs vary widely, a general estimate for a new construction wet installation ranges from $8 to $15 per square foot. Retrofit dry installations can be more expensive, ranging from $12 to $20 per square foot. To calculate the potential return on investment (ROI), consider the following:
- Estimate your annual energy savings: Compare your current energy bills to projected bills with radiant floor heating, considering the potential 20-40% reduction.
- Calculate the total installation cost: Include materials, labor, and any necessary permits.
- Determine the payback period: Divide the total installation cost by the annual energy savings to estimate how long it will take to recoup your investment.
Don't forget to factor in potential government rebates and incentives for energy-efficient upgrades. Energy Star, for example, often provides guidelines for energy-efficient appliances and building practices, which can help you qualify for rebates. Local utility companies may also offer incentives for installing radiant floor heating systems. Researching and taking advantage of these programs can significantly reduce the overall cost of the project.
Choosing the Right Heat Source
The heat source is a critical component of any radiant floor heating system. Several options are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Boilers: High-efficiency condensing boilers are a popular choice for radiant floor heating systems. They are highly efficient at heating water and can be fueled by natural gas, propane, or oil.
- Heat Pumps: Air-source and geothermal heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and ability to provide both heating and cooling. Geothermal heat pumps are particularly well-suited for radiant floor heating, as they provide a consistent and stable heat source.
- Solar Thermal Systems: Solar thermal systems use solar collectors to heat water, which can then be used to heat the concrete slab. This is a highly sustainable option, but it may require a backup heat source for periods of low solar radiation.
The best heat source for your radiant floor heating system will depend on your location, energy costs, and environmental priorities. Consulting with a qualified HVAC contractor is essential to determine the most appropriate option.
Smart Home Integration
Integrating your concrete slab radiant floor heating system with smart home technology can further enhance its energy efficiency and comfort. Smart thermostats allow you to control the temperature of each zone independently, optimizing energy usage and personalizing comfort levels. Features such as:
- Remote access and control: Adjust the temperature from your smartphone or tablet, even when you're away from home.
- Programmable schedules: Set schedules to automatically adjust the temperature based on your daily routines.
- Learning algorithms: Some smart thermostats use machine learning to learn your heating preferences and optimize energy usage accordingly.
- Zoning capabilities: Control the temperature of individual rooms or zones, ensuring that you only heat the areas you're using.
- Integration with other smart home devices: Connect your thermostat to other smart home devices, such as occupancy sensors and window sensors, to further optimize energy efficiency. For example, the system can automatically lower the temperature when a room is unoccupied or when a window is opened.
The combination of concrete slab radiant floor heating and smart home technology provides unparalleled control over your home's heating system, resulting in significant energy savings and a more comfortable living environment. Smart sensors can also monitor floor temperatures and adjust the water flow accordingly, preventing overheating and ensuring even heat distribution.
Installation Considerations
Proper installation is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of a concrete slab radiant floor heating system. It's essential to hire a qualified and experienced HVAC contractor with expertise in radiant floor heating systems. Here are some key considerations during installation:
- Slab Insulation: Insulating the concrete slab is essential to prevent heat loss to the ground. This is typically achieved by installing a layer of rigid foam insulation beneath the slab.
- PEX Tubing Installation: The PEX tubing must be installed correctly to ensure even heat distribution and prevent leaks. The tubing should be securely fastened to the rebar or wire mesh within the slab.
- Manifold Placement: The manifold, which distributes the hot water to the individual zones, should be located in an accessible area for maintenance and repairs.
- Pressure Testing: After the tubing is installed, it should be pressure tested to ensure that there are no leaks.
- Concrete Pouring: The concrete should be poured carefully to avoid damaging the PEX tubing.
Following industry best practices and adhering to building codes are essential for a successful installation. Regular maintenance, such as flushing the system to remove debris and inspecting the manifold for leaks, will help to ensure the long-term performance of the system.
Conclusion
Concrete slab radiant floor heating offers a compelling combination of energy efficiency, comfort, and design flexibility. While the initial investment may be higher than that of traditional heating systems, the long-term cost savings and improved indoor air quality can make it a worthwhile investment. By choosing the right heat source, integrating smart home technology, and ensuring proper installation, you can maximize the benefits of this innovative heating solution. For homeowners and businesses looking to reduce their energy bills, improve their comfort, and create a more sustainable environment, concrete slab radiant floor heating is an excellent option to consider. Consult with a qualified HVAC contractor to determine if it's the right choice for your needs. Embrace the warmth and efficiency of radiant heat, and step into a more comfortable and sustainable future.