Cost Of Home Air Conditioner Replacement

Replacing a home air conditioner is a significant investment, and understanding the associated costs is crucial for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers alike. This comprehensive guide will break down the various factors that influence the price of a new AC system, helping you make informed decisions. We’ll cover everything from the initial equipment costs to installation fees, energy efficiency considerations, and long-term maintenance expenses.
Factors Influencing Air Conditioner Replacement Costs
Several key factors contribute to the overall cost of replacing an air conditioner. These include the type of AC system, its size and efficiency, the complexity of the installation, and regional labor rates.
Type of Air Conditioner
The type of AC system is a primary cost driver. Here's a breakdown of common types:
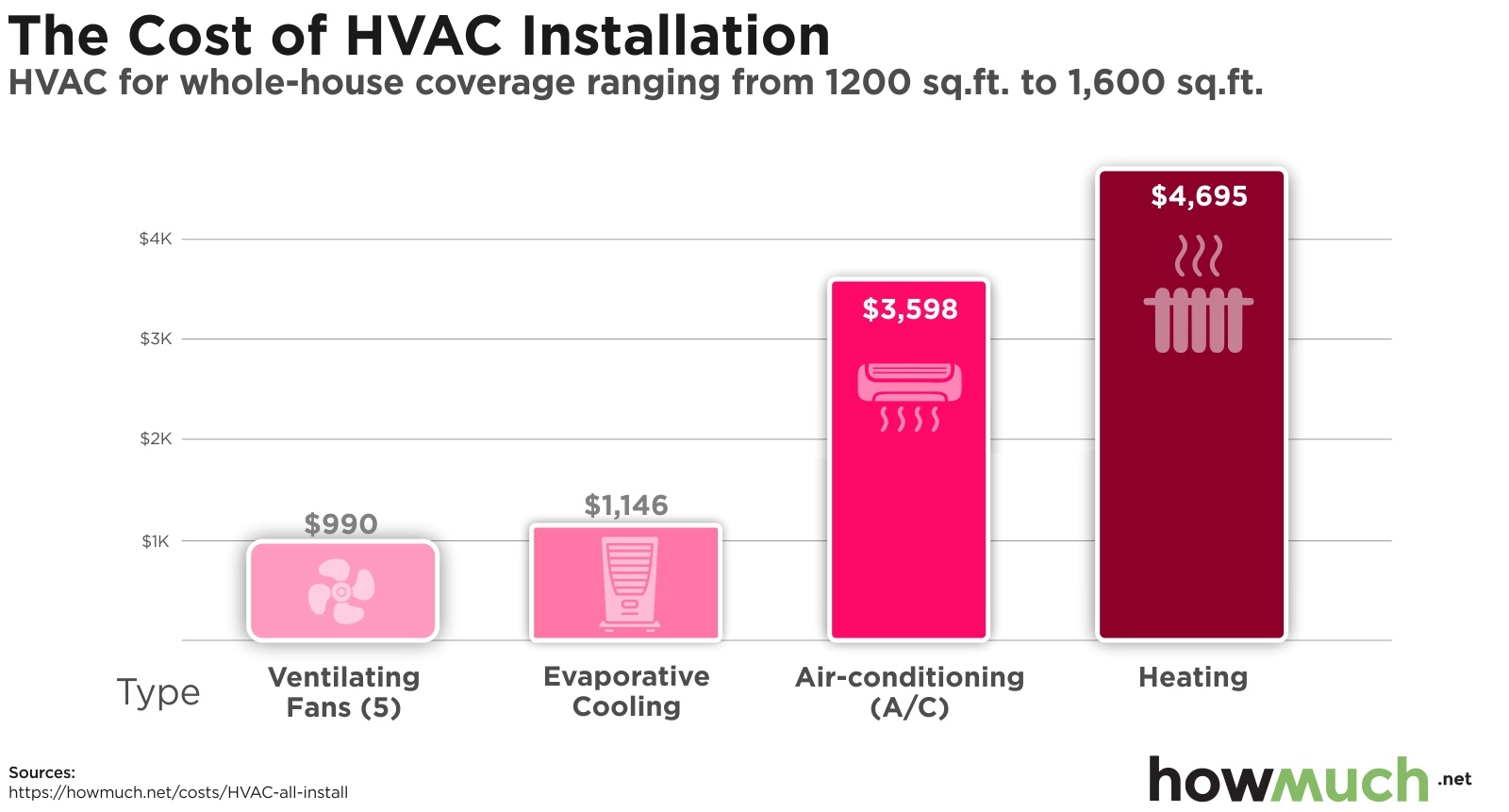
- Central Air Conditioners: These are the most common type for residential homes. They consist of an outdoor condenser unit and an indoor evaporator coil, connected by refrigerant lines. Replacement costs typically range from $4,000 to $12,000, including installation. A split system central air conditioner is often the most cost-effective choice for existing homes with ductwork.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ideal for homes without existing ductwork or for adding cooling to specific rooms. These systems have an outdoor unit and one or more indoor air handlers. Costs range from $3,000 to $15,000 or more, depending on the number of indoor units and the complexity of the installation. Technicians appreciate the relative ease of installation, though proper refrigerant line placement is critical.
- Heat Pumps: These systems can both heat and cool a home, making them a versatile option. Replacement costs are similar to central air conditioners, typically ranging from $4,500 to $13,000, including installation. They're a good choice for climates with moderate winters.
- Window Air Conditioners: The least expensive option, suitable for cooling a single room. Prices range from $150 to $800 per unit. They offer limited cooling capacity and energy efficiency compared to central systems.
- Portable Air Conditioners: Similar to window units, but they can be moved from room to room. Prices range from $300 to $1000. They require venting to the outside, typically through a window.
Size and Efficiency (BTU & SEER)
The size of the air conditioner, measured in BTU (British Thermal Units), and its efficiency, measured in SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), directly impact the price.
- BTU: A larger home requires a higher BTU rating. A correctly sized unit will efficiently cool your home. An undersized unit will struggle to maintain temperature, while an oversized unit will cycle on and off frequently, leading to poor dehumidification and wasted energy.
- SEER: The SEER rating indicates how efficiently the AC unit converts electricity into cooling. Higher SEER ratings mean lower energy bills. Current minimum SEER standards are 14 or 15, depending on the region. High-efficiency units can have SEER ratings of 20 or higher. Higher SEER units generally cost more upfront but offer significant long-term savings. Consider a SEER rating of at least 16 for maximum energy efficiency.
For example, replacing a 2-ton (24,000 BTU) AC unit with a 14 SEER rating might cost $4,000, while upgrading to a 3-ton (36,000 BTU) unit with a 18 SEER rating could cost $6,000 or more.
Installation Complexity
The complexity of the installation significantly affects labor costs. Factors that increase complexity include:
- Ductwork Modifications: If your existing ductwork needs repair, modification, or replacement, this will add to the overall cost. Older homes often have leaky or poorly designed ductwork that reduces efficiency.
- Accessibility: Difficult access to the outdoor unit location or the indoor evaporator coil can increase labor time.
- Electrical Upgrades: If your existing electrical panel is insufficient to handle the new AC unit's power requirements, you'll need to upgrade it, adding to the cost.
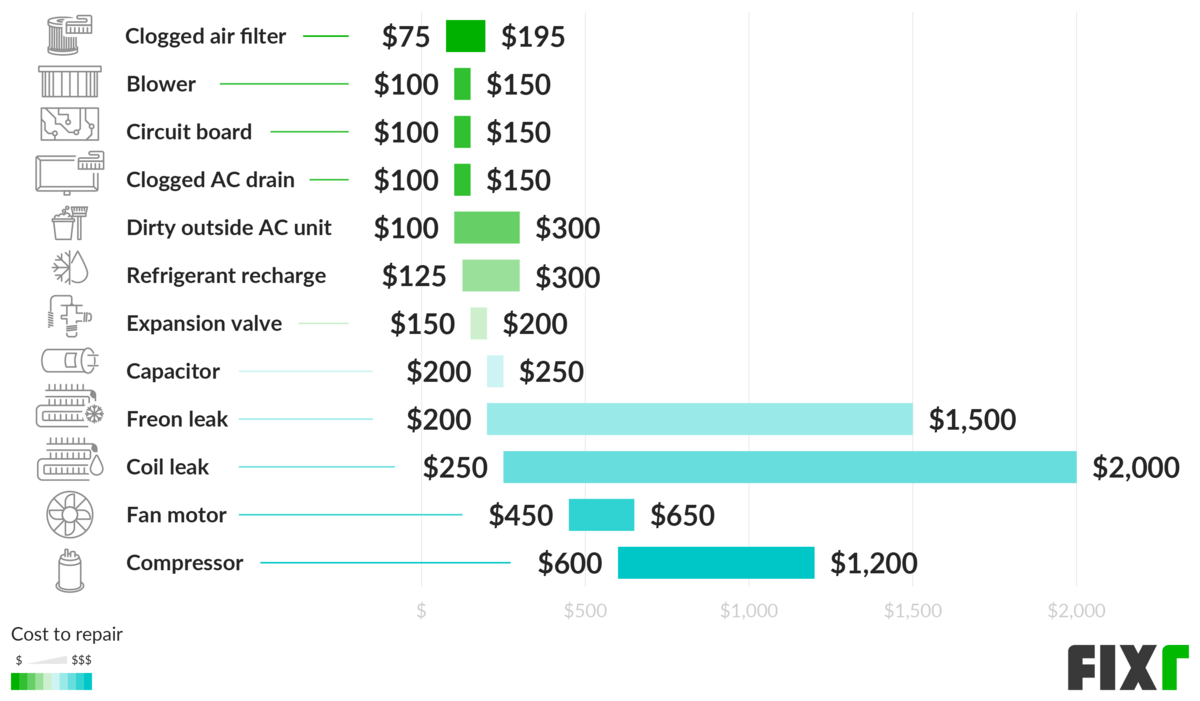
- Refrigerant Line Replacement: Replacing old or damaged refrigerant lines adds to the labor and material costs. Ensure the installer uses appropriate line sizes for the system's capacity.
A straightforward AC replacement in an easily accessible location might take 8-12 hours, while a more complex installation with ductwork modifications could take 16 hours or more.
Regional Labor Rates
Labor rates for HVAC technicians vary significantly across the country. Metropolitan areas typically have higher labor costs than rural areas. Expect to pay anywhere from $75 to $150 per hour for qualified HVAC technicians.
Breaking Down the Costs
Let's look at a more detailed breakdown of the costs involved in replacing an air conditioner:
- Equipment Costs: This is the cost of the AC unit itself (condenser and evaporator coil or mini-split unit). Prices vary depending on the type, size, and efficiency. Expect to pay $2,500 to $8,000 for the equipment alone.
- Installation Labor: This includes the cost of labor to remove the old unit, install the new unit, connect the refrigerant lines, and perform electrical connections. Installation labor can range from $1,500 to $4,000, depending on the complexity.
- Permits and Inspections: Most municipalities require permits for AC replacements to ensure compliance with building codes. Permit fees typically range from $50 to $300. Inspections are also required to verify the installation meets code standards.
- Refrigerant: The cost of refrigerant is usually included in the installation price, but it's important to confirm. R-410A is a common refrigerant, but newer refrigerants with lower global warming potential are becoming more prevalent.
- Ductwork Modifications: As mentioned earlier, any necessary ductwork repairs or modifications will add to the cost. This can range from a few hundred dollars for minor repairs to several thousand dollars for a complete ductwork replacement.
- Electrical Upgrades: If an electrical upgrade is required, expect to pay several hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the extent of the work.
- Disposal Fees: There may be a fee for disposing of the old AC unit, as it contains refrigerants that must be handled properly.
Long-Term Costs: Energy Efficiency and Maintenance
The initial cost of replacing an AC unit is only part of the equation. It's important to consider the long-term costs associated with energy consumption and maintenance.
Energy Efficiency Savings
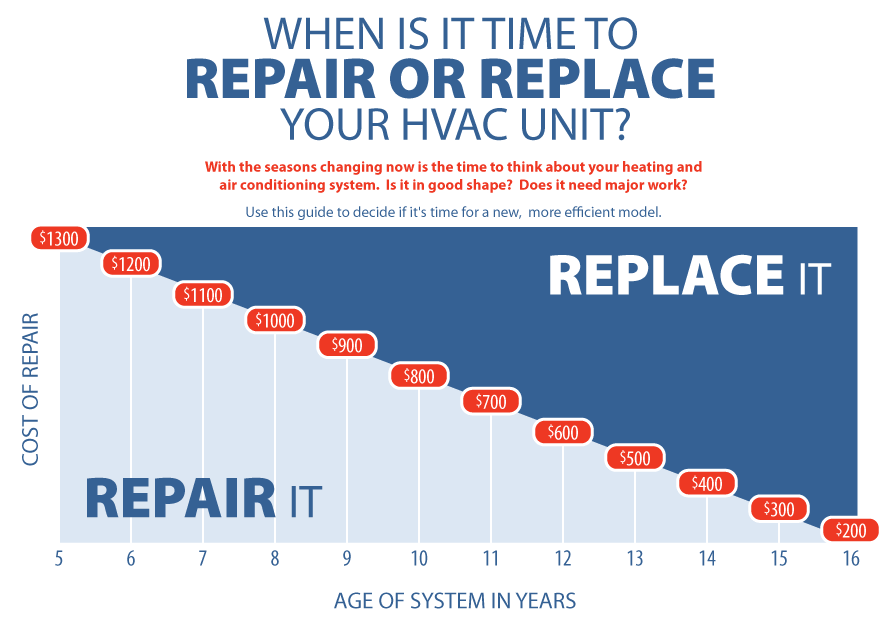
Upgrading to a higher SEER unit can significantly reduce your energy bills. For example, replacing a 10 SEER unit with a 16 SEER unit can save you 37.5% on your cooling costs. Over the lifespan of the unit (15-20 years), these savings can add up to thousands of dollars.
Use this formula to estimate potential energy savings: [(Old SEER - New SEER) / Old SEER] x 100 = Percentage Savings
Always factor in your local electricity rates and the number of hours per year you typically use your AC to estimate the actual dollar savings.
Maintenance Costs
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your AC unit running efficiently and to prolong its lifespan. Maintenance tasks include:
- Changing Air Filters: Dirty air filters restrict airflow and reduce efficiency. Replace air filters every 1-3 months.
- Cleaning Coils: The condenser and evaporator coils can become dirty, reducing heat transfer. Clean the coils annually.
- Checking Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can indicate a leak, which needs to be repaired promptly.
- Inspecting Electrical Components: Check wiring and connections for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Consider purchasing a maintenance agreement from your HVAC contractor. These agreements typically include annual tune-ups and discounts on repairs. A typical maintenance agreement might cost $150-$300 per year.
Obtaining Quotes and Choosing a Contractor
Getting multiple quotes from reputable HVAC contractors is essential to ensure you're getting a fair price and quality service. Here are some tips for obtaining quotes:
- Get at least three quotes: This allows you to compare prices and services.
- Ask for a detailed breakdown of costs: The quote should include the cost of equipment, installation labor, permits, and any other associated fees.
- Check the contractor's credentials: Make sure the contractor is licensed and insured.
- Read online reviews: See what other customers have to say about the contractor's work.
- Ask for references: Speak to previous customers to get firsthand feedback.
Choosing the right contractor is just as important as choosing the right AC unit. A reputable contractor will provide expert advice, quality installation, and reliable service.
Tip: When comparing quotes, don't just focus on the lowest price. Consider the contractor's experience, reputation, and the quality of the equipment they're offering.
Conclusion
Replacing a home air conditioner is a significant investment that requires careful planning. By understanding the factors that influence the cost, you can make informed decisions and choose the right system for your needs and budget. Remember to consider long-term energy efficiency and maintenance costs to maximize your investment and ensure years of comfortable cooling.