Cost Of New Gas Furnace And Installation

A cold house in the middle of winter is more than just uncomfortable; it can be a safety hazard. Your gas furnace, responsible for keeping your home warm, can sometimes fail. This article provides a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting common gas furnace issues and identifying when professional help is necessary.
Understanding the Basics of a Gas Furnace
Before diving into troubleshooting, it's helpful to understand the basic components of a gas furnace:
- Thermostat: Controls the temperature settings and signals the furnace to turn on or off.
- Gas Valve: Regulates the flow of natural gas or propane to the burners.
- Burners: Where the gas mixes with air and ignites to produce heat.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers the heat from the burning gas to the air that circulates through your home.
- Blower Motor: Circulates the heated air through the ductwork and into your rooms.
- Ignition System: Lights the gas in the burners (can be a pilot light, spark igniter, or hot surface igniter).
- Flame Sensor: Detects the presence of a flame and ensures the gas valve stays open.
- Control Board: The brains of the furnace, controlling all the other components.
- Flue Pipe: Vents combustion gases safely outside your home.
Safety First! Before attempting any troubleshooting, turn off the power to the furnace at the breaker box. Also, familiarize yourself with the location of your gas shut-off valve. If you smell gas at any time, immediately evacuate your home and call your gas company from a safe location.
Common Furnace Problems and DIY Troubleshooting
1. The Furnace Won't Turn On
This is a common issue. Here's how to troubleshoot it:
- Check the Thermostat:
- Is the thermostat set to "Heat"? Make sure it's not accidentally set to "Cool" or "Off."
- Is the temperature set high enough? Increase the setpoint temperature a few degrees above the current room temperature.
- Are the batteries in the thermostat good? Low batteries can cause malfunctions. Replace them with new ones.
- Check the Power Supply:
- Is the furnace switch turned on? Most furnaces have a dedicated on/off switch near the unit. Make sure it's in the "On" position.
- Check the circuit breaker: Locate the breaker for the furnace in your electrical panel. If it's tripped, reset it. If it trips again immediately, *do not* continue resetting it. This indicates a short circuit and requires professional attention.
- Check the Furnace Filter:
- A clogged air filter restricts airflow, which can cause the furnace to overheat and shut down as a safety measure. Remove the filter and hold it up to the light. If you can't see much light through it, it needs to be replaced. Replace the filter with a new one of the correct size and type.
When to Call a Pro: If you've checked the thermostat, power supply, and filter, and the furnace still won't turn on, there may be a more complex issue, such as a faulty control board, gas valve, or ignition system. Call a qualified HVAC technician.
2. The Furnace Turns On But Doesn't Produce Heat
If the furnace is running, but you're not getting any heat, here's what to check:
- Check the Pilot Light (if applicable):
- Some older furnaces have a pilot light that needs to be lit manually. If the pilot light is out, follow the manufacturer's instructions to relight it. These instructions are usually found on a sticker near the pilot light assembly.
- Important Safety Note: If you smell gas while trying to light the pilot, *immediately* stop and evacuate the area. Call your gas company from a safe location.
- Check the Flame Sensor:
- The flame sensor is a small metal rod located near the burner. If it's dirty, it may not be able to detect the flame, causing the furnace to shut off.
- DIY Cleaning (with caution): Turn off the power to the furnace and locate the flame sensor. Carefully remove it and clean it with a piece of fine-grit sandpaper or steel wool. Reinstall the sensor and try restarting the furnace. Be gentle; the sensor is fragile.
- Check the Gas Valve:
- Ensure the gas valve is in the "On" position.
- When to Call a Pro: *Do not* attempt to repair or adjust the gas valve yourself. Gas valves require specialized knowledge and tools. Any tampering can create a dangerous situation.
When to Call a Pro: If the pilot light won't stay lit, the flame sensor doesn't fix the issue, or you suspect a problem with the gas valve, call a qualified HVAC technician immediately.
3. The Furnace is Making Strange Noises
Unusual noises from your furnace can indicate various problems:
- Blower Motor Issues:
- Squealing: Could indicate a worn-out blower motor bearing.
- Rattling: Could be loose components or debris in the blower wheel.
- When to Call a Pro: Blower motor repairs are best left to professionals, as they involve electrical work and specialized tools.
- Ductwork Problems:
- Banging or Popping: Can be caused by expanding and contracting ductwork.
- Whistling: Could be caused by leaks in the ductwork.
- DIY Fix: Check visible ductwork connections for leaks and seal them with duct tape (not regular tape). For extensive ductwork issues, it's best to consult with a professional.
- Gas Valve Issues:
- Clicking or Gurgling: Could indicate a problem with the gas valve.
- When to Call a Pro: *Do not* attempt to repair or adjust the gas valve yourself. This requires professional expertise.
When to Call a Pro: If you hear any loud or persistent noises that you can't identify or resolve yourself, it's best to have a professional inspect the furnace.
4. Uneven Heating Throughout the House
If some rooms are much warmer or colder than others, it could be due to the following:
- Closed or Blocked Vents: Make sure all vents are open and unobstructed by furniture or rugs.
- Ductwork Issues: Leaks, disconnected ducts, or poorly insulated ducts can cause uneven heating.
- DIY Fix: Check for and seal any accessible duct leaks with duct tape.
- Insulation Problems: Inadequate insulation in walls, ceilings, or floors can contribute to temperature imbalances.
- DIY assessment: Check attic insulation levels. If it's below your floor joists, add more.
- Zoning Issues: Some homes have zoned heating systems that allow you to control the temperature in different areas. Make sure the zones are properly configured.
When to Call a Pro: If you've checked the vents and suspect ductwork or insulation issues, it's best to consult with a professional for a thorough assessment and repair.
When to Call a Professional HVAC Technician
While some furnace problems can be resolved with simple DIY fixes, others require the expertise of a qualified HVAC technician. Here are some situations where professional help is necessary:
- You smell gas.
- The furnace continues to malfunction after attempting basic troubleshooting.
- You suspect a problem with the gas valve, heat exchanger, or control board.
- You are uncomfortable working with gas or electricity.
- You are unsure about any step in the troubleshooting process.
Finding a Qualified Technician: Look for HVAC technicians who are licensed, insured, and experienced. Ask for references and read online reviews. A reputable technician will be able to diagnose the problem accurately and provide a cost-effective solution.
Preventive Maintenance for Your Gas Furnace
Regular maintenance can help prevent many furnace problems and extend the life of your unit. Consider the following:
- Change the air filter regularly (every 1-3 months).
- Schedule an annual furnace inspection and tune-up by a qualified HVAC technician.
- Keep the area around the furnace clean and free of debris.
- Inspect the flue pipe for any signs of damage or blockage.
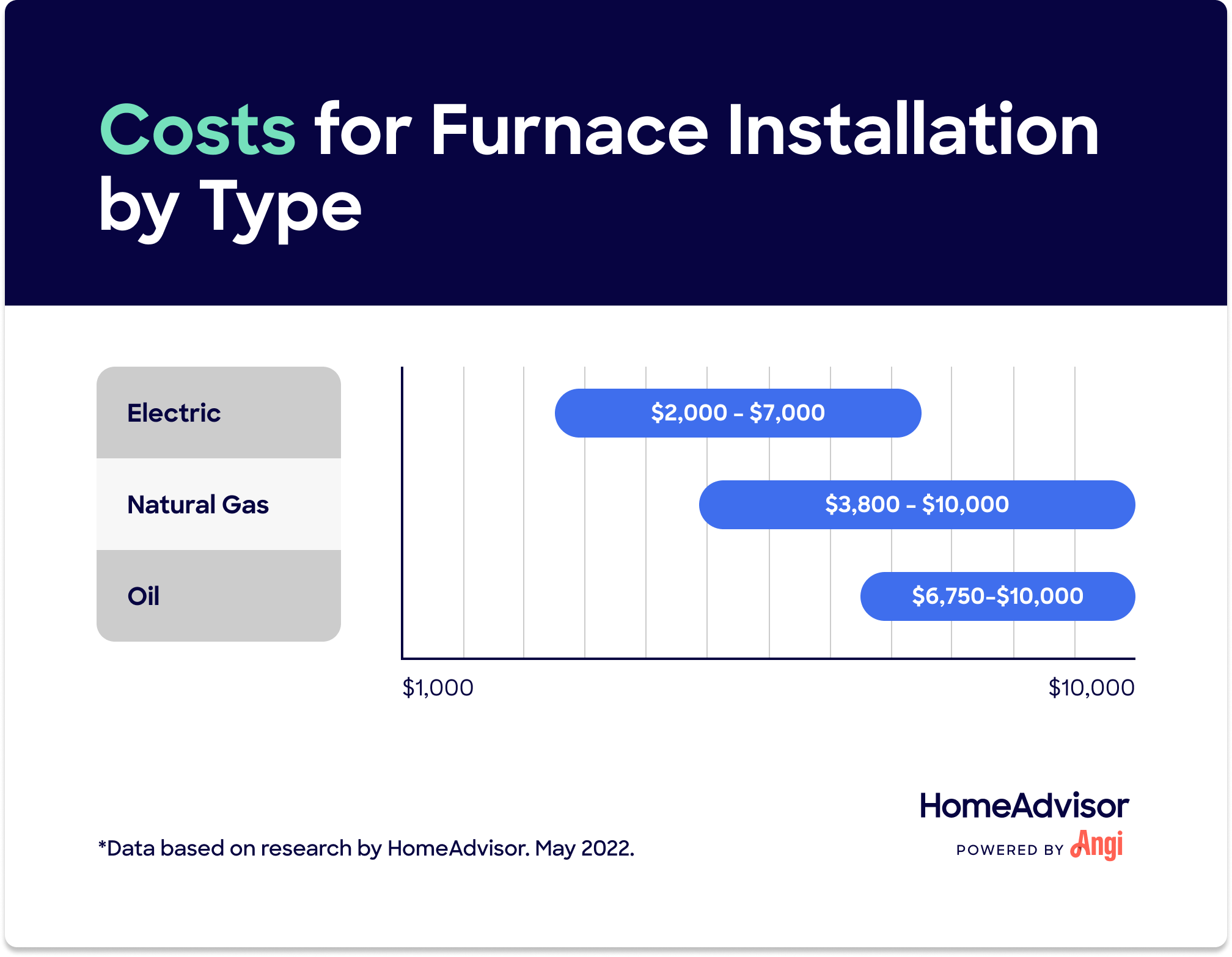
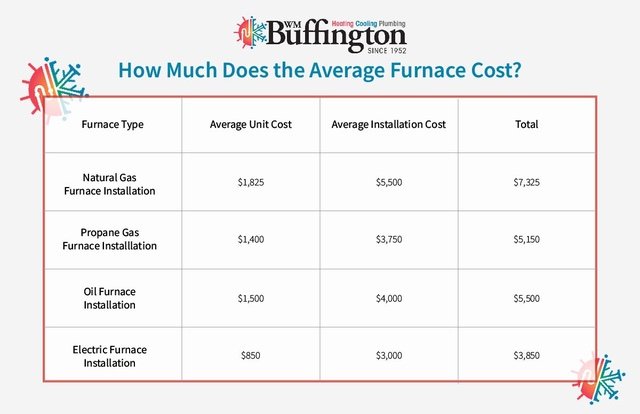
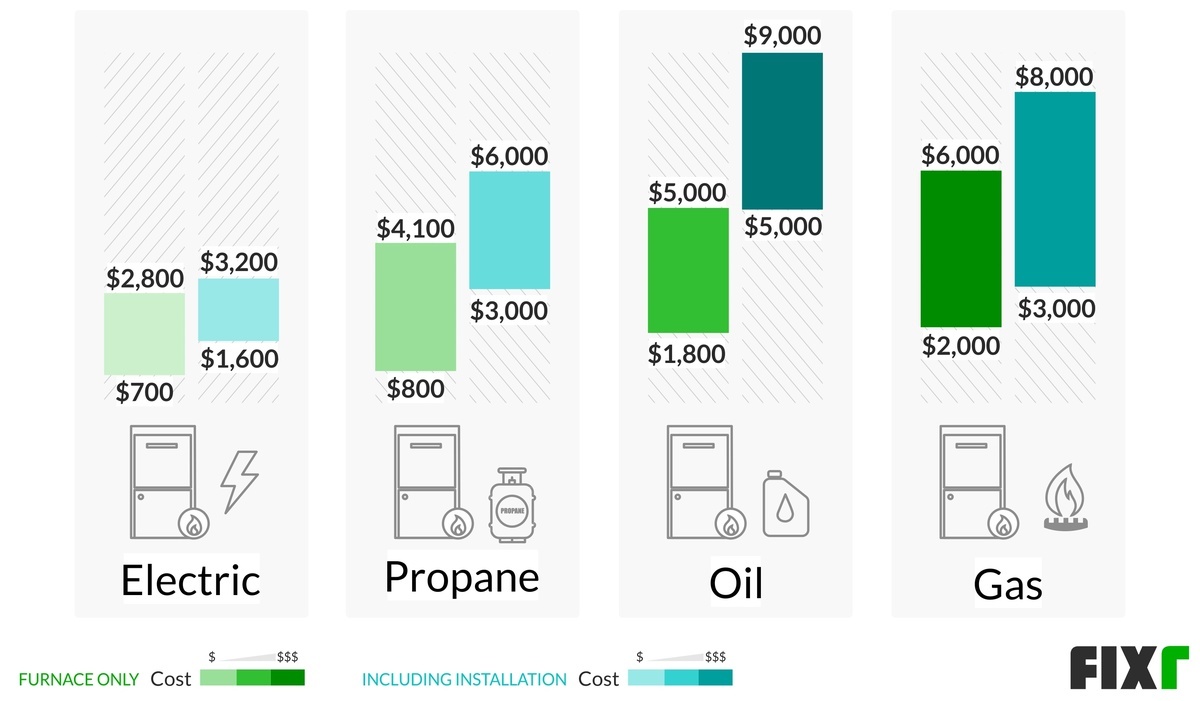
Cost Considerations
While this article focuses on troubleshooting, it's important to acknowledge the elephant in the room: the potential cost of a new furnace. Costs can vary widely based on:
- Furnace Type and Efficiency: Higher efficiency models cost more upfront but can save money on energy bills in the long run. Consider AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings.
- Furnace Size: The size of your home and its heating needs will determine the appropriate furnace size.
- Installation Complexity: Difficult installations (e.g., requiring significant ductwork modifications) will increase labor costs.
- Brand and Model: Some brands are known for their reliability and performance, and their models tend to be at the higher end of the price range.
- Location: Labor and material costs can vary depending on your geographic location.
Get Multiple Quotes: If you suspect your furnace needs replacing, get quotes from at least three different HVAC contractors. Be sure each quote includes the cost of the furnace, installation, and any related permits or fees. Don't automatically go with the lowest bid; consider the contractor's experience, reputation, and warranty offerings.
By following these troubleshooting steps and performing regular maintenance, you can keep your gas furnace running efficiently and safely for years to come. Remember to prioritize safety and call a professional when needed.