Cost To Buy And Install Air Conditioning

Understanding the Cost to Buy and Install Air Conditioning
Air conditioning is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for comfortable living, especially during scorching summer months. Understanding the costs associated with buying and installing an AC unit is crucial for budgeting and making informed decisions. This guide breaks down the different factors affecting the price, from the type of AC unit to installation complexities.
Types of Air Conditioning Systems and Their Costs
The first step is knowing the various AC systems available. Each has a different price point and suitability depending on your home and needs.
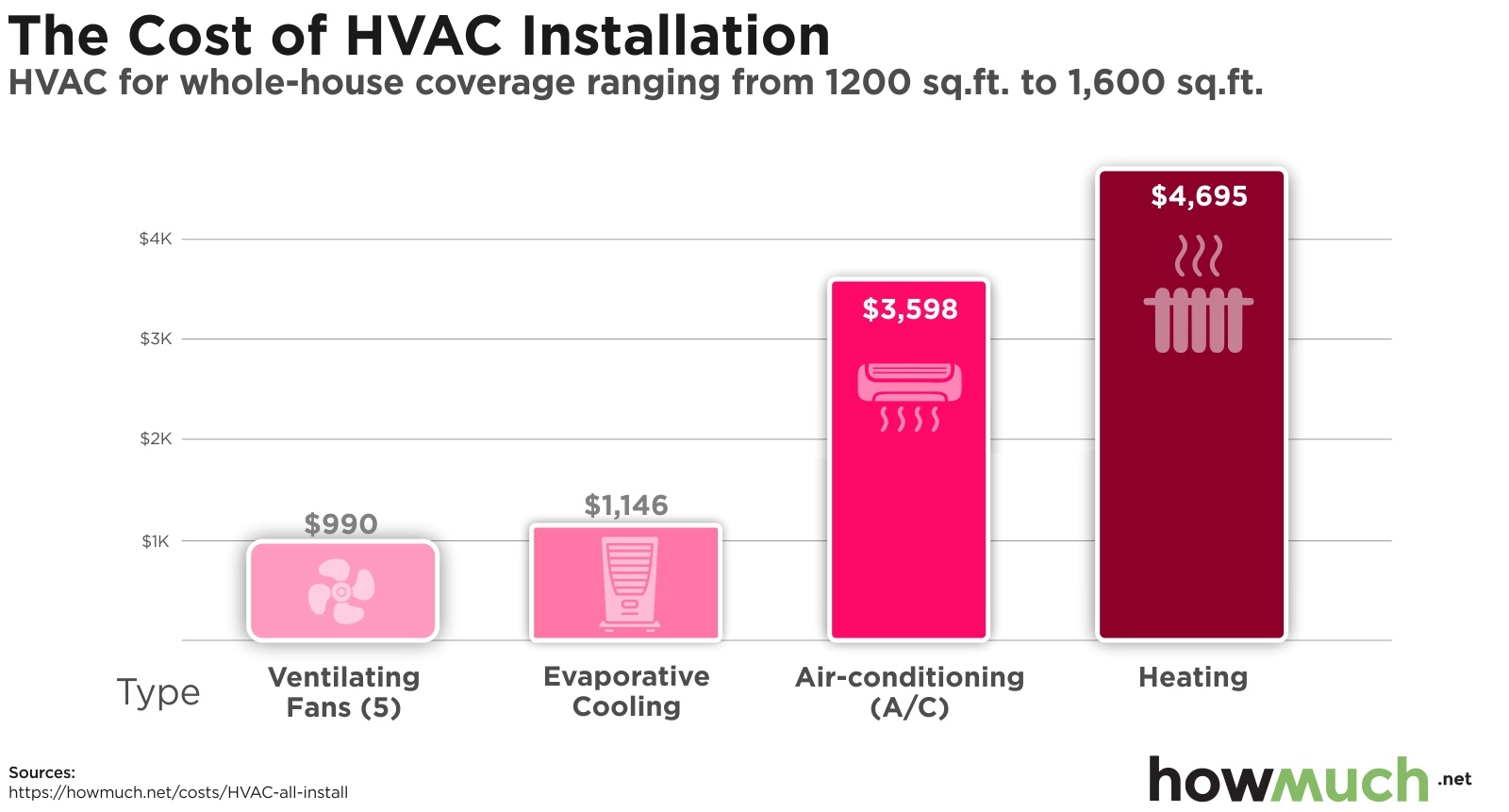
- Central Air Conditioning: This is the most common type for whole-house cooling. It uses a network of ducts to distribute cool air throughout your home. Expect to pay $3,000 - $7,000 for the unit itself, plus $1,500 - $5,000 for installation.
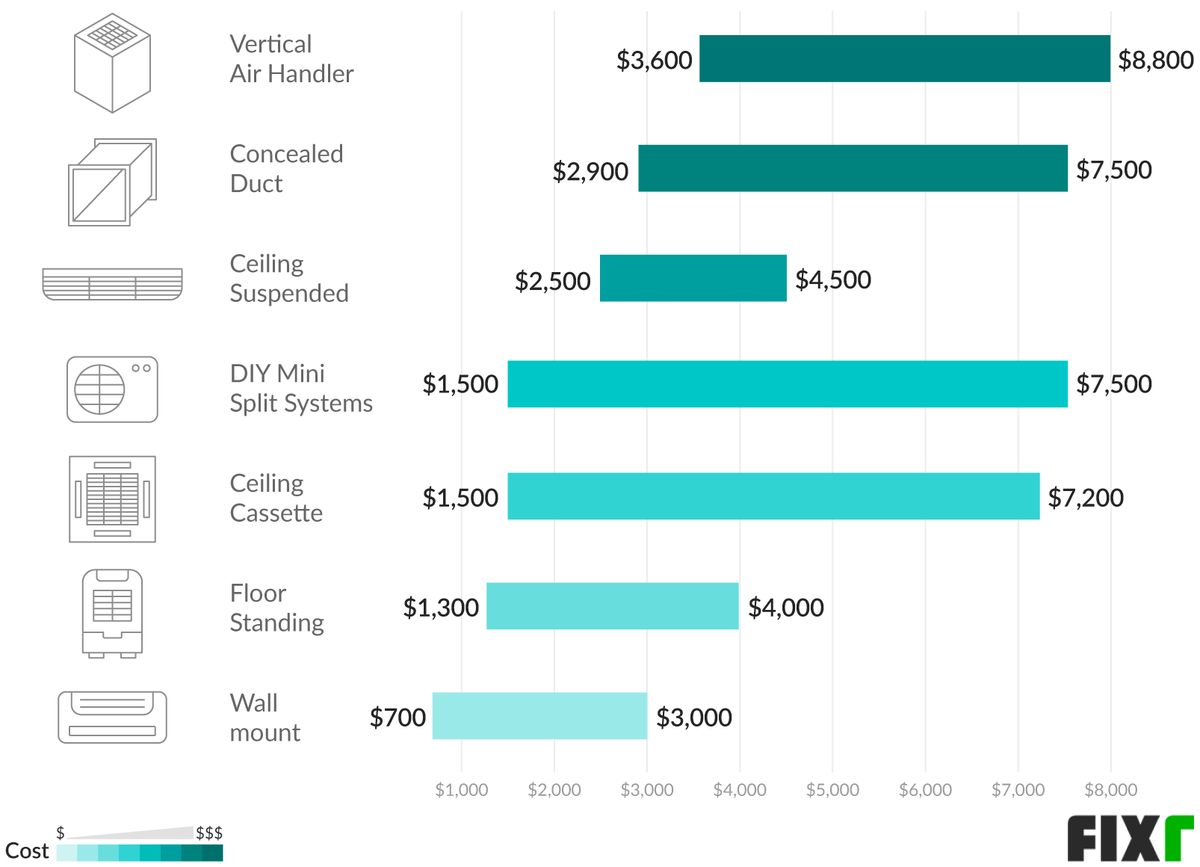
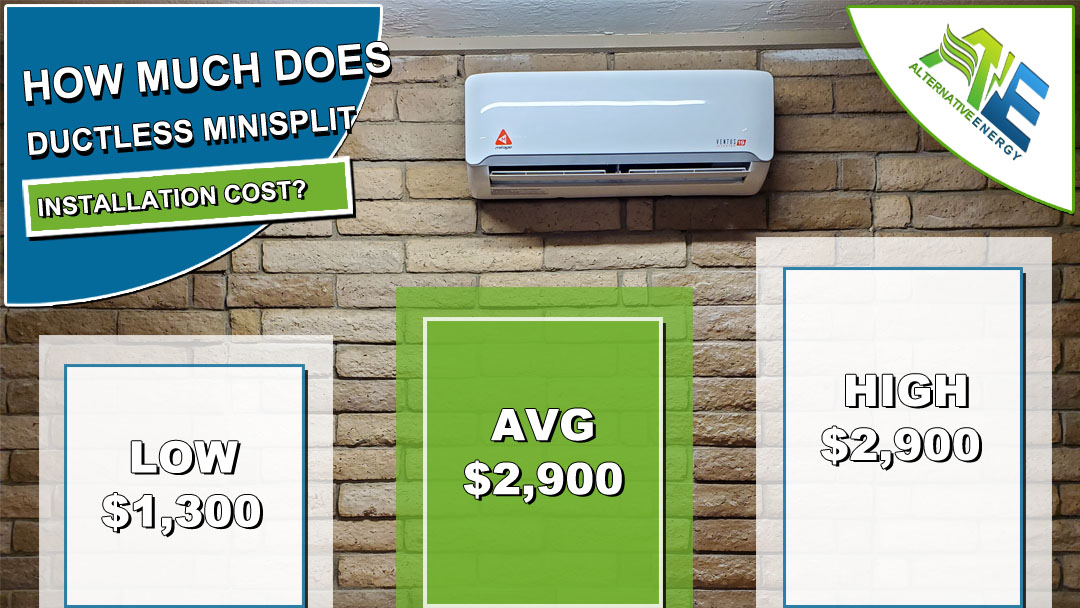
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ideal for homes without existing ductwork or for targeted cooling of specific rooms. These systems have an outdoor compressor connected to one or more indoor units. The cost ranges from $1,500 - $4,000 per indoor unit, plus $500 - $1,500 for installation per unit.
- Window Air Conditioners: A budget-friendly option for cooling a single room. They are easy to install yourself. Prices range from $150 - $800 depending on the BTU rating and features.
- Portable Air Conditioners: These units are on wheels and can be moved from room to room. They require venting to the outside, usually through a window. Expect to pay $200 - $600.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps: While pricier upfront, geothermal systems are highly energy-efficient and can provide both heating and cooling. They use the earth's constant temperature to regulate the home's temperature. Installation costs can range from $20,000 - $45,000.
Factors Affecting AC Unit Cost
Several factors influence the price of the AC unit itself:
- BTU (British Thermal Units): This measures the cooling capacity of the unit. Higher BTU units are more expensive but can cool larger spaces.
- SEER Rating (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): A higher SEER rating indicates better energy efficiency, which translates to lower energy bills. However, units with higher SEER ratings typically have a higher upfront cost. Look for Energy Star certified models.
- Brand Reputation: Well-known brands often come with a premium price tag, but they also tend to offer better reliability and warranty coverage.
- Features: Advanced features like smart thermostats, programmable timers, and multi-stage compressors can increase the cost.
Installation Costs: What to Expect
Installation costs can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the job. Here are some factors to consider:
- Type of System: Central AC installation is generally more expensive than installing a window unit. Mini-split installation costs depend on the number of indoor units.
- Ductwork: If you're installing central AC in a home without existing ductwork, the cost will be significantly higher. Ductwork installation can add thousands of dollars to the overall price.
- Electrical Work: Your home's electrical system may need to be upgraded to handle the increased load of a new AC unit. This can involve running new circuits or upgrading the electrical panel.
- Permits and Inspections: Most municipalities require permits for AC installation. The cost of permits varies by location. Inspections ensure the installation meets local codes.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs vary depending on the contractor and your location. Get quotes from multiple contractors to compare prices.
DIY vs. Professional Installation
While some AC units, like window units and portable units, are designed for DIY installation, central AC and mini-split systems typically require professional installation. Here's a breakdown:
DIY Installation:
Pros:
- Save on labor costs.
- Convenience of doing it yourself.
Cons:
- Risk of improper installation, which can lead to reduced efficiency, damage to the unit, and voided warranties.
- Potential safety hazards, especially when dealing with electrical wiring and refrigerant.
Professional Installation:
Pros:
- Proper installation ensures optimal performance and longevity of the unit.
- Warranty protection.
- Compliance with local codes and regulations.
- Peace of mind knowing the job is done correctly.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost due to labor charges.
Safety Tip: Never attempt to handle refrigerant lines unless you are a licensed HVAC technician. Refrigerant can cause serious burns and respiratory problems.
When to Call a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of the installation process, it's always best to call a professional. This is especially true for central AC and mini-split systems.
Cost-Saving Tips for Buying and Installing Air Conditioning
Here are some tips to help you save money on your AC purchase and installation:
- Get Multiple Quotes: Contact several HVAC contractors and compare their prices.
- Consider Energy-Efficient Models: While they may cost more upfront, energy-efficient models can save you money on your energy bills in the long run. Look for Energy Star certified models and consider SEER ratings.
- Schedule Installation During Off-Peak Season: HVAC contractors may offer lower prices during the off-season (spring or fall).
- Take Advantage of Rebates and Incentives: Check with your local utility company for rebates and incentives on energy-efficient AC units.
- Maintain Your Existing System: Regular maintenance can extend the life of your AC unit and prevent costly repairs. This includes cleaning the air filters, cleaning the condenser coils, and checking the refrigerant levels.
Common AC Problems and Troubleshooting
Before calling a professional, you can troubleshoot some common AC problems yourself. Remember to always turn off the power to the unit before attempting any repairs.
- AC Not Cooling:
- Check the thermostat settings.
- Clean or replace the air filter.
- Check the outdoor unit for obstructions.
- Ensure the circuit breaker hasn't tripped.
- AC Leaking Water:
- Check the condensate drain line for clogs.
- Ensure the drain pan is not overflowing.
- AC Making Strange Noises:
- Check for loose parts.
- Lubricate the fan motor.
- Call a professional if you hear loud banging or grinding noises.
Tools You Might Need:
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Wrench set
- Multimeter
- Vacuum pump (for refrigerant line servicing - only for licensed technicians)
- Fin comb (for straightening condenser fins)
Parts You Might Need:
- Air filters
- Capacitors
- Contactor
- Fan motor
Warning: Working with electricity and refrigerant can be dangerous. If you are not comfortable performing these tasks, call a professional. Improper repairs can damage your AC unit and pose a safety risk.
Understanding SEER Ratings
The SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner or heat pump. A higher SEER rating means the unit is more energy-efficient, which can translate to lower energy bills. The minimum SEER rating currently required by the Department of Energy is 14 for most regions. However, models with SEER ratings of 16 or higher are becoming increasingly common.
When choosing an AC unit, consider the following:
- Climate: If you live in a hot climate, a higher SEER rating will provide more significant energy savings.
- Upfront Cost: Units with higher SEER ratings typically have a higher upfront cost.
- Long-Term Savings: Calculate the potential energy savings over the lifespan of the unit to determine if the higher upfront cost is worth it.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your AC unit running efficiently and extending its lifespan. Here are some essential maintenance tasks:
- Change Air Filters Regularly: Dirty air filters restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Change them every 1-3 months, or more often if you have pets or allergies.
- Clean the Condenser Coils: The condenser coils are located on the outdoor unit. Clean them regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Check the Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can reduce cooling performance and damage the compressor. Have a professional check the refrigerant levels annually.
- Inspect the Ductwork: Leaky ductwork can waste energy and reduce cooling efficiency. Seal any leaks with duct tape or mastic.
- Schedule Annual Maintenance: Have a qualified HVAC technician inspect your AC unit annually to identify and address any potential problems.
Choosing the Right Size AC Unit
Selecting the right size AC unit is crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency. An undersized unit will struggle to cool your home, while an oversized unit will cycle on and off frequently, leading to uneven temperatures and higher energy bills. A professional HVAC technician can perform a load calculation to determine the appropriate size unit for your home based on factors such as square footage, insulation, window size, and climate.
By understanding the costs associated with buying and installing air conditioning, you can make informed decisions and ensure that your home stays cool and comfortable during the hottest months of the year. Remember to prioritize safety and call a professional when needed.