Cost To Install Forced Air Furnace
Understanding the Cost of Installing a Forced Air Furnace
Replacing or installing a new forced air furnace is a significant investment for any homeowner. Understanding the factors influencing the cost can help you budget effectively and make informed decisions. This article will break down the various components contributing to the final price, from the unit itself to labor and potential additional expenses.
Factors Influencing Furnace Installation Cost
Several key factors play a role in determining the overall cost of a new furnace installation:
- Furnace Type and Efficiency: The type of furnace (gas, oil, electric) and its efficiency (AFUE rating) significantly impact the price. High-efficiency models generally cost more upfront but offer long-term savings on energy bills.
- Furnace Size (BTU): The heating capacity of the furnace, measured in British Thermal Units (BTU), must be appropriately sized for your home. An undersized furnace will struggle to heat your home, while an oversized one will cycle on and off frequently, leading to inefficiency and potential wear and tear.
- Brand and Model: Different brands offer varying levels of quality, features, and warranty coverage. Well-established brands often come with a higher price tag.
- Installation Complexity: The complexity of the installation can significantly affect labor costs. Factors include the existing ductwork condition, accessibility of the installation location, and any necessary modifications to gas lines, electrical wiring, or venting systems.
- Labor Costs: Labor rates vary depending on your geographic location, the experience of the HVAC contractor, and the time required to complete the installation.
- Permits and Inspections: Most jurisdictions require permits and inspections for furnace installations to ensure compliance with safety codes. These fees add to the overall cost.
- Additional Components: Depending on your existing setup, you may need to replace or upgrade components such as the thermostat, ductwork, or flue pipe.
Breaking Down the Costs: Parts and Labor
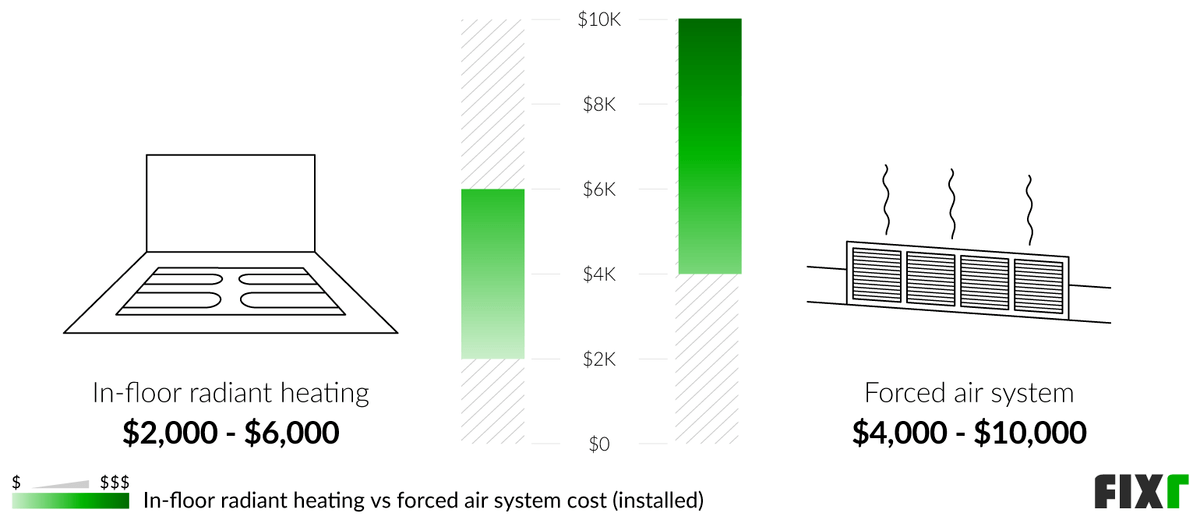
A typical furnace installation involves two primary cost components: the furnace unit itself and the labor required for installation.
Furnace Unit Cost
The cost of the furnace unit varies widely depending on the factors mentioned earlier. Here's a general price range:
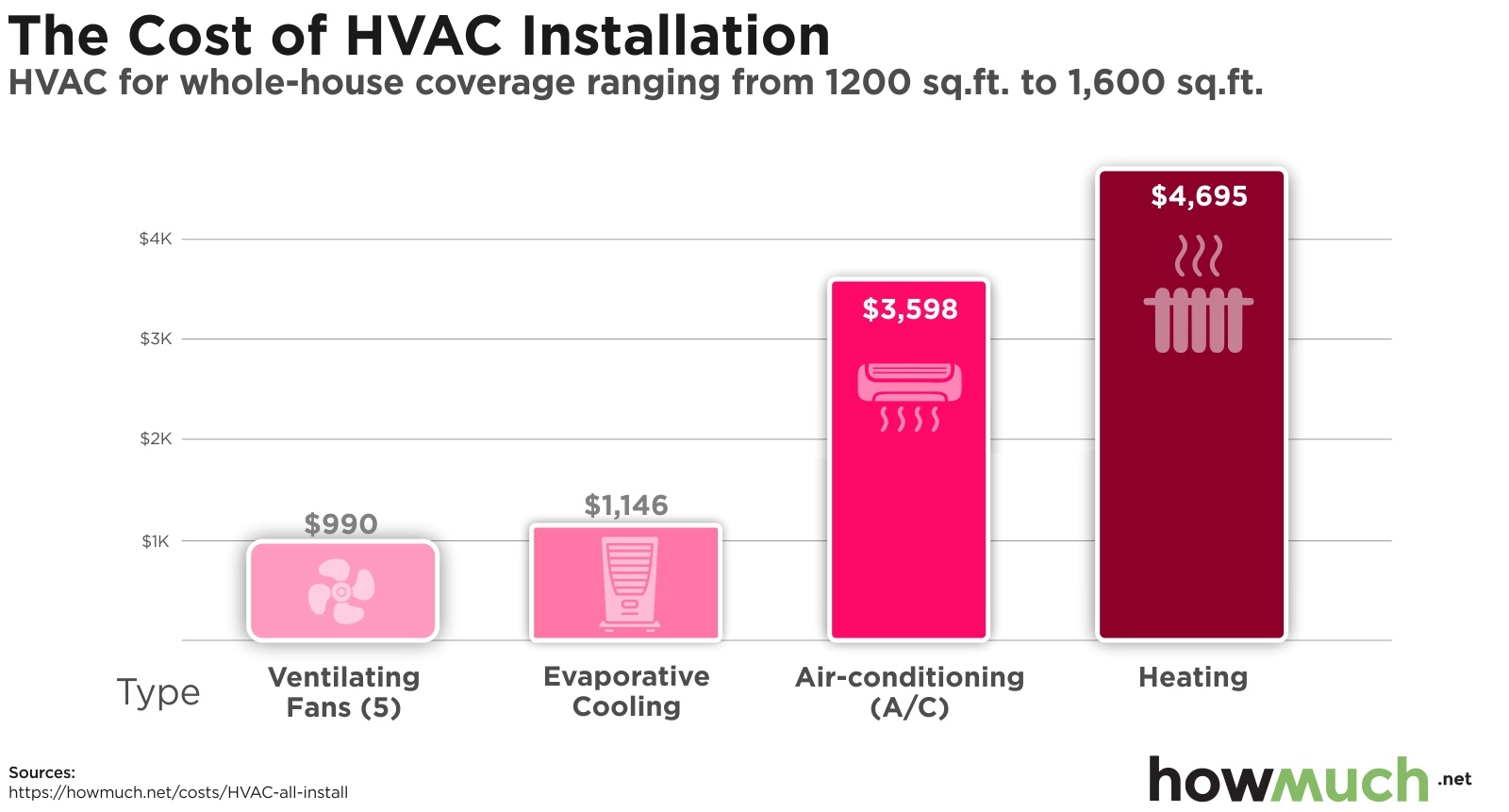
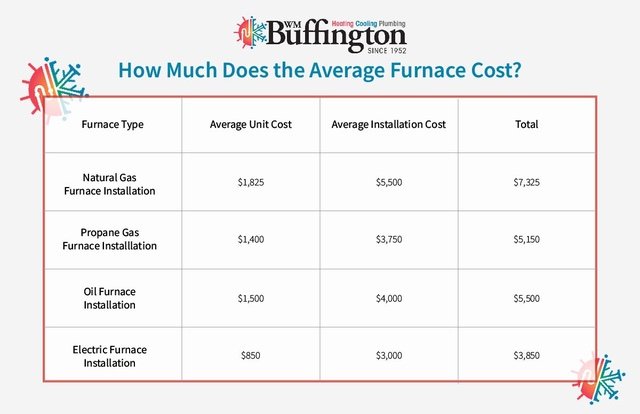
- Low-Efficiency Gas Furnace (80% AFUE): $2,000 - $4,000
- Mid-Efficiency Gas Furnace (90-95% AFUE): $3,000 - $6,000
- High-Efficiency Gas Furnace (95%+ AFUE): $4,500 - $8,000+
- Electric Furnace: $1,500 - $4,000
- Oil Furnace: $2,500 - $5,500
These are just estimates, and the actual price can vary based on the specific brand, model, and retailer.
Labor Costs
Labor costs typically range from $500 to $2,500, depending on the complexity of the installation. More straightforward replacements will generally be on the lower end, while installations involving ductwork modifications or complex venting will be more expensive.
Estimating the Total Installation Cost
To estimate the total cost, combine the furnace unit cost with the labor cost. For example, a mid-efficiency gas furnace costing $4,000 with a $1,000 labor charge would result in a total installation cost of $5,000.
Important Note: These are just estimates. Always obtain multiple quotes from qualified HVAC contractors to get an accurate assessment of the cost for your specific situation.
Potential Additional Costs
Be aware of potential additional costs that may arise during the installation process:
- Ductwork Modifications or Replacement: Damaged or poorly designed ductwork can significantly reduce furnace efficiency. Repairing or replacing ductwork can add several hundred to several thousand dollars to the total cost.
- Thermostat Upgrade: A new smart thermostat can improve energy efficiency and provide convenient control over your home's heating.
- Gas Line Modifications: If the existing gas line is inadequate or needs to be rerouted, you'll incur additional costs for gas line modifications.
- Electrical Work: Upgrading the electrical panel or running new wiring may be necessary, especially for electric furnaces.
- Flue Pipe Replacement: A corroded or damaged flue pipe needs to be replaced to ensure proper venting of combustion gases.
- Asbestos Abatement: If asbestos is present in the existing ductwork or insulation, it must be professionally removed before the new furnace can be installed. This can be a significant expense.
DIY Furnace Installation: Proceed with Caution
While some homeowners with extensive HVAC experience may consider installing a furnace themselves, it's generally not recommended for the following reasons:
- Safety Risks: Working with gas lines, electrical wiring, and combustion gases poses significant safety risks. Improper installation can lead to gas leaks, carbon monoxide poisoning, or electrical fires.
- Warranty Voidance: Most furnace manufacturers require professional installation to maintain the warranty.
- Building Codes and Permits: Furnace installations must comply with local building codes and require permits and inspections. DIY installations may not meet these requirements.
- Efficiency and Performance: Proper furnace sizing, ductwork sealing, and airflow balancing are crucial for optimal performance and efficiency. Professionals have the expertise and tools to ensure these aspects are addressed correctly.
When to Call a Professional:
- You lack experience working with gas lines or electrical wiring.
- Your existing ductwork is damaged or needs significant modifications.
- You are unsure about the correct furnace size for your home.
- You need to obtain permits and schedule inspections.
- You want to ensure the furnace is installed safely and efficiently.
Troubleshooting Common Furnace Problems (DIY-Friendly)
While a full furnace installation is best left to the pros, some basic troubleshooting steps can be safely performed by homeowners:
- Furnace Not Turning On:
- Check the thermostat settings and batteries.
- Ensure the power switch to the furnace is turned on.
- Check the circuit breaker for the furnace and reset it if necessary.
- Inspect the furnace filter and replace it if it's dirty. A clogged filter can restrict airflow and cause the furnace to shut down.
- Furnace Runs But Doesn't Heat:
- Check the gas valve to ensure it's open.
- Inspect the pilot light (for older furnaces) to ensure it's lit.
- Make sure the vents are open and not blocked.
- Unusual Noises:
- Check for loose panels or debris inside the furnace.
- Listen for squealing or grinding noises, which may indicate a problem with the blower motor.
Safety First: Always turn off the power to the furnace before performing any troubleshooting steps. If you are uncomfortable working with electrical or gas components, call a qualified HVAC technician.
Choosing the Right HVAC Contractor
Selecting a reputable and qualified HVAC contractor is essential for a successful furnace installation. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Licensing and Insurance: Verify that the contractor is properly licensed and insured.
- Experience and Expertise: Choose a contractor with extensive experience installing furnaces similar to the one you're considering.
- References and Reviews: Check online reviews and ask for references from previous customers.
- Written Estimates: Obtain detailed written estimates from multiple contractors, outlining the scope of work, materials, and labor costs.
- Warranty Coverage: Inquire about the contractor's warranty on labor and the manufacturer's warranty on the furnace unit.
Financing Options
Furnace installation can be a significant expense, so explore financing options to make it more affordable:
- HVAC Contractor Financing: Many HVAC contractors offer financing options to help customers spread out the cost of installation.
- Home Equity Loans or Lines of Credit: Using your home equity can provide access to low-interest financing.
- Personal Loans: Personal loans can be used to finance furnace installation, but interest rates may be higher than other options.
- Rebates and Tax Credits: Check for available rebates and tax credits from your utility company or government agencies for energy-efficient furnace installations.
Maintaining Your New Furnace
Proper maintenance is crucial for extending the life of your new furnace and ensuring its efficient operation. Here are some essential maintenance tasks:
- Regular Filter Changes: Change the furnace filter every 1-3 months, depending on the type of filter and the air quality in your home.
- Annual Inspections: Schedule annual inspections and tune-ups with a qualified HVAC technician.
- Clean the Blower Motor: Periodically clean the blower motor to remove dust and debris.
- Inspect the Flue Pipe: Check the flue pipe for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Keep the Area Around the Furnace Clear: Ensure there is adequate clearance around the furnace for proper ventilation and access.
Conclusion
The cost of installing a forced air furnace can vary significantly based on several factors. By understanding these factors and following the advice in this article, you can budget effectively, choose the right furnace for your home, and ensure a safe and efficient installation. Remember to prioritize safety, obtain multiple quotes from qualified HVAC contractors, and maintain your new furnace regularly to maximize its lifespan and performance.