Csst Gas Line Underground

Underground CSST Gas Lines: A Homeowner's Guide to Safe and Efficient Fuel Delivery
For homeowners, real estate investors, and contractors, understanding the ins and outs of underground fuel delivery is crucial. Corrugated Stainless Steel Tubing (CSST) gas lines offer a flexible and often cost-effective solution for bringing natural gas or propane to your property, especially when an underground installation is required. This guide explores the pros, cons, installation best practices, and maintenance considerations for underground CSST gas lines.
What is CSST?
CSST, or Corrugated Stainless Steel Tubing, is a flexible piping system used to distribute natural gas or propane within a building. Unlike rigid black iron pipe, CSST's corrugated design allows it to bend and flex, making installation faster and easier, especially in complex or hard-to-reach areas. While primarily used indoors, CSST can also be installed underground with specific protective measures.
Underground CSST: Benefits and Drawbacks
Advantages of Using CSST Underground:
- Flexibility: CSST's flexibility reduces the need for couplings and fittings, minimizing potential leak points. This is particularly beneficial in underground applications where accessing and repairing leaks can be challenging.
- Faster Installation: Compared to rigid piping, CSST installation is generally quicker, reducing labor costs. The ability to snake the tubing around obstacles simplifies trenching and routing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In many cases, CSST can be more economical than traditional steel pipe, considering material and labor expenses.
- Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel offers good resistance to corrosion, although proper grounding and bonding are critical (more on that later).
- Fewer Joints: Fewer joints minimize potential leak locations compared to traditional black iron pipe. This can lead to increased safety.
Disadvantages of Using CSST Underground:
- Lightning Strike Vulnerability: CSST is susceptible to damage from lightning strikes if not properly grounded and bonded. This is a *critical* safety concern.
- Puncture Risk: While durable, CSST can be punctured by sharp objects during or after installation. Proper backfilling and marking of the gas line are essential.
- Soil Corrosion: While stainless steel resists corrosion, prolonged exposure to certain soil conditions can still lead to degradation. Protective sleeving is often required.
- Installation Requirements: Strict adherence to manufacturer specifications and local codes is paramount for safe and compliant installation. Improper installation can lead to leaks and potential hazards.
- Cost of Protection: Adding necessary protection measures, such as cathodic protection or specialized coatings, can increase the overall cost.
Key Considerations for Underground CSST Installation
Proper Grounding and Bonding:
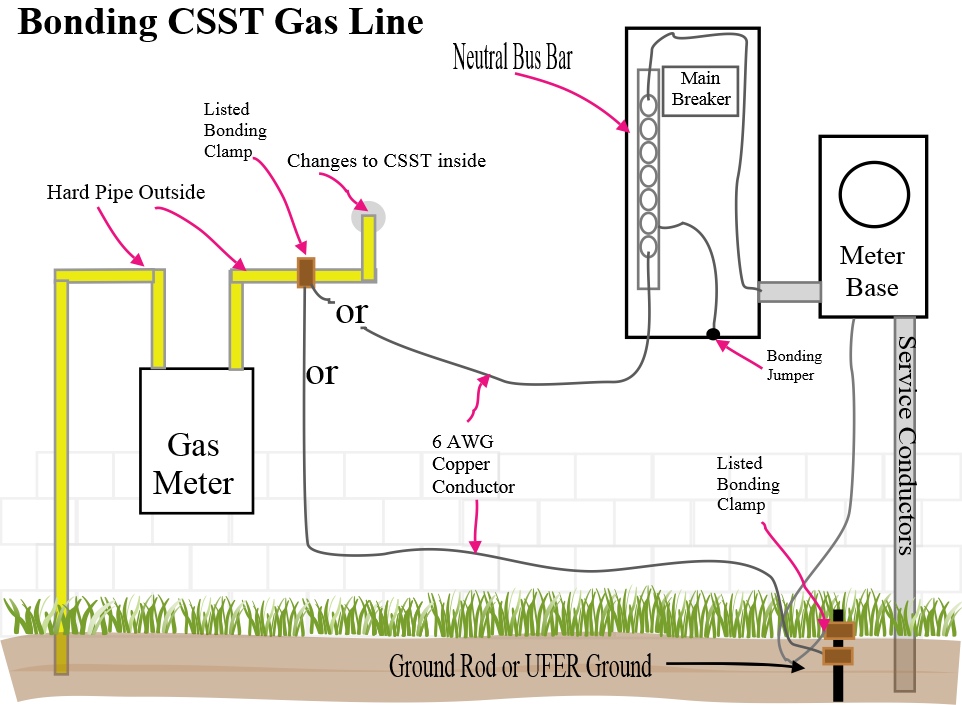
The most crucial aspect of CSST safety is proper grounding and bonding. This helps to mitigate the risk of damage from lightning strikes and electrical faults. Ensure the CSST system is bonded to the electrical service grounding electrode system according to local codes and the manufacturer's instructions. This is *not* a DIY project; hire a qualified electrician and plumber.
Protective Sleeving and Coatings:
To protect CSST from soil corrosion and physical damage, it's typically encased in a protective sleeve or coating. This sleeve should be compatible with underground use and resistant to the chemicals and moisture present in the surrounding soil. Consult with the CSST manufacturer or a qualified installer to determine the appropriate protection for your specific soil conditions.
Depth of Burial:
Local codes dictate the minimum depth at which gas lines must be buried. This depth ensures the line is protected from accidental damage during excavation or other activities. Always check with your local building department for specific requirements in your area. Typically, a depth of at least 18 inches is required.
Backfilling and Marking:
When backfilling the trench, use clean, granular material that is free from sharp rocks or debris that could damage the CSST. Compact the backfill in layers to provide adequate support. Install tracer wire above the gas line to make it easily locatable in the future. Also, use warning tape labeled "Gas Line Buried Below" a few inches above the pipe to warn future excavators.
Pressure Testing:
After installation, the gas line must be pressure tested to ensure there are no leaks. This involves pressurizing the line with air or nitrogen and monitoring for any pressure drop. A qualified professional should perform this test and document the results.
Permitting and Inspections:
Always obtain the necessary permits before starting any gas line installation work. A qualified inspector will examine the installation to ensure it complies with local codes and safety standards. Don't skip this step; it's essential for your safety and legal compliance.
Popular CSST Brands
Several reputable manufacturers produce CSST gas piping systems. Here are a few of the most popular:
- Wardflex: Wardflex is a widely recognized brand known for its quality and comprehensive line of fittings and accessories.
- Gastite: Gastite is another popular brand offering a range of CSST products, including fittings, manifolds, and safety devices.
- TracPipe: TracPipe is known for its ease of installation and durable construction.
When choosing a CSST brand, consider the availability of fittings and accessories in your area, the manufacturer's warranty, and the reputation of the brand.
CSST vs. Black Iron Pipe for Underground Use
The traditional alternative to CSST is black iron pipe. Here's a quick comparison:
| Feature | CSST | Black Iron Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Highly Flexible | Rigid |
| Installation Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Number of Joints | Fewer | More |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (with proper protection) | Requires Coating for Underground Use |
| Cost | Potentially Lower | Potentially Higher |
| Lightning Strike Vulnerability | Higher (requires grounding) | Lower (still requires grounding) |
Ultimately, the best choice depends on the specific application, budget, and local code requirements. Consult with a qualified professional to determine the most suitable option for your needs.
Maintenance and Inspection
While underground CSST gas lines are designed for long-term reliability, regular maintenance and inspection can help prevent problems and ensure safe operation.
Routine Inspections:
Periodically inspect the exposed portions of the gas line, such as where it enters the building or connects to appliances, for signs of damage or corrosion. Look for kinks, dents, or rust. If you notice anything suspicious, contact a qualified professional for further evaluation.
Leak Detection:
If you suspect a gas leak, evacuate the area immediately and contact your local gas company or emergency services. Do not attempt to locate the leak yourself.
Professional Inspections:
Consider having your gas line inspected by a qualified professional every few years. This can help identify potential problems early on and prevent costly repairs or safety hazards. A professional can also check the grounding and bonding system to ensure it's functioning correctly.
Cost Considerations
The cost of installing an underground CSST gas line varies depending on several factors, including:
- Length of the Gas Line: Longer lines require more material and labor.
- Depth of Burial: Deeper trenches are more expensive to excavate.
- Soil Conditions: Rocky or difficult soil can increase excavation costs.
- Protective Measures: The cost of sleeving, coatings, and grounding materials.
- Labor Rates: Local labor rates can vary significantly.
- Permitting and Inspection Fees: These fees are typically a small percentage of the overall cost.
To get an accurate estimate, obtain quotes from several qualified contractors. Be sure to ask for a detailed breakdown of the costs, including materials, labor, permits, and inspection fees.
Hiring a Qualified Installer
Installing an underground CSST gas line is not a DIY project. It requires specialized knowledge, skills, and equipment. Always hire a licensed and insured contractor with experience in gas line installation. Check their credentials, read online reviews, and ask for references before hiring. A qualified installer will ensure the job is done safely and in accordance with local codes.
Conclusion
Underground CSST gas lines offer a convenient and cost-effective solution for fuel delivery when installed correctly. However, it's *critical* to prioritize safety by adhering to all applicable codes, employing proper grounding and bonding techniques, and using appropriate protective measures. By understanding the benefits, drawbacks, and installation requirements of underground CSST, homeowners, real estate investors, and contractors can make informed decisions and ensure a safe and reliable gas supply.