Diagram Of A Car Air Conditioning System
Understanding Your Car's Air Conditioning System: A Detailed Guide
While seemingly simple, the car air conditioning (AC) system is a complex interplay of components working together to keep you cool on the road. Understanding the basics of how it functions can help you troubleshoot minor issues, communicate effectively with mechanics, and potentially save money on repairs. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the car AC system, its key components, common problems, and basic maintenance tips.
The Basic Diagram: A Closed-Loop System
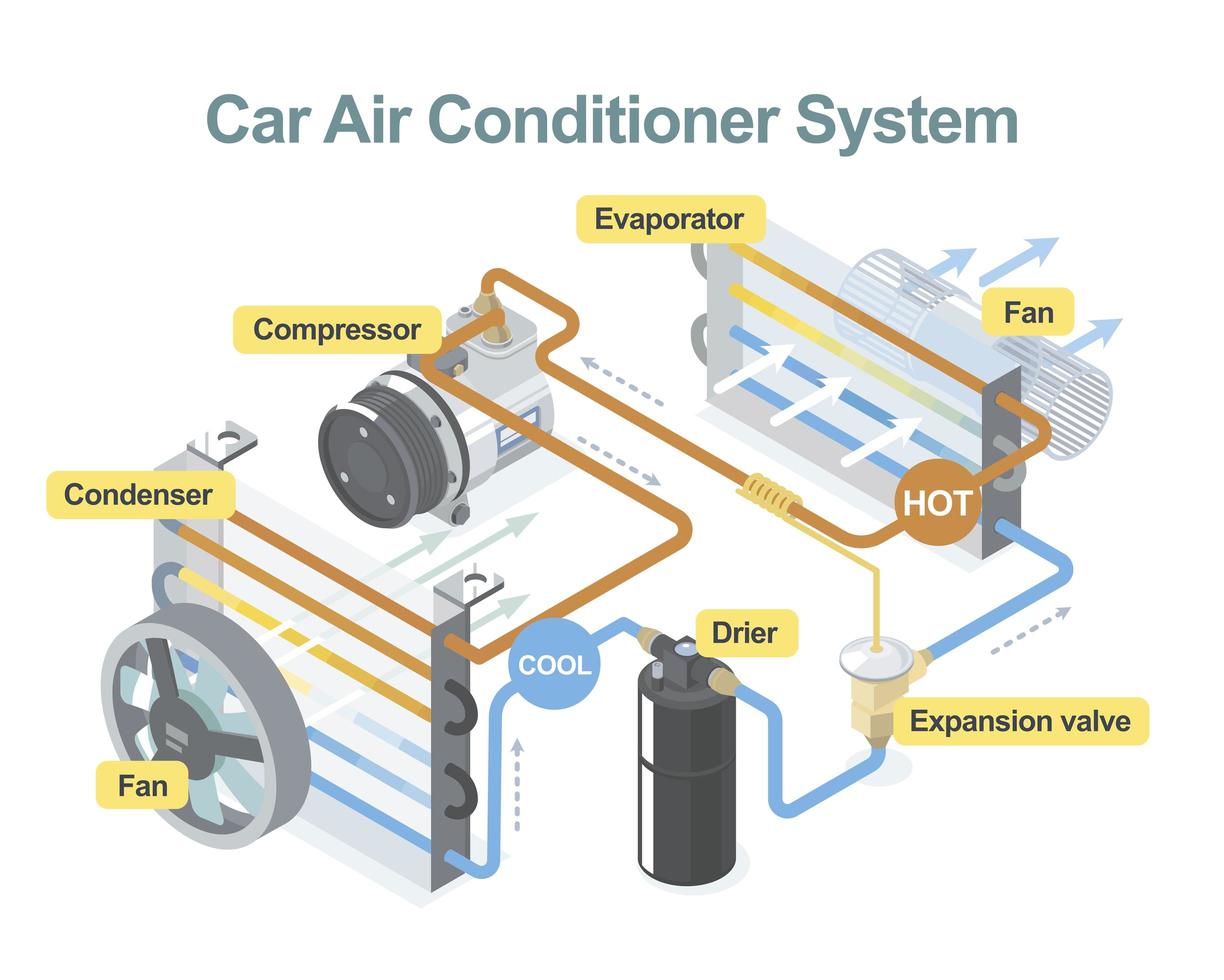
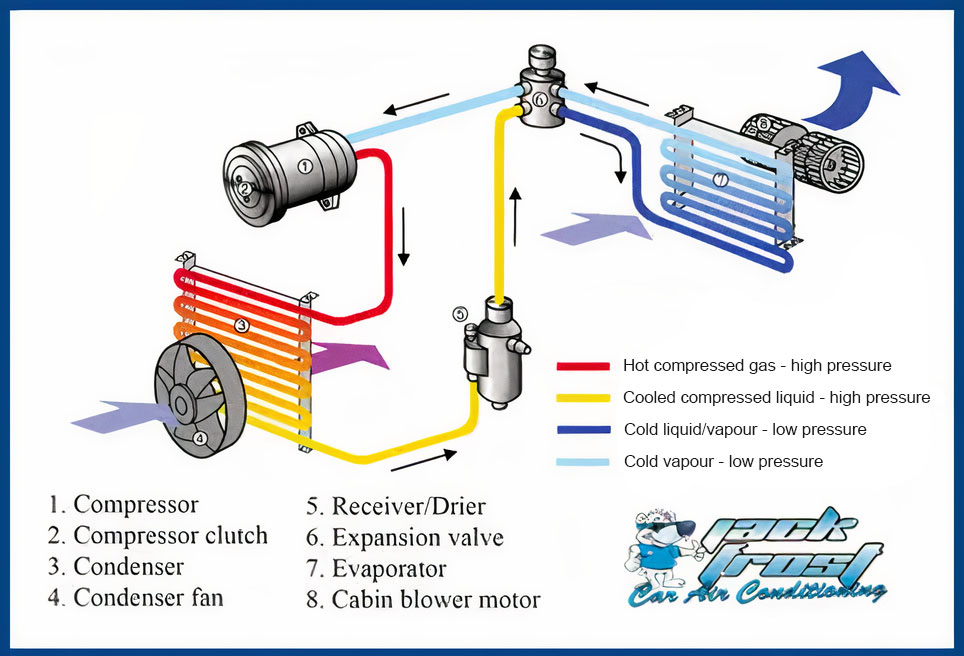
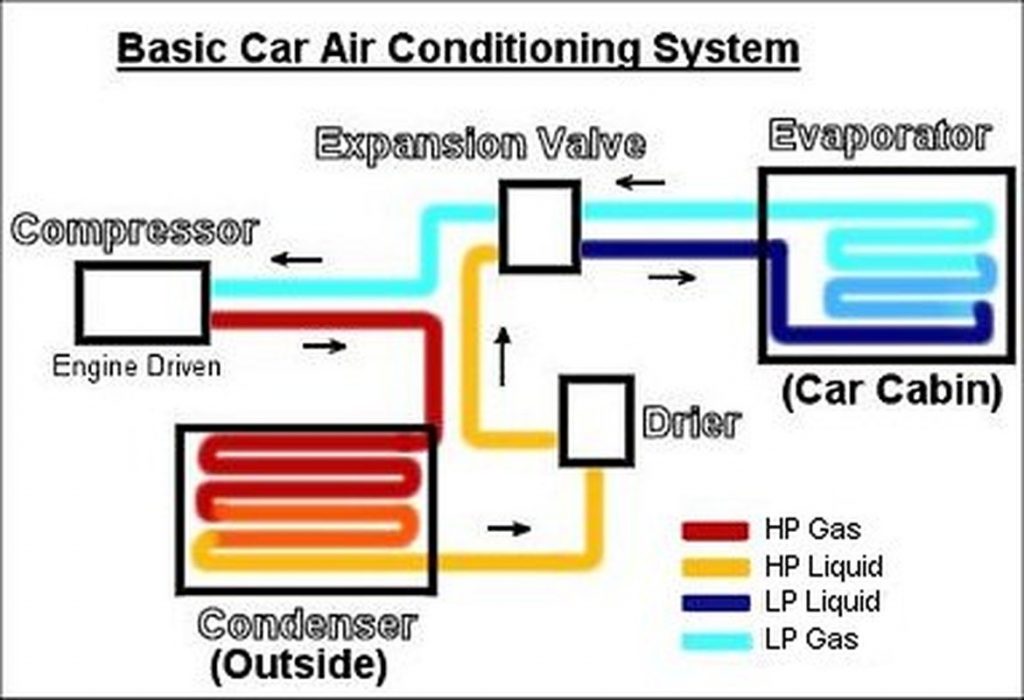
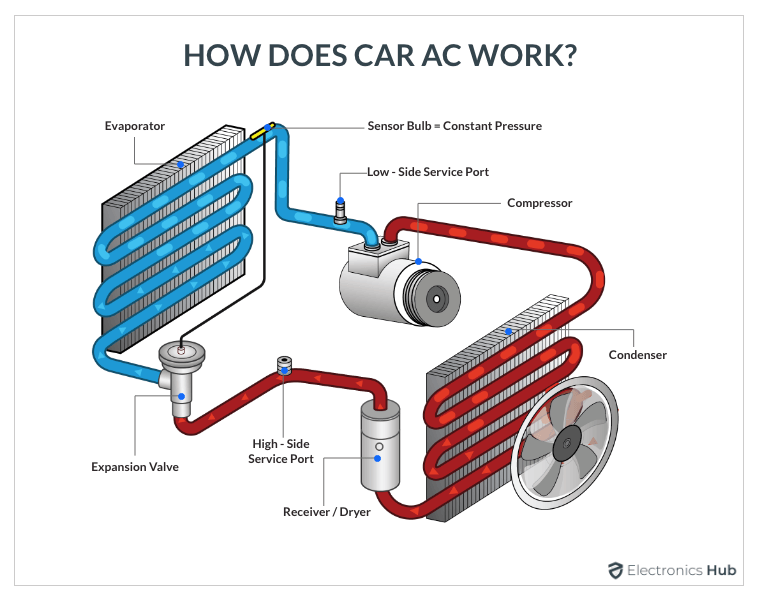
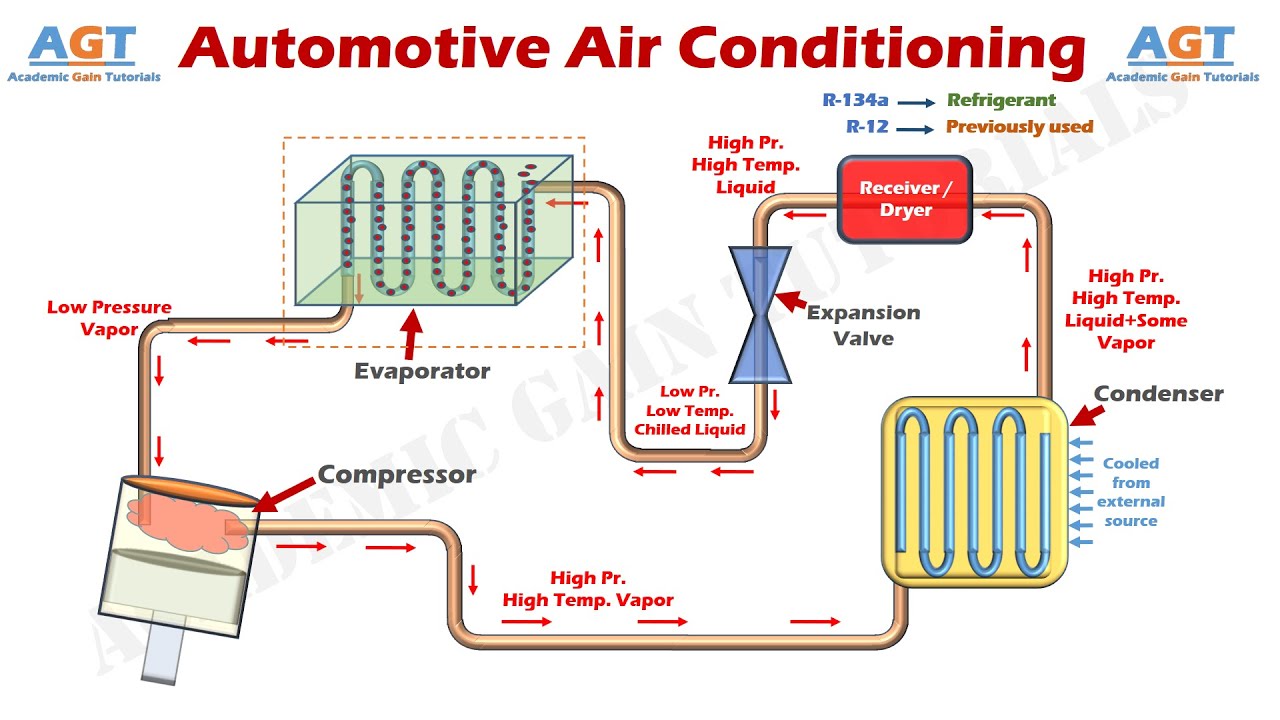
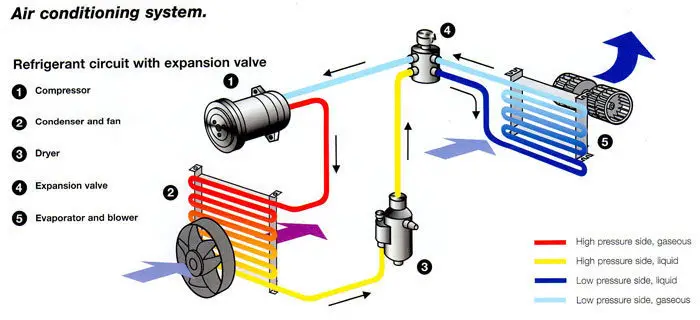
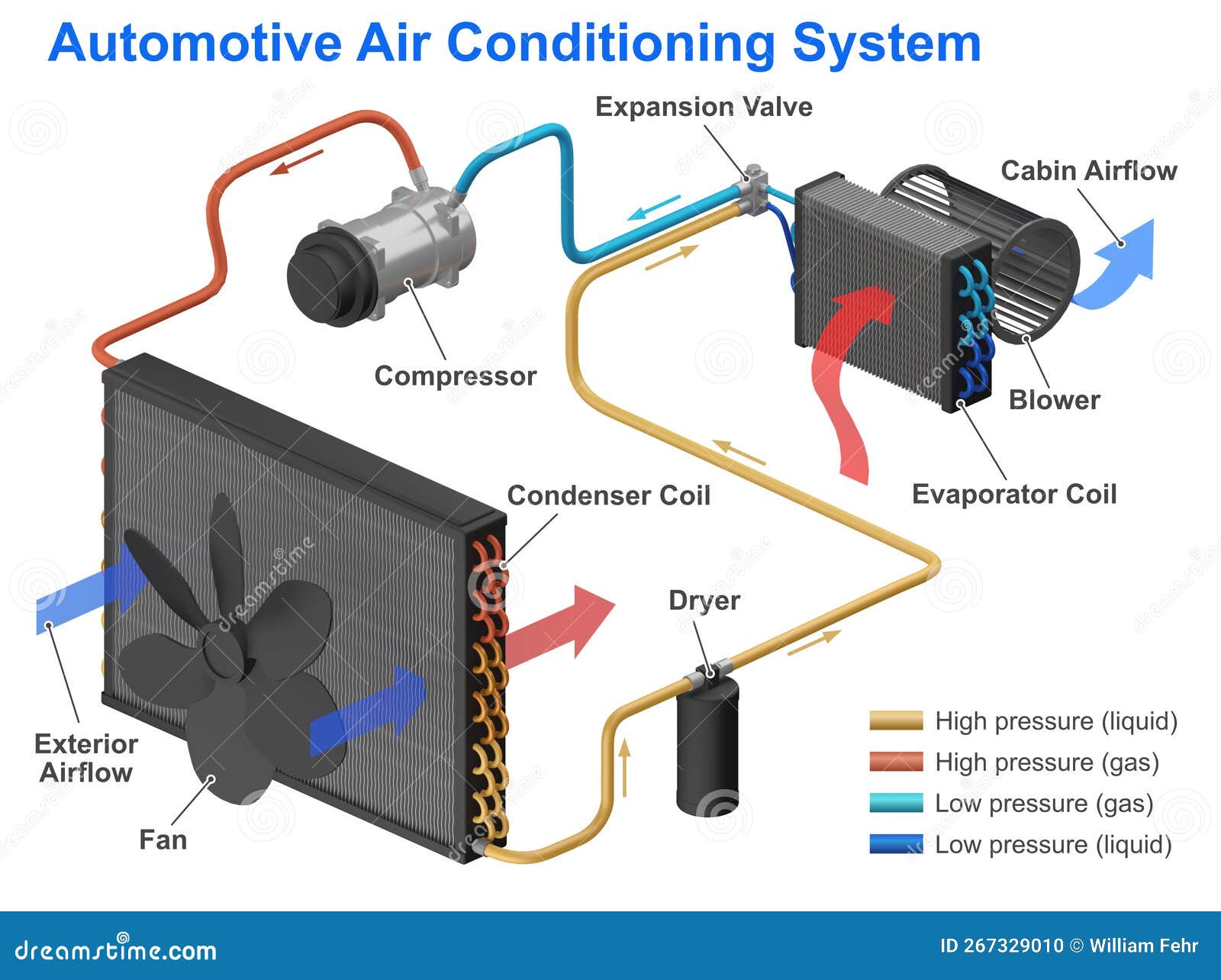
The car AC system is a closed-loop system, meaning the refrigerant, the lifeblood of the system, circulates continuously. Here's a simplified overview of the cycle:
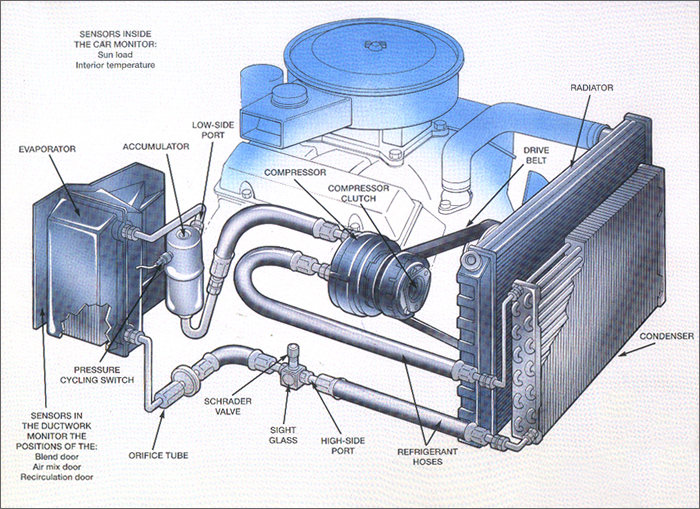
- Compressor: The refrigerant, in a low-pressure, gaseous state, enters the compressor. This component, driven by the engine's accessory belt, compresses the refrigerant, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- Condenser: The high-pressure, hot refrigerant then flows into the condenser. Located at the front of the car, usually near the radiator, the condenser dissipates heat from the refrigerant, causing it to change from a gas to a high-pressure liquid.
- Receiver-Drier (or Accumulator): The high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the receiver-drier (in systems with a thermal expansion valve) or the accumulator (in systems with an orifice tube). These components filter out moisture and debris from the refrigerant, ensuring optimal system performance. The accumulator, specifically, stores excess refrigerant and prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor, which could cause damage.
- Expansion Valve (or Orifice Tube): Next, the refrigerant flows through the expansion valve (also known as a thermal expansion valve or TXV) or the orifice tube. This component is a metering device that controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, causing it to rapidly expand and cool.
- Evaporator: The low-pressure, cold refrigerant then enters the evaporator, located inside the passenger compartment, typically behind the dashboard. Here, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air blowing across the evaporator core. This process cools the air, which is then blown into the cabin through the vents. The refrigerant, having absorbed heat, turns back into a low-pressure gas.
- Back to the Compressor: The low-pressure gas refrigerant returns to the compressor, completing the cycle.
Key Components Explained in Detail
Compressor
The compressor is the heart of the AC system. It's responsible for circulating the refrigerant and maintaining the pressure differential needed for efficient cooling. Compressors can be one of several types, including:
- Piston compressors
- Rotary compressors
- Scroll compressors
A faulty compressor can lead to poor cooling performance or complete AC failure. Regular maintenance, including checking the drive belt and refrigerant levels, is crucial for compressor longevity.
Condenser
The condenser acts as a radiator for the refrigerant. It's designed to dissipate heat quickly and efficiently. Blocked or damaged condenser fins can reduce its effectiveness, leading to reduced cooling capacity. Debris such as leaves and insects should be regularly cleaned from the condenser.
Receiver-Drier and Accumulator
These components are essential for maintaining the purity and dryness of the refrigerant. The receiver-drier, used in systems with a TXV, contains a desiccant that absorbs moisture. The accumulator, used in systems with an orifice tube, not only removes moisture but also acts as a reservoir for excess refrigerant. Both should be replaced periodically, especially when the system is opened for repairs, to prevent corrosion and damage to other components.
Expansion Valve and Orifice Tube
The expansion valve and orifice tube both perform the same function: controlling the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator and reducing its pressure. The expansion valve is a more sophisticated component that automatically adjusts the refrigerant flow based on the evaporator temperature. The orifice tube is a simpler, fixed-size restriction. A clogged or malfunctioning expansion valve or orifice tube can restrict refrigerant flow, leading to poor cooling.
Evaporator
The evaporator is where the cooling magic happens. It absorbs heat from the air passing through it, cooling the cabin. The evaporator is susceptible to corrosion and leaks, especially in humid environments. A clogged evaporator can also restrict airflow, reducing cooling performance. Cleaning the evaporator core periodically can improve airflow and cooling efficiency.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant is the working fluid of the AC system. Older vehicles typically used R-12 refrigerant, which is now phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties. Modern vehicles use R-134a or the newer R-1234yf refrigerant. Using the wrong type of refrigerant can damage the system.
Common Car AC Problems and Troubleshooting
Several issues can affect the performance of your car's AC system:
- Refrigerant Leaks: Low refrigerant levels are a common cause of poor cooling. Leaks can occur at various points in the system, including hoses, fittings, and components. A refrigerant leak test can pinpoint the source of the leak.
- Compressor Failure: A failing compressor can result in no cooling or intermittent cooling. Symptoms include unusual noises from the compressor, a clutch that doesn't engage, or a lack of pressure in the system.
- Clogged Condenser or Evaporator: Blockages can restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Cleaning the condenser and evaporator cores can often resolve this issue.
- Faulty Expansion Valve or Orifice Tube: A malfunctioning expansion valve or orifice tube can restrict refrigerant flow, leading to poor cooling.
- Electrical Problems: Problems with the AC system's electrical components, such as relays, switches, or sensors, can prevent the system from functioning properly.
- Blend Door Actuator Issues: The blend door controls the mixture of hot and cold air entering the cabin. A faulty blend door actuator can cause the AC to blow only hot or only cold air, regardless of the temperature setting.
Basic AC Maintenance Tips
Preventive maintenance can help keep your car's AC system running smoothly:
- Run the AC Regularly: Even during the winter months, run the AC for a few minutes each week to circulate the refrigerant and lubricate the compressor seals.
- Check the Refrigerant Level: Periodically check the refrigerant level using a gauge. If the level is low, have the system inspected for leaks.
- Clean the Condenser: Regularly clean the condenser fins to remove debris.
- Replace the Cabin Air Filter: A clogged cabin air filter can restrict airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Replace the filter according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Have the System Serviced Regularly: Schedule regular AC servicing with a qualified mechanic to check for leaks, inspect the components, and recharge the refrigerant as needed.
When to Seek Professional Help
While some AC problems can be addressed with basic troubleshooting, others require professional expertise. If you experience any of the following, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic:
- Refrigerant leaks
- Compressor problems
- Electrical issues
- Complex system diagnostics
AC System Upgrades and Enhancements
Beyond basic repairs, there are several ways to upgrade or enhance your car's AC system:
- Upgraded Condenser: A high-performance condenser can improve cooling efficiency, especially in hot climates.
- Electric Cooling Fans: Upgrading to electric cooling fans can improve airflow across the condenser, especially at low speeds.
- Performance Refrigerant: Certain aftermarket refrigerants are designed to provide better cooling performance than standard refrigerants. However, it's essential to ensure that the refrigerant is compatible with your vehicle's AC system.
Conclusion
Understanding the diagram and functioning of your car's air conditioning system can empower you to maintain it effectively and address minor issues promptly. Regular maintenance, combined with timely professional service, will ensure that your AC system keeps you cool and comfortable for years to come. By familiarizing yourself with the components, common problems, and basic maintenance practices outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to keep your car's AC system in top condition.