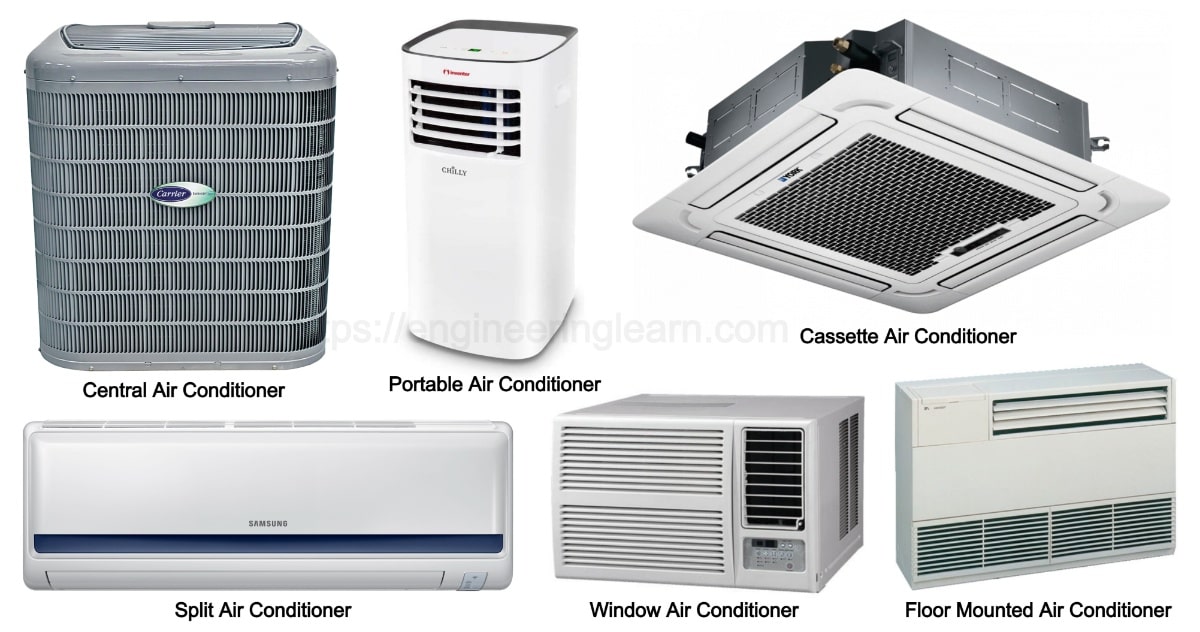
Different Types Of Home Air Conditioners

Choosing the right air conditioning system for your home or building is a crucial decision that impacts comfort, energy consumption, and overall cost. Understanding the different types of air conditioners available is the first step in making an informed choice. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the various AC systems, their pros and cons, and factors to consider when selecting the ideal solution.
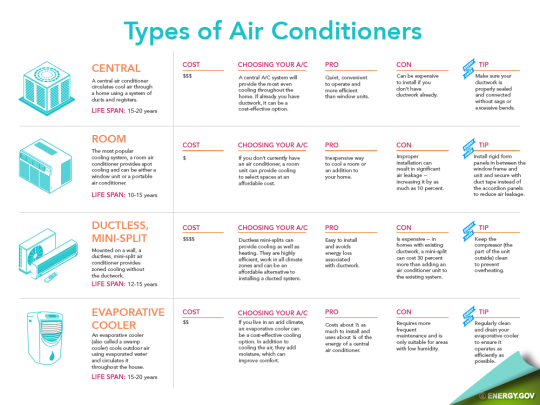
Central Air Conditioning Systems
Central air conditioning is the most common type of air conditioning in many parts of the world, particularly in larger homes and commercial buildings. These systems use a network of ducts to distribute cool air throughout the building.
Components of a Central Air System
A typical central air system consists of two main components:
- Outdoor Unit (Condenser): This unit houses the compressor, condenser coil, and fan. The compressor pumps refrigerant, the condenser coil releases heat, and the fan dissipates that heat into the outside air.
- Indoor Unit (Evaporator): Usually paired with a furnace or air handler, this unit contains the evaporator coil. The evaporator coil absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling it. A blower fan then circulates the cooled air through the ductwork.
How Central Air Conditioning Works
The central air conditioning process involves a refrigerant circulating between the indoor and outdoor units. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air in the evaporator coil, turning it into a gas. This gaseous refrigerant is then pumped to the outdoor unit where the compressor increases its pressure and temperature. The hot, high-pressure refrigerant passes through the condenser coil, releasing heat into the outside air and condensing back into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant then flows back to the indoor unit, completing the cycle.
Pros of Central Air Conditioning
- Consistent Cooling: Provides even cooling throughout the entire building.
- Improved Air Quality: Works in conjunction with air filters to remove dust, pollen, and other allergens.
- Convenience: Easily controlled by a thermostat.
- Increased Home Value: Considered a desirable feature by many home buyers.
Cons of Central Air Conditioning
- Higher Installation Cost: More expensive to install than other types of AC systems.
- Ductwork Required: Requires existing ductwork, which may not be present in older homes. Ductwork installation can be costly and disruptive.
- Potential for Duct Leakage: Leaky ducts can reduce efficiency and increase energy costs.
- Zoning Challenges: Cooling entire house even when only certain rooms are occupied.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan
The cost of a central air conditioning system can range from $3,000 to $7,000+ installed, depending on the size of the home and the efficiency of the unit. SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings indicate the efficiency of the unit. Higher SEER ratings mean greater energy savings. Central air systems typically last 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Ductless mini-split systems, also known as split-ductless systems, are a popular alternative to central air conditioning, particularly in homes without existing ductwork, additions, or spaces requiring individual temperature control.
Components of a Mini-Split System
Mini-split systems consist of two main components:
- Outdoor Unit: Contains the compressor, condenser coil, and fan, similar to a central air system.
- Indoor Unit (Air Handler): A wall-mounted unit that delivers cool air directly into the room. One outdoor unit can often support multiple indoor units.
How Mini-Split Systems Work
Mini-split systems use the same refrigerant cycle as central air conditioners. However, instead of using ductwork, refrigerant lines connect the outdoor and indoor units directly. Each indoor unit can be controlled independently, allowing for zoning and personalized temperature settings.
Pros of Mini-Split Systems
- Zoned Cooling: Allows for individual temperature control in different rooms.
- Easy Installation: Relatively easy to install, requiring only a small hole in the wall for the refrigerant lines.
- Energy Efficiency: Often more energy-efficient than central air systems due to the absence of duct losses.
- Quiet Operation: Generally quieter than window units or central air systems.
- Heating and Cooling: Many mini-split systems offer both heating and cooling capabilities.
Cons of Mini-Split Systems
- Higher Upfront Cost: Can be more expensive than window units, especially when multiple indoor units are required.
- Aesthetic Concerns: The wall-mounted indoor units can be visually intrusive.
- Maintenance: Requires regular cleaning of the filters and coils.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan
The cost of a mini-split system can range from $1,500 to $5,000+ per indoor unit installed. SEER and HSPF (Heating Season Performance Factor) ratings are used to measure efficiency. Mini-split systems can last 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
Window Air Conditioners
Window air conditioners are a simple and affordable cooling solution for individual rooms. These self-contained units are installed in a window and exhaust hot air to the outside.
How Window Air Conditioners Work
Window air conditioners contain all the components of a central air system – compressor, condenser coil, evaporator coil, and fan – within a single unit. The unit draws in warm air from the room, cools it using refrigerant, and blows the cool air back into the room. Hot air is expelled from the back of the unit to the outside.
Pros of Window Air Conditioners
- Low Cost: The least expensive type of air conditioner.
- Easy Installation: Relatively easy to install and remove.
- Portability: Can be easily moved from one window to another.
- No Ductwork Required: A simple plug-and-play solution.
Cons of Window Air Conditioners
- Limited Cooling Capacity: Only suitable for cooling small rooms.
- Noisy Operation: Can be quite noisy.
- Security Concerns: Can be a security risk if not properly secured.
- Obstructed Window View: Blocks part of the window.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan
Window air conditioners are the least expensive option, ranging from $100 to $500+ depending on the size and features. Efficiency is measured by the EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio). Window units typically last 5-10 years.
Portable Air Conditioners
Portable air conditioners are self-contained units that can be moved from room to room. They exhaust hot air through a vent hose that is typically placed in a window.
How Portable Air Conditioners Work
Portable air conditioners work similarly to window air conditioners, but they are mounted on wheels and can be easily moved. They draw in warm air, cool it with refrigerant, and exhaust hot air through a vent hose.
Pros of Portable Air Conditioners
- Portability: Can be moved from room to room as needed.
- No Permanent Installation: No permanent installation required.
Cons of Portable Air Conditioners
- Lower Efficiency: Generally less efficient than window units.
- Bulky and Noisy: Can be bulky and noisy.
- Requires Venting: Requires a vent hose to be placed in a window.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan
Portable air conditioners cost between $300 and $800+. They have lower EER ratings than window units. They last about 5-10 years.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground source heat pumps, use the Earth's constant temperature to provide both heating and cooling.
How Geothermal Heat Pumps Work
Geothermal systems circulate a refrigerant through a loop of underground pipes. In the summer, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the building and transfers it to the cooler ground. In the winter, the process is reversed, and the refrigerant absorbs heat from the warmer ground and transfers it to the building.
Pros of Geothermal Heat Pumps
- High Efficiency: Extremely energy-efficient.
- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Heating and Cooling: Provides both heating and cooling.
- Quiet Operation: Very quiet operation.
Cons of Geothermal Heat Pumps
- High Installation Cost: The most expensive type of HVAC system to install.
- Requires Land: Requires sufficient land for the underground loop.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan
Geothermal systems can cost $15,000 to $30,000+ installed. They have very high Coefficient of Performance (COP) ratings. Geothermal systems can last 20-25 years or more.
Evaporative Coolers (Swamp Coolers)
Evaporative coolers, also known as swamp coolers, use the evaporation of water to cool the air. They are most effective in dry climates.
How Evaporative Coolers Work
Evaporative coolers draw in warm, dry air and pass it through a wet pad. As the water evaporates, it cools the air, which is then blown into the room.
Pros of Evaporative Coolers
- Low Cost: Relatively inexpensive to purchase and operate.
- Energy Efficient: Uses less energy than air conditioners.
- Environmentally Friendly: Uses water instead of refrigerant.
Cons of Evaporative Coolers
- Limited Effectiveness: Only effective in dry climates.
- Increases Humidity: Increases humidity levels indoors.
- Requires Water Supply: Requires a continuous water supply.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan
Evaporative coolers cost between $200 and $1,000+. Their effectiveness is highly dependent on humidity levels. They last about 5-10 years.
Choosing the Right Air Conditioner
When choosing an air conditioner, consider the following factors:
- Climate: The climate will influence the type of AC system that is most effective.
- Size of the Space: The size of the space will determine the cooling capacity required.
- Budget: Consider the initial cost of the system, as well as the operating costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Choose a system with a high SEER, EER, HSPF, or COP rating.
- Installation Requirements: Consider the installation requirements, such as ductwork or land availability.
- Personal Preferences: Consider your personal preferences, such as noise level and aesthetic appeal.
By carefully considering these factors and understanding the different types of air conditioners available, you can make an informed decision and choose the best cooling solution for your needs.
Consult with a qualified HVAC technician for professional advice and installation.