Does Central Heat Use Gas Or Electricity
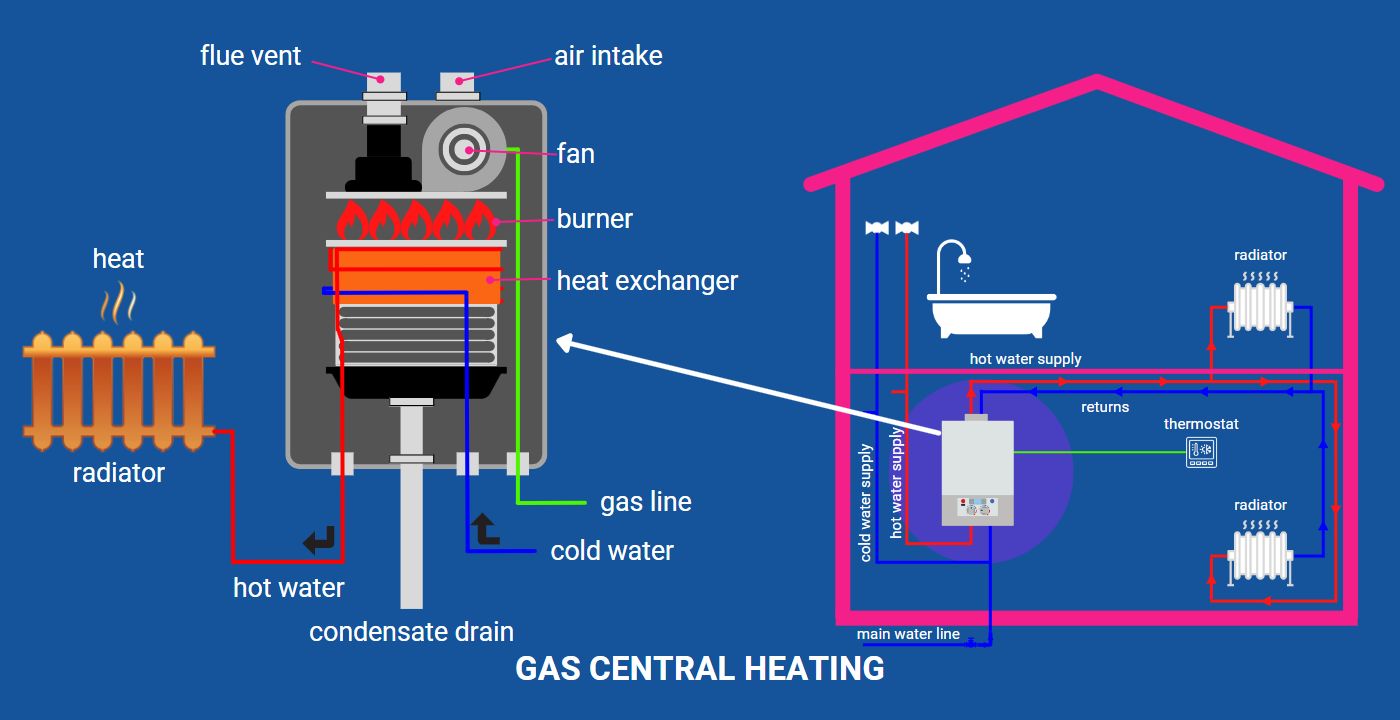
Understanding how your central heating system works is crucial for managing energy costs and making informed decisions about your home's comfort. A fundamental question for many homeowners is: Does central heat use gas or electricity? The answer isn't always straightforward, as both gas and electricity can power central heating systems, and the specific type you have significantly impacts efficiency and cost.
Understanding the Basics of Central Heating
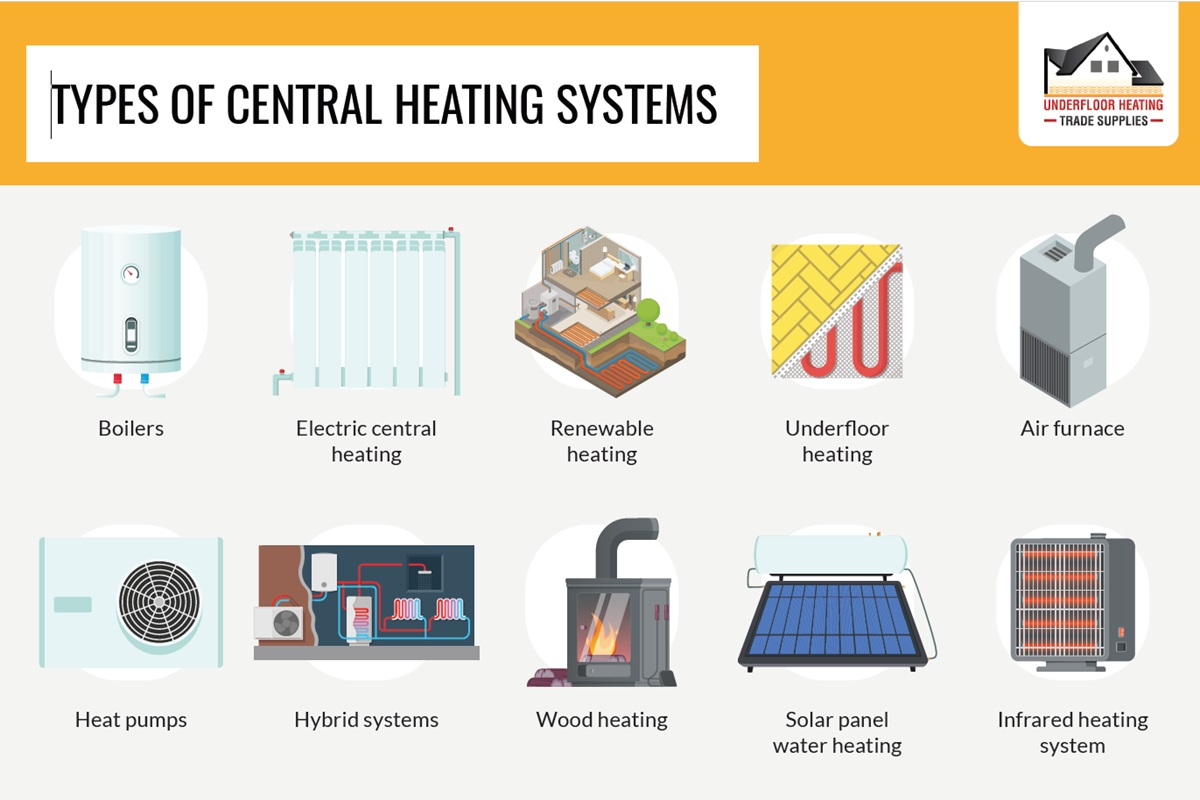
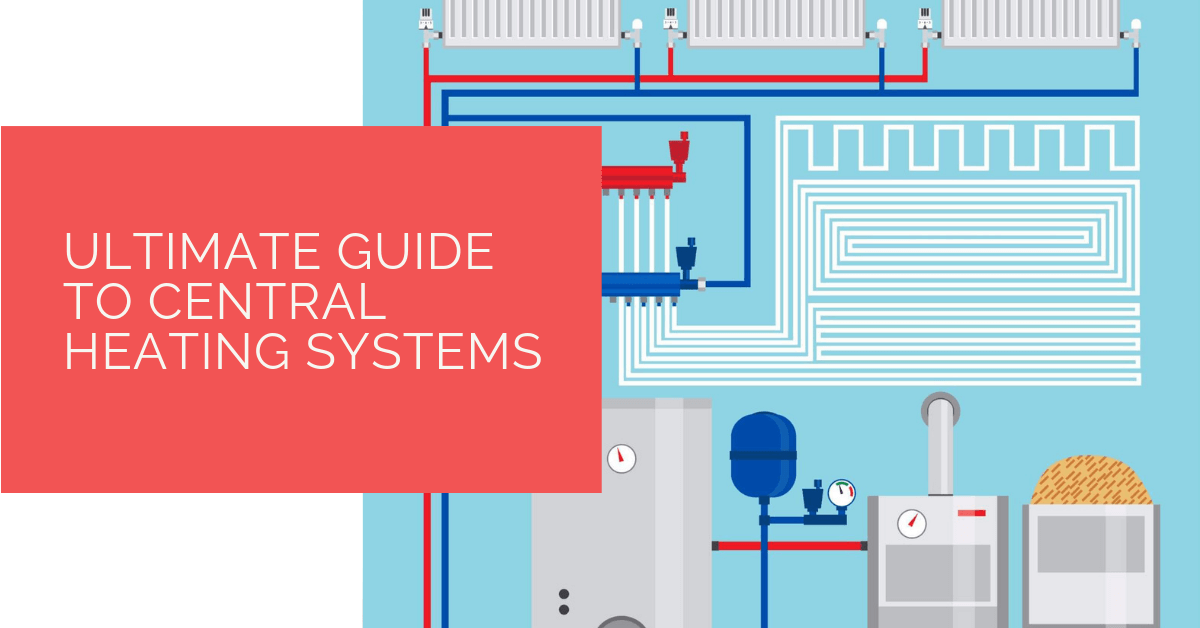
Central heating systems are designed to warm an entire house from a single source. This contrasts with localized heating solutions like space heaters, which only heat a specific room. Central heating involves a central unit that generates heat and a distribution system that carries the heat to different parts of the house. The most common distribution methods are:
- Ductwork: A network of metal or fiberglass ducts that carry heated air.
- Radiators: Individual heating units placed in rooms, connected to a central boiler via pipes.
- Baseboard heaters: Electric or hydronic (water-based) heaters installed along the baseboards of walls.
The source of the heat, however, can be either gas or electricity, leading to different types of central heating systems.
Gas-Powered Central Heating
Furnaces: The Most Common Gas Option
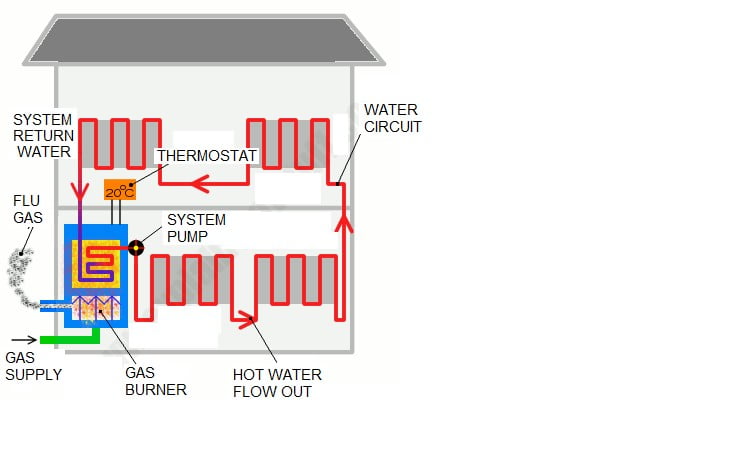
Gas furnaces are the most prevalent type of central heating system in many regions. They burn natural gas (or propane) to generate heat. The combustion process heats a heat exchanger, a set of metal coils or chambers. Air from your home's ductwork is then blown across the heat exchanger, warming the air. This heated air is then circulated throughout your home via the ductwork.
The exhaust gases produced by the combustion process are vented outside through a chimney or flue. Newer, high-efficiency furnaces have improved venting systems and can extract more heat from the exhaust gases, resulting in better energy savings.
Advantages of Gas Furnaces:
- Lower operating costs (in many areas): Natural gas is often cheaper than electricity, making gas furnaces more economical to run, particularly in regions with low gas prices.
- Fast heating: Gas furnaces can heat a home quickly and efficiently.
- High heat output: They can generate a substantial amount of heat, making them suitable for colder climates.
Disadvantages of Gas Furnaces:
- Potential for carbon monoxide leaks: Although rare with proper maintenance, gas furnaces pose a risk of carbon monoxide poisoning if not properly maintained or vented.
- Requires gas line: You need access to a natural gas line (or a propane tank) for a gas furnace to operate.
- Higher initial cost: Gas furnaces typically have a higher upfront cost compared to electric furnaces.
Boilers: Heating Water for Radiators or Radiant Floors
Boilers are another type of gas-powered central heating system. Instead of heating air, boilers heat water (or sometimes steam). This heated water is then circulated through pipes to radiators or radiant floor systems throughout the house.
Radiators transfer heat to the air in the room, while radiant floor systems warm the floor directly, providing a comfortable and even heat distribution.
Advantages of Boilers:
- Even heat distribution: Radiant heating systems provide a more even and comfortable heat compared to forced-air systems.
- Quiet operation: Boilers are generally quieter than furnaces.
- Efficient: Modern boilers can be very efficient, especially when used with radiant floor heating.
Disadvantages of Boilers:
- Slower heating: Boilers can take longer to heat a home compared to furnaces.
- Higher installation cost: Installing a boiler system can be more expensive than installing a furnace.
- Potential for leaks: Water leaks can be a problem with boiler systems.
Electric-Powered Central Heating
Electric Furnaces: A Direct Heat Approach
Electric furnaces use electric resistance coils to generate heat. When electricity flows through these coils, they heat up, and a blower fan circulates air across the coils, distributing the warmed air through the ductwork.
Electric furnaces are simpler in design than gas furnaces, as they don't involve combustion.
Advantages of Electric Furnaces:
- Lower upfront cost: Electric furnaces are typically cheaper to purchase and install than gas furnaces.
- Safer: They don't produce carbon monoxide, eliminating the risk of poisoning.
- Easier installation: Installation is generally simpler and requires no venting.
Disadvantages of Electric Furnaces:
- Higher operating costs (in many areas): Electricity is often more expensive than natural gas, making electric furnaces more costly to run.
- Less efficient: Electric furnaces typically have a lower energy efficiency rating compared to gas furnaces.
- Can strain electrical system: Electric furnaces require a significant amount of electricity, which can strain your home's electrical system.
Heat Pumps: Efficiently Transferring Heat
Heat pumps are different from furnaces in that they don't generate heat; instead, they transfer heat from one place to another. In the winter, a heat pump extracts heat from the outside air (even when it's cold) and transfers it inside your home. In the summer, it reverses the process, removing heat from your home and transferring it outside, acting as an air conditioner.
Think of refrigerant as the "blood" of the heat pump system, carrying heat from inside to outside (or vice versa).
Advantages of Heat Pumps:
- Energy-efficient: Heat pumps are very energy-efficient, especially in moderate climates.
- Dual function: They can provide both heating and cooling.
- Environmentally friendly: They use electricity and don't produce greenhouse gases directly.
Disadvantages of Heat Pumps:
- Less effective in extremely cold climates: Heat pumps lose efficiency in very cold weather, often requiring a backup heating system.
- Higher upfront cost: Heat pumps can be more expensive to install than furnaces.
- Slower heating: Heat pumps may take longer to heat a home compared to furnaces, especially when it's very cold outside.
Electric Baseboard Heaters: Individual Room Control
Electric baseboard heaters are individual heating units that are installed along the baseboards of walls. Each heater contains an electric resistance coil that heats up when electricity flows through it. These heaters provide localized heat, allowing you to control the temperature in each room independently.
While they offer individual control, they are generally considered a less efficient and less comfortable form of central heating compared to other options.
Advantages of Electric Baseboard Heaters:
- Low upfront cost: Electric baseboard heaters are relatively inexpensive to purchase and install.
- Individual room control: You can control the temperature in each room independently.
- Easy installation: Installation is straightforward.
Disadvantages of Electric Baseboard Heaters:
- High operating costs: Electric baseboard heaters are typically the most expensive form of central heating to operate.
- Uneven heat distribution: They can create hot spots near the heater and cold spots in other parts of the room.
- Can be unsightly: Some people find them unattractive.
Making the Right Choice: Gas vs. Electric
Choosing between gas and electric central heating depends on several factors, including:
- Climate: In colder climates, gas furnaces are often a more cost-effective option due to their high heat output and lower operating costs (if gas is cheaper than electricity). In milder climates, heat pumps can be a very efficient choice.
- Fuel costs: Compare the cost of natural gas and electricity in your area to determine which fuel source is more economical.
- Installation costs: Consider the upfront costs of installing different types of heating systems.
- Energy efficiency: Look for systems with high energy efficiency ratings (AFUE for furnaces, HSPF for heat pumps) to minimize your energy bills.
- Environmental concerns: If you're concerned about the environment, heat pumps are a good choice as they don't produce greenhouse gases directly.
Key Considerations for Your Decision:
- Long-Term Costs: Don't just focus on the initial purchase price. Consider the long-term operating costs, including fuel and maintenance.
- Professional Advice: Consult with a qualified HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) contractor to assess your specific needs and recommend the best system for your home.
- Home's Insulation: Properly insulating your home will significantly reduce your heating needs, regardless of the type of system you choose.
In conclusion, both gas and electricity can power central heating systems. Gas furnaces and boilers are common choices, offering high heat output and potentially lower operating costs (depending on fuel prices). Electric furnaces and heat pumps provide alternative options, with heat pumps offering energy-efficient heating and cooling in moderate climates. The best choice for your home depends on your climate, fuel costs, installation costs, and energy efficiency goals. Carefully consider these factors and seek professional advice to make an informed decision.