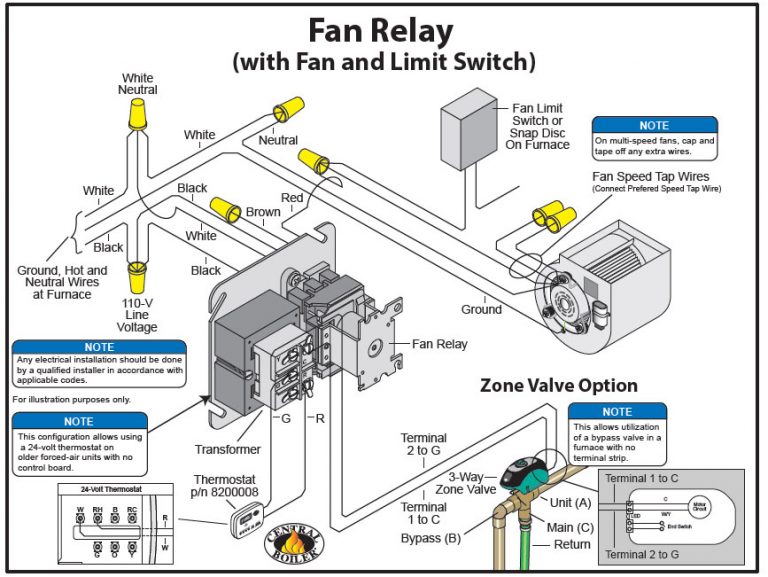
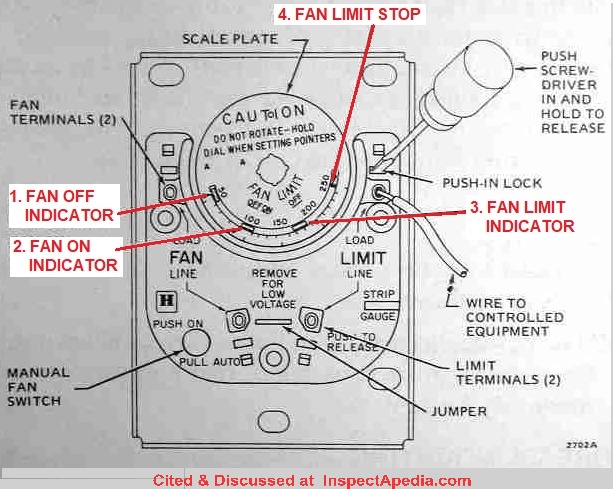
Fan Limit Switch For Wood Furnace

The fan limit switch is a critical safety component in wood furnaces, and indeed, many other types of heating systems. While often overlooked, it plays a vital role in ensuring efficient operation and preventing potentially dangerous overheating. Understanding its function, troubleshooting common issues, and knowing when to replace it are essential for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers alike.
What is a Fan Limit Switch?
In essence, the fan limit switch is a temperature-sensitive control device. It’s typically located near the heat exchanger within the furnace. Its primary purpose is twofold: to control the blower fan's operation based on the furnace's internal temperature and to act as a safety shut-off in case of overheating.
Think of it as a thermostat specifically dedicated to managing the blower fan and preventing unsafe conditions. It has two key functions:
- Fan On/Off Control: The switch senses the temperature of the heat exchanger. Once the heat exchanger reaches a pre-set "fan-on" temperature, the switch activates the blower fan, circulating warm air throughout the building. When the furnace cycles off and the heat exchanger cools down, the switch deactivates the fan at a pre-set "fan-off" temperature. This prevents the fan from blowing cold air after the heating cycle is complete.
- High-Limit Safety: If the furnace starts to overheat due to a malfunction (e.g., blocked flue, dirty air filter, faulty blower motor), the fan limit switch acts as a fail-safe. If the temperature exceeds a pre-set high-limit threshold, the switch shuts down the burner to prevent further overheating and potential damage or fire hazards.
The "fan-on," "fan-off," and "high-limit" temperatures are typically printed directly on the switch itself. These temperatures are chosen by the furnace manufacturer and should not be arbitrarily changed.
How it Works: A Technical Overview
Most fan limit switches are bimetallic strip devices. A bimetallic strip is made of two different metals bonded together. These metals expand and contract at different rates when heated. As the heat exchanger's temperature increases, the bimetallic strip bends. This bending action mechanically opens or closes electrical contacts within the switch.
There are two main types of fan limit switches:
- Combination Fan and Limit Switch: This type incorporates both the fan control and the high-limit safety functions into a single unit. It typically has three wires: one for power in, one for the fan circuit, and one for the high-limit circuit.
- Separate Fan and Limit Switches: Some furnaces use separate switches for fan control and high-limit safety. This provides an extra layer of redundancy.
When the heat exchanger temperature reaches the "fan-on" setpoint, the bimetallic strip bends and closes the contacts in the fan circuit, energizing the blower motor. As the heat exchanger cools, the strip straightens, opening the contacts and de-energizing the fan. If the temperature exceeds the "high-limit" setpoint, the bimetallic strip bends further, opening the contacts in the burner circuit, shutting down the furnace.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
A malfunctioning fan limit switch can cause several problems:
- Fan Runs Constantly: If the fan limit switch is stuck in the "on" position, the blower fan may run continuously, even when the furnace is not actively heating. This wastes energy and can lead to discomfort.
- Fan Doesn't Turn On: If the switch is stuck in the "off" position, the fan may not turn on at all, leading to overheating and potentially triggering the high-limit safety.
- Furnace Overheats and Shuts Down: Repeatedly tripping the high-limit safety indicates a potential problem with airflow, a faulty blower motor, or a malfunctioning fan limit switch.
- Short Cycling: The furnace cycles on and off too frequently.
Here's a basic troubleshooting guide:
- Visual Inspection: Check the switch for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or corrosion.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the switch at different temperatures. At room temperature, the fan circuit should be open, and the high-limit circuit should be closed. When the switch is heated (carefully! Use a heat gun, not an open flame), the fan circuit should close, and the high-limit circuit should open if overheated.
- Wiring Check: Ensure all wires are securely connected and free from damage.
- Temperature Verification: Use a surface thermometer to verify the actual temperature of the heat exchanger against the switch's setpoints.
Important Safety Note: Always disconnect power to the furnace before performing any electrical testing or repairs. If you are not comfortable working with electricity, consult a qualified HVAC technician.
When to Replace a Fan Limit Switch
If troubleshooting reveals a faulty fan limit switch, replacement is usually the best option. The cost of a replacement switch is relatively low, typically ranging from $20 to $50, depending on the type and brand. Labor costs for professional installation can vary, but typically range from $75 to $200, depending on the complexity of the job.
Consider replacement if:
- The switch fails a continuity test.
- The switch shows signs of physical damage.
- The furnace is experiencing repeated overheating issues.
- The switch is old and unreliable (typically after 10-15 years).
When replacing the switch, be sure to use the correct replacement part specified by the furnace manufacturer. Using the wrong switch can compromise safety and performance.
Preventative Maintenance
Regular preventative maintenance can help extend the life of your fan limit switch and prevent problems:
- Change Air Filters Regularly: A dirty air filter restricts airflow, causing the furnace to work harder and potentially overheat.
- Inspect Blower Motor: Ensure the blower motor is running smoothly and efficiently. A failing blower motor can reduce airflow and lead to overheating.
- Check Flue Vent: Ensure the flue vent is clear of obstructions. A blocked flue can cause the furnace to overheat.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule regular professional HVAC inspections to identify and address potential problems before they become major issues.
The Fan Limit Switch in Different Settings
The core function of the fan limit switch remains consistent across various applications, but the specific implementation and considerations can differ:
- Homeowners: Understanding the basic function of the switch allows homeowners to identify potential problems early and communicate effectively with HVAC technicians. Regular filter changes and visual inspections are key preventative measures.
- HVAC Technicians: Technicians need a thorough understanding of the switch's operation, troubleshooting techniques, and proper replacement procedures. Accurate diagnosis and correct part selection are crucial.
- Facility Managers: In large buildings, multiple furnaces may be in operation. A robust preventative maintenance program, including regular fan limit switch inspections, is essential to ensure reliable heating and prevent costly downtime. Integrating furnace monitoring systems can provide real-time data and alert facility managers to potential problems.
Beyond Wood Furnaces: Applications in Other Heating Systems
While this article focuses on wood furnaces, the fan limit switch principle extends to other heating systems, including:
- Gas Furnaces: The switch operates similarly in gas furnaces, controlling the blower fan and providing high-limit protection.
- Oil Furnaces: The function remains the same, ensuring efficient heating and safety.
- Electric Furnaces: Although electric furnaces use heating elements rather than a heat exchanger, a similar type of temperature-sensitive switch may be used to control the blower fan and prevent overheating of the elements.
Conclusion
The fan limit switch is a simple yet essential component in wood furnaces and other heating systems. Understanding its function, recognizing potential problems, and performing regular maintenance can help ensure efficient operation, prevent costly repairs, and maintain a safe and comfortable indoor environment. Whether you're a homeowner, an HVAC technician, or a facility manager, a solid grasp of the fan limit switch is a valuable asset.