Federal Tax Credit For Energy Efficiency

The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, increasing energy efficiency awareness, and supportive government policies. One of the most impactful of these policies is the Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency, which provides incentives for homeowners to invest in energy-saving HVAC equipment and home improvements. Understanding this tax credit is crucial for HVAC professionals, students entering the field, and employers looking to capitalize on industry growth.
Decoding the Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency
The Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency, often referred to as the 25C tax credit, aims to encourage energy conservation by offering tax breaks to homeowners who purchase and install qualified energy-efficient equipment. This credit not only benefits homeowners by reducing their tax burden and energy bills but also stimulates demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems and drives innovation within the industry.
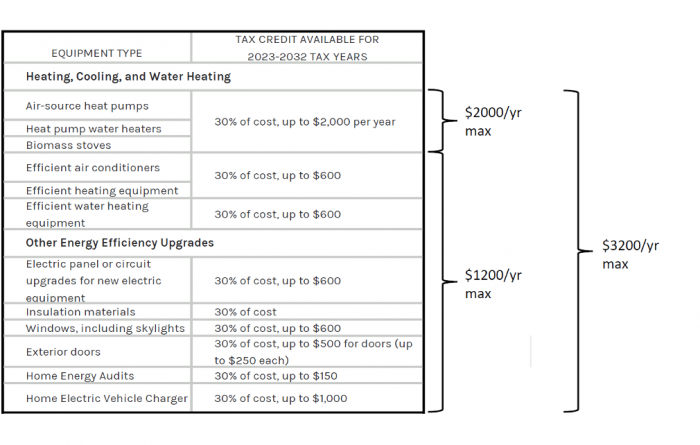
As of [Insert Current Year], the credit allows homeowners to claim a percentage of the cost of qualified energy-efficient improvements made to their homes. This includes expenses related to:
- High-efficiency HVAC systems (furnaces, air conditioners, heat pumps)
- Energy-efficient windows, doors, and skylights
- Insulation
- Energy-efficient water heaters
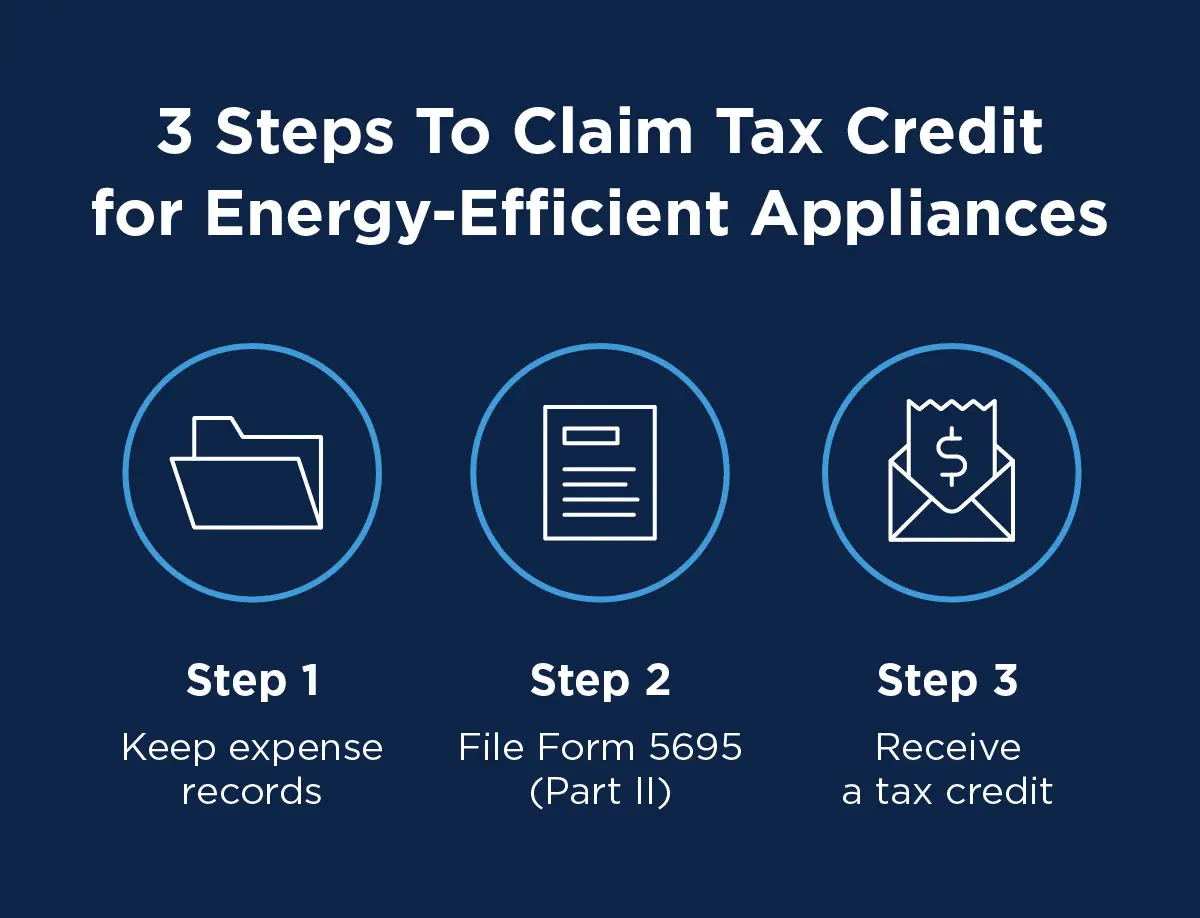
The specific percentage and maximum credit amount can vary depending on the type of equipment and the year of purchase. It is essential to consult the official IRS guidelines and Energy Star website for the most up-to-date information.
Why This Matters to HVAC Professionals
The Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency directly impacts the HVAC industry by:
- Boosting Demand: The credit makes energy-efficient HVAC systems more affordable for homeowners, leading to increased demand for these systems. This translates to more job opportunities for HVAC technicians and installers.
- Driving Innovation: To qualify for the tax credit, HVAC equipment must meet strict energy efficiency standards. This encourages manufacturers to develop and produce more innovative and efficient systems.
- Increasing Customer Awareness: The tax credit raises awareness among homeowners about the benefits of energy-efficient HVAC systems. This leads to more informed customers who are more likely to invest in high-quality, energy-saving equipment.
Career Paths and the Energy Efficiency Boom
The increased demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems creates a wealth of career opportunities for aspiring and experienced professionals alike. Here are some common career paths:
- HVAC Technician/Installer: Install, maintain, and repair HVAC systems, including energy-efficient models. Entry-level positions typically require a high school diploma or equivalent and completion of a vocational training program or apprenticeship. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for HVAC technicians and installers was around $51,470 in 2022, with job growth projected to be faster than average over the next decade.
- HVAC System Designer: Design and develop energy-efficient HVAC systems for residential and commercial buildings. This role typically requires a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering or a related field.
- Energy Auditor: Assess the energy efficiency of buildings and recommend improvements to reduce energy consumption. Certification as a Building Performance Institute (BPI) Building Analyst is often required.
- Sales and Marketing Professionals: Promote and sell energy-efficient HVAC systems to homeowners and businesses. Strong communication and sales skills, as well as knowledge of HVAC technology, are essential.
The Importance of Certifications
Earning relevant certifications can significantly enhance your career prospects in the HVAC industry, particularly in the area of energy efficiency. Some key certifications include:
- NATE (North American Technician Excellence): NATE certification demonstrates a technician's knowledge and skills in specific areas of HVAC, such as installation, service, and energy efficiency.
- EPA Section 608 Certification: Required for technicians who handle refrigerants. This certification ensures that technicians understand and follow proper procedures for refrigerant recovery and disposal, minimizing environmental impact.
- Energy Star Certification: Training related to Energy Star guidelines can help technicians better understand and install energy-efficient equipment.
- Building Performance Institute (BPI): BPI offers certifications for energy auditors and home performance contractors, demonstrating expertise in building science and energy efficiency.
Example: Consider a technician who has completed an apprenticeship program and obtained NATE certification. They are now highly sought after by employers looking to install and service energy-efficient HVAC systems. Their expertise allows them to command a higher salary and enjoy greater job security.
Salaries and Job Outlook
The HVAC industry offers competitive salaries and a positive job outlook. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for HVAC technicians and installers is projected to grow [Insert Current Percentage]% from [Insert Starting Year] to [Insert Ending Year], which is faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by:
- Increasing demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems
- The need to replace aging HVAC equipment
- Population growth and new construction
Salary ranges for HVAC professionals vary depending on experience, education, certification, and location. Here's a general overview:
- Entry-Level HVAC Technician: $35,000 - $45,000 per year
- Experienced HVAC Technician: $45,000 - $65,000 per year
- HVAC Supervisor/Manager: $65,000 - $85,000+ per year
- HVAC System Designer/Engineer: $70,000 - $100,000+ per year
These are estimates, and actual salaries may vary.
Opportunities for Employers
For HVAC employers, the Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency presents a significant opportunity to grow their businesses and attract top talent. By focusing on energy-efficient HVAC systems, employers can:
- Increase Sales: Promote energy-efficient HVAC systems to homeowners who are looking to take advantage of the tax credit.
- Attract and Retain Skilled Workers: Offer training and certification opportunities to employees to enhance their skills and expertise in energy efficiency.
- Build a Reputation for Quality and Innovation: Partner with manufacturers of energy-efficient HVAC equipment and promote your company as a leader in energy-saving solutions.
- Leverage Government Incentives: Stay informed about the latest tax credits and rebates and use them to attract new customers and incentivize employees.
Staying Updated
The Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency is subject to change, so it's crucial to stay informed about the latest updates and regulations. Here are some resources to consult:
- IRS Website: The official IRS website provides detailed information about the tax credit, including eligibility requirements and claim procedures.
- Energy Star Website: The Energy Star website offers a wealth of information about energy-efficient products and practices.
- HVAC Trade Associations: Organizations like ACCA (Air Conditioning Contractors of America) and ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) provide valuable resources and training for HVAC professionals.
Conclusion
The Federal Tax Credit for Energy Efficiency is a powerful driver of growth and innovation in the HVAC industry. By understanding the tax credit and its implications, HVAC professionals, students, and employers can position themselves for success in this rapidly evolving field. Investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems not only benefits homeowners but also contributes to a more sustainable future.
Remember to always consult official sources for the most up-to-date information regarding tax credits and industry regulations. Embracing energy efficiency is not just a trend; it's a fundamental shift that will shape the future of the HVAC industry for years to come.

.png)