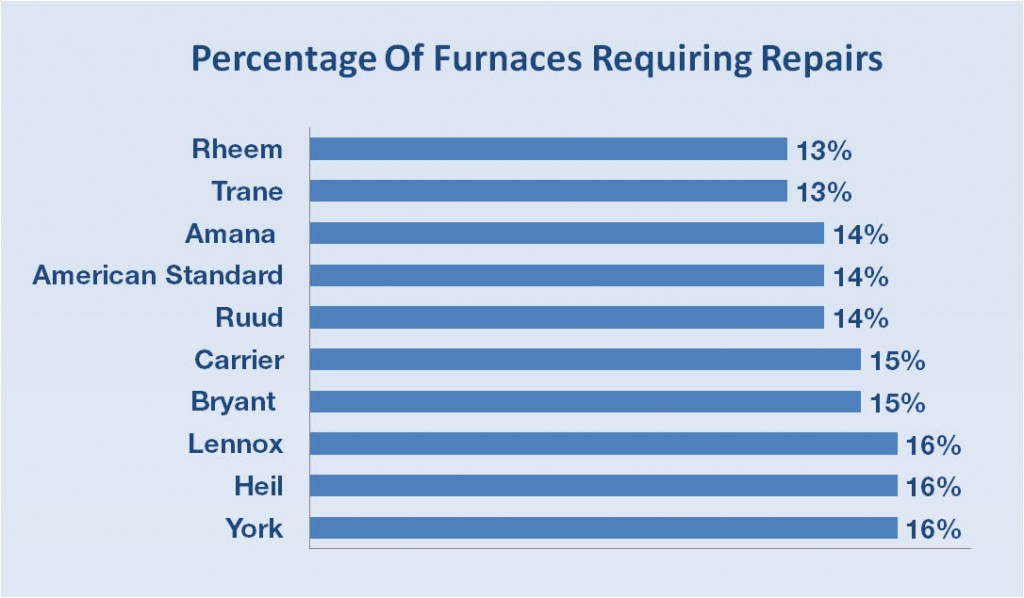
Furnace Review Consumer Reports

Choosing a new furnace is a significant investment, and navigating the options can feel overwhelming. Understanding the factors that contribute to performance, efficiency, and overall value is crucial. While Consumer Reports provides valuable insights, it's essential to consider a holistic view encompassing independent reviews, professional opinions, and specific homeowner needs. This article offers a detailed guide to evaluating furnace options, drawing from various sources, including Consumer Reports data, and offering practical advice for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers.
Understanding Furnace Types and Efficiency
Before diving into specific models, it's important to understand the fundamental furnace types and efficiency ratings. Furnaces primarily use natural gas, propane, or electricity as fuel. The choice depends on fuel availability and cost in your region. Gas furnaces are the most common, offering a balance of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Furnace Types:
- Single-Stage Furnaces: These are the simplest and least expensive. They operate at only one heat output level – full blast. This can lead to temperature swings and less efficient operation, particularly in milder weather.
- Two-Stage Furnaces: These offer two heat output levels – high and low. The low setting is typically sufficient for most heating needs, providing more consistent temperatures and improved efficiency.
- Modulating Furnaces: These are the most advanced and efficient. They adjust their heat output in small increments to precisely match the heating demand. This results in the most consistent temperatures and the highest efficiency.
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency):
AFUE is the standard measure of furnace efficiency. It indicates the percentage of fuel that is converted into usable heat. A higher AFUE rating means less fuel is wasted and lower heating bills. Modern furnaces typically have AFUE ratings ranging from 80% to 98%.
For example, an 80% AFUE furnace converts 80% of the fuel into heat, while the remaining 20% is lost up the flue. A 95% AFUE furnace is significantly more efficient, losing only 5% of the fuel.
Consumer Reports often highlights AFUE ratings in their furnace reviews, but it's important to note that the actual energy savings will depend on your climate, insulation levels, and thermostat settings.
Key Features to Consider
Beyond AFUE, several other features contribute to furnace performance and reliability:
- Variable-Speed Blowers: These blowers adjust their speed to match the heating demand, providing more consistent airflow and improved comfort. They also tend to be quieter and more energy-efficient than single-speed blowers.
- Sealed Combustion: Sealed combustion furnaces draw air from outside the home, eliminating the need to use indoor air for combustion. This improves safety and efficiency.
- Self-Diagnostics: Modern furnaces have built-in self-diagnostic systems that can help technicians quickly identify and resolve problems.
- Warranty: A good warranty provides peace of mind and protects against unexpected repair costs. Look for furnaces with at least a 10-year warranty on the heat exchanger and a 5-year warranty on other components.
Analyzing Consumer Reports and Other Reviews
Consumer Reports offers valuable data on furnace reliability and owner satisfaction. Their testing typically involves evaluating furnace performance under various conditions and surveying owners about their experiences. However, it’s crucial to remember that Consumer Reports ratings are just one piece of the puzzle.
Limitations of Consumer Reports:
- Limited Sample Size: The number of furnaces tested by Consumer Reports may be limited, and the results may not be representative of all models on the market.
- Subjective Ratings: Owner satisfaction ratings can be subjective and influenced by factors unrelated to the furnace itself, such as installation quality and homeowner expectations.
- Lack of Long-Term Data: Consumer Reports ratings typically reflect performance over a limited time frame, and they may not accurately predict long-term reliability.
Complementary Resources:
To get a more complete picture, supplement Consumer Reports data with information from other sources, such as:
- HVAC Technician Opinions: Consult with local HVAC technicians about their experiences with different furnace brands and models. They can provide valuable insights into real-world performance and reliability.
- Online Reviews: Read online reviews from other homeowners who have purchased the furnaces you are considering. Pay attention to recurring themes and patterns in the reviews.
- Industry Publications: Read articles and reviews in industry publications such as ACHR News and The Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration NEWS, which offer in-depth technical analysis of HVAC equipment.
- Energy Star Website: The Energy Star website provides a list of energy-efficient furnaces that meet specific performance criteria.
Cost Considerations
The cost of a furnace includes the purchase price, installation costs, and operating costs. The purchase price can vary widely depending on the type of furnace, its efficiency rating, and its features. Installation costs can also vary depending on the complexity of the installation and the local labor rates.
Upfront Costs vs. Long-Term Savings:
While a high-efficiency furnace may have a higher upfront cost, it can save you money on heating bills over the long term. To determine the true cost of a furnace, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes the purchase price, installation costs, operating costs, and maintenance costs over the furnace's lifespan.
Example: A homeowner is choosing between an 80% AFUE furnace that costs $2,500 installed and a 95% AFUE furnace that costs $4,000 installed. The homeowner estimates that the 95% AFUE furnace will save them $200 per year on heating bills. Over a 15-year lifespan, the 95% AFUE furnace will save the homeowner $3,000 on heating bills, making it the more cost-effective choice in the long run, despite the higher upfront cost.
Rebates and Incentives:
Check for available rebates and incentives from your local utility company or government agencies. These rebates can help offset the upfront cost of a high-efficiency furnace.
Installation Quality
The quality of the furnace installation is just as important as the quality of the furnace itself. A poorly installed furnace will not perform efficiently and may even be unsafe. Hire a qualified and experienced HVAC contractor to install your furnace. Look for contractors who are licensed, insured, and have a good reputation.
Common Installation Mistakes:
- Improper Ductwork: Leaky or undersized ductwork can significantly reduce furnace efficiency.
- Incorrect Gas Pressure: Incorrect gas pressure can lead to inefficient combustion and safety hazards.
- Improper Venting: Improper venting can allow dangerous carbon monoxide to leak into the home.
Verifying Installation Quality:
After the installation is complete, have the contractor inspect the system to ensure that it is operating correctly. Ask the contractor to provide you with documentation of the installation, including the gas pressure readings and the airflow measurements.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regular maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your furnace. Schedule annual maintenance checks with a qualified HVAC technician. During these checks, the technician will clean the furnace, inspect the components, and make any necessary adjustments.
Typical Maintenance Tasks:
- Cleaning the Burners: Dirty burners can reduce furnace efficiency and lead to incomplete combustion.
- Inspecting the Heat Exchanger: The heat exchanger is a critical component that can crack or corrode over time.
- Checking the Gas Pressure: Incorrect gas pressure can lead to inefficient combustion and safety hazards.
- Replacing the Air Filter: A dirty air filter can restrict airflow and reduce furnace efficiency.
Expected Lifespan:
A well-maintained furnace can last for 15 to 20 years. However, the actual lifespan will depend on the quality of the furnace, the quality of the installation, and the frequency of maintenance. If your furnace is more than 15 years old, it may be time to consider replacing it with a more efficient model.
Conclusion
Choosing the right furnace requires careful consideration of various factors, including furnace type, efficiency rating, features, cost, installation quality, and maintenance. While Consumer Reports provides valuable information, it's important to supplement their data with other sources, such as HVAC technician opinions, online reviews, and industry publications. By taking a holistic approach, you can make an informed decision and choose a furnace that meets your specific needs and budget. Remember that proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your new furnace. Consult with a qualified HVAC professional to assess your home's heating needs and recommend the best furnace for your situation.