Heat Pump Efficiency During Cold Weather

Heat Pump Efficiency During Cold Weather: Staying Warm and Saving Green
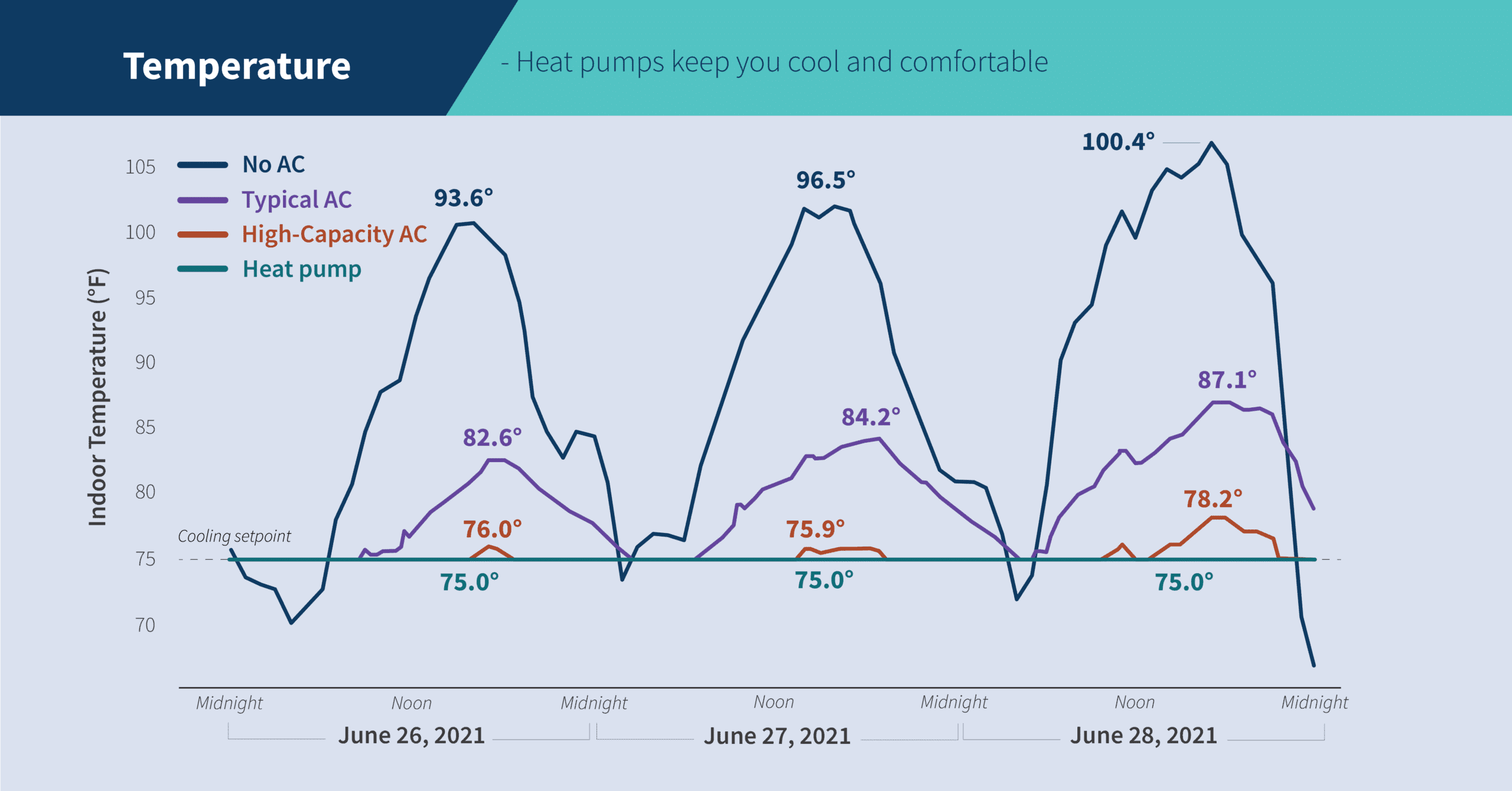
Heat pumps are increasingly popular for their energy efficiency, offering both heating and cooling from a single system. But a common question, especially in colder climates, is: How efficient are heat pumps when temperatures plummet? The answer is nuanced, but with the right information and system choices, you can ensure your heat pump performs optimally and saves you money, even when Jack Frost is nipping at your nose.
Understanding Heat Pump Operation: It's All About Heat Transfer
Unlike furnaces that generate heat by burning fuel, heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another. In the winter, they extract heat from the outdoor air and transfer it inside. Even when it feels frigid outside, there's still some heat energy present that a heat pump can utilize. The efficiency of this process is measured by two key metrics:
- Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF): Measures the heating efficiency of a heat pump over an entire heating season. The higher the HSPF rating, the more efficient the unit. Energy Star certified heat pumps typically have an HSPF of 8.5 or higher.
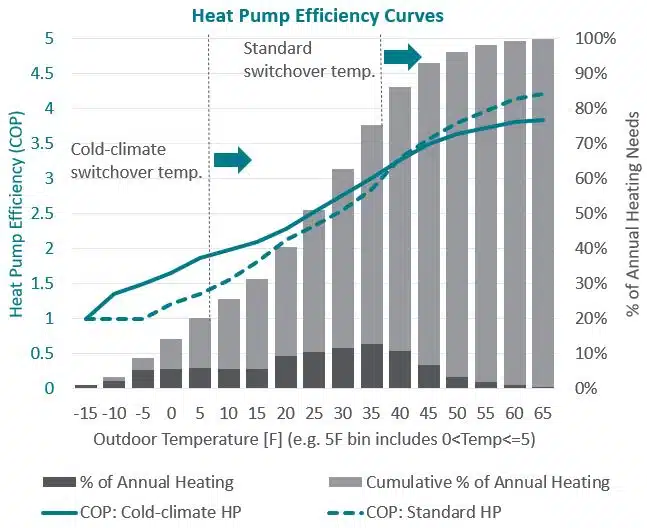
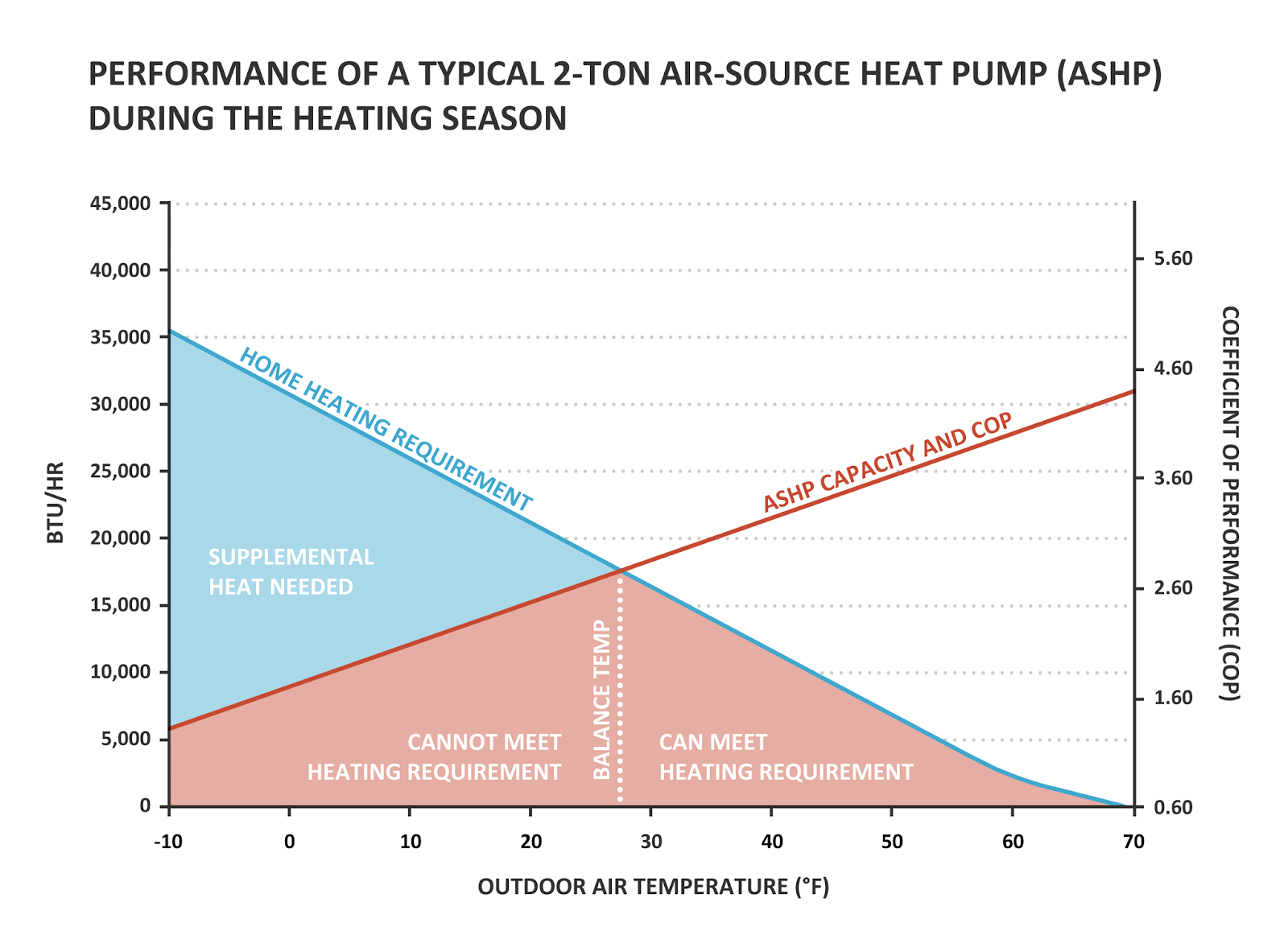
- Coefficient of Performance (COP): Represents the ratio of heating output to energy input at a specific temperature. For example, a COP of 3 means the heat pump produces 3 units of heat for every 1 unit of electricity it consumes.
As the outdoor temperature drops, the COP of a heat pump also decreases. This is because it requires more energy to extract heat from colder air. However, advancements in heat pump technology have significantly improved cold-weather performance, making them a viable option even in traditionally furnace-dominated regions.
The Cold-Weather Challenge and Technological Solutions
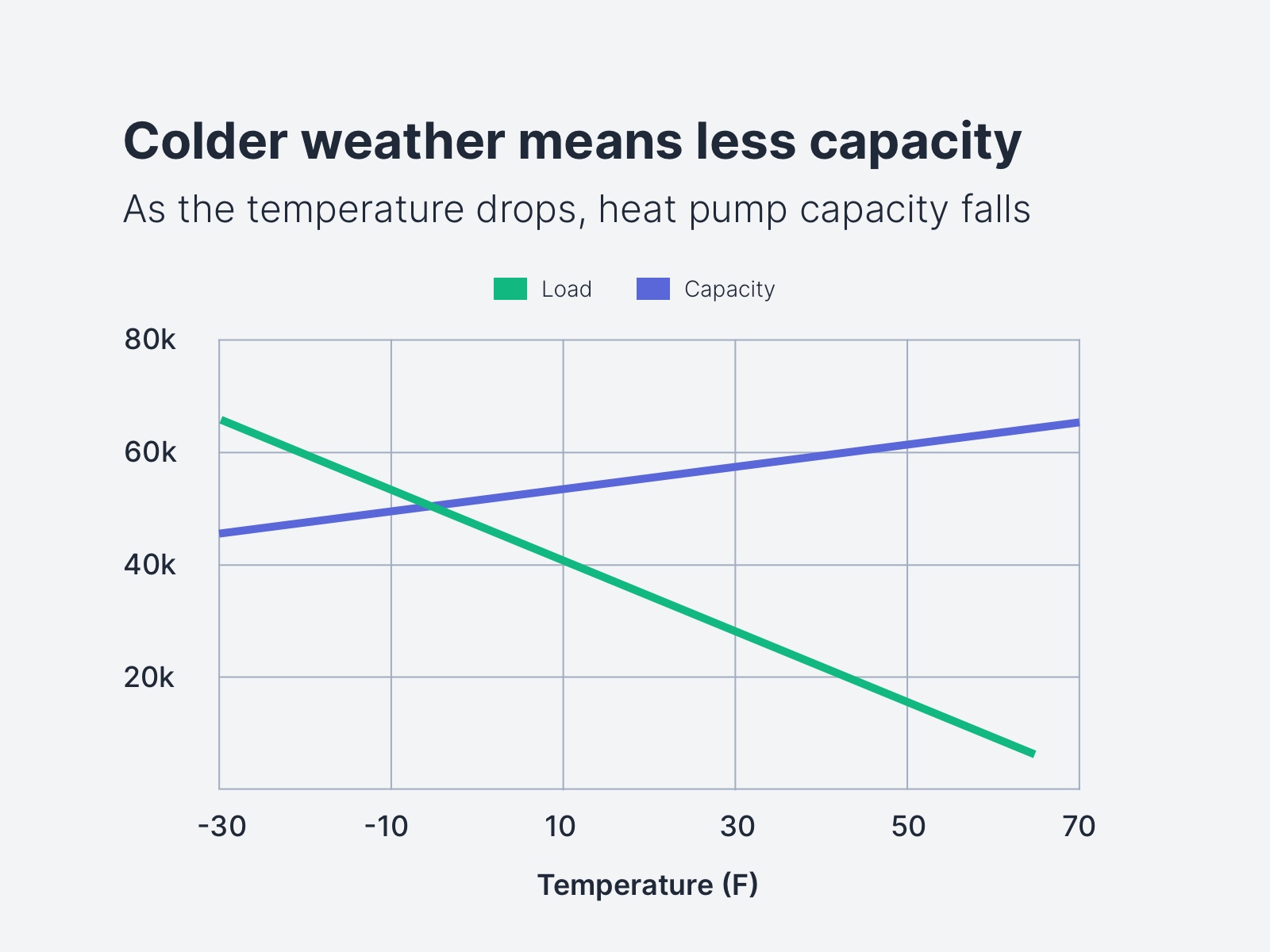
The biggest challenge for heat pumps in cold weather is their reduced capacity and efficiency as temperatures drop. Older heat pumps often struggled when temperatures fell below freezing (32°F or 0°C), requiring backup electric resistance heating to kick in. This backup heat is much less efficient than the heat pump itself, driving up energy bills. Modern heat pumps, however, employ several strategies to combat this:
- Inverter Technology: Variable-speed compressors, powered by inverter technology, allow the heat pump to adjust its output to precisely match the heating demand. This avoids the on-off cycling of traditional systems, which is less efficient and can lead to temperature fluctuations.
- Improved Compressors and Refrigerants: Advanced compressors and refrigerants are designed to operate efficiently at lower temperatures. Some refrigerants, like R-32, offer better performance and lower global warming potential than older refrigerants like R-410A.
- Basepan Heaters: These heaters prevent ice from building up on the outdoor coil, which can impede airflow and reduce efficiency.
- Advanced Defrost Cycles: Sophisticated defrost cycles minimize the time spent defrosting the outdoor coil, ensuring continuous heating and reducing energy waste. Some systems use "intelligent" defrost, only activating when needed rather than on a fixed schedule.
Cold climate heat pumps are specifically engineered for optimal performance in colder regions. These models often maintain a high COP even at very low temperatures (e.g., -13°F or -25°C) and can provide sufficient heating without relying heavily on backup resistance heat. For example, Mitsubishi's Hyper-Heating INVERTER (H2i) technology is known for its ability to deliver consistent heating capacity at extremely low temperatures.
Maximizing Heat Pump Efficiency in Winter: Tips and Tricks
Even with a high-efficiency heat pump, there are steps you can take to maximize its performance during the winter months and keep your energy bills down:
- Proper Insulation and Air Sealing: Ensure your home is adequately insulated in walls, attics, and floors. Seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings. This reduces heat loss and allows your heat pump to work less hard.
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule annual maintenance with a qualified HVAC technician. They can clean coils, check refrigerant levels, and ensure all components are functioning properly. A dirty coil can significantly reduce efficiency.
- Smart Thermostat Integration: A smart thermostat learns your heating and cooling patterns and adjusts the temperature accordingly. It can also be programmed to lower the temperature when you're away from home, saving energy. Many smart thermostats offer features like geofencing and occupancy sensors to further optimize energy use.
- Auxiliary Heat Management: Understand how your auxiliary (backup) heat works. Some smart thermostats allow you to set a temperature threshold below which the auxiliary heat will engage. By carefully managing this setting, you can minimize its use and rely more on the heat pump itself.
- Keep Outdoor Unit Clear: Ensure the area around your outdoor unit is free of snow, ice, and debris. This allows for proper airflow and prevents the unit from working harder than necessary.
- Strategic Thermostat Settings: Avoid drastically changing the thermostat temperature. Heat pumps are most efficient when maintaining a consistent temperature. Instead of turning the thermostat way up when you get home, set it to a comfortable temperature and let the heat pump gradually warm the space.
- Consider a Hybrid System: In extremely cold climates, a hybrid system that combines a heat pump with a gas furnace can offer the best of both worlds. The heat pump handles heating during milder temperatures, while the furnace provides backup heat during the coldest periods.
ROI and Energy Savings: Making the Financial Case
Investing in a high-efficiency heat pump can provide significant long-term cost savings. While the initial investment may be higher than a traditional furnace, the lower operating costs can quickly offset the difference. Here's how to calculate the potential ROI:
- Calculate Annual Heating Costs: Determine your current annual heating costs using your utility bills.
- Estimate Heat Pump Operating Costs: Use the heat pump's HSPF rating and your local electricity rates to estimate the annual operating costs. You can find online calculators to help with this.
- Factor in Rebates and Incentives: Many utility companies and government agencies offer rebates and tax credits for installing energy-efficient heat pumps. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost. Energy Star's website is a great place to find information on available rebates.
- Calculate Payback Period: Divide the initial cost difference between the heat pump and your existing system (minus any rebates) by the annual savings in operating costs. This will give you the payback period, which is the number of years it will take for the energy savings to offset the initial investment.
For example, upgrading from an old furnace with 80% efficiency to a high-efficiency heat pump with an HSPF of 10 could save you 30-50% on your annual heating bills. Over the lifespan of the heat pump (typically 15-20 years), these savings can add up to thousands of dollars.
"Upgrading to a heat pump is a win-win. You get a more comfortable home, lower energy bills, and a smaller carbon footprint." - Sarah Jones, Energy Efficiency Expert
Smart Home Integration: Taking Control of Your Comfort and Savings
Integrating your heat pump with a smart home system can further enhance its efficiency and convenience. Smart thermostats, sensors, and voice assistants allow you to control your heating and cooling remotely, monitor energy usage in real-time, and automate temperature settings based on your preferences.
Here are some benefits of smart HVAC integration:
- Remote Control: Adjust the temperature from anywhere using your smartphone or tablet.
- Energy Monitoring: Track your energy consumption and identify areas where you can save more.
- Geofencing: Automatically adjust the temperature when you leave or approach your home.
- Voice Control: Control your HVAC system with voice commands using devices like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant.
- Zone Control: Create different temperature zones in your home for personalized comfort and energy savings.
For instance, you could use a smart thermostat to lower the temperature in unoccupied rooms or schedule the heat pump to run at a lower setting overnight. Some smart systems can even integrate with weather forecasts to proactively adjust the temperature based on upcoming changes in the weather.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump: A Contractor's Perspective
Selecting the right heat pump is crucial for optimal performance and energy savings. Here are some key considerations when choosing a heat pump, from an HVAC contractor's point of view:
- Climate: Consider the climate in your area. If you live in a cold climate, opt for a cold climate heat pump specifically designed for low-temperature operation.
- Home Size and Insulation: Choose a heat pump with the appropriate capacity for your home size and insulation levels. An undersized unit will struggle to heat your home, while an oversized unit will cycle on and off frequently, reducing efficiency.
- HSPF and SEER Ratings: Look for heat pumps with high HSPF (heating) and SEER (cooling) ratings. These ratings indicate the unit's energy efficiency.
- Inverter Technology: Opt for a heat pump with inverter technology for variable-speed operation and improved efficiency.
- Refrigerant Type: Consider heat pumps that use environmentally friendly refrigerants with low global warming potential.
- Warranty and Service: Choose a heat pump from a reputable manufacturer with a good warranty and reliable service support.
- Professional Installation: Proper installation is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Hire a qualified HVAC contractor with experience installing heat pumps.
Remember to get multiple quotes from different contractors and ask for detailed explanations of their recommendations. A good contractor will assess your home's specific needs and recommend the best heat pump for your situation.
Conclusion: Heat Pumps in Cold Weather - A Smart Investment
While heat pumps may have once been considered unsuitable for cold climates, advancements in technology have made them a viable and energy-efficient heating option for many regions. By understanding how heat pumps work, choosing the right system, and implementing smart energy-saving strategies, you can enjoy a comfortable home, lower energy bills, and a reduced carbon footprint, even when the temperature drops. Investing in a high-efficiency heat pump is not just about saving money; it's about creating a more sustainable and comfortable future for yourself and generations to come.