Heat Pump Vs Gas Furnace Cost Calculator

Choosing between a heat pump and a gas furnace is a major decision for any homeowner or business. Both systems offer reliable heating, but their energy efficiency, upfront costs, and long-term operational expenses can vary dramatically. A heat pump vs. gas furnace cost calculator can be an invaluable tool in navigating this complex landscape. This article will explore the factors influencing your decision, offering insights into energy savings, potential rebates, and the benefits of integrating smart home technology.
Understanding the Basics: Heat Pumps and Gas Furnaces
Before diving into cost comparisons, it’s essential to understand how each system works.
Heat Pumps: Moving Heat, Not Generating It
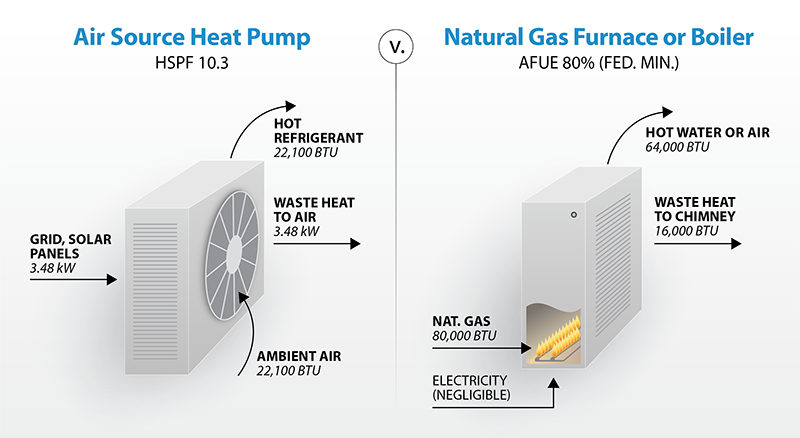
Heat pumps don’t generate heat; instead, they transfer it. In the winter, they extract heat from the outside air (yes, even in cold weather!) and pump it inside. In the summer, the process reverses, pulling heat from inside your home and releasing it outdoors, acting like an air conditioner. There are two main types: air-source and geothermal.
- Air-source heat pumps: The most common type, using the outside air as a heat source or sink.
- Geothermal heat pumps: Use the earth’s constant temperature as a heat source or sink, offering significantly higher efficiency but requiring a larger upfront investment.
Gas Furnaces: Burning Fuel for Warmth
Gas furnaces burn natural gas, propane, or oil to generate heat. The heat is then distributed throughout your home via ductwork. The efficiency of a gas furnace is measured by its Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating. The higher the AFUE, the more efficient the furnace.
Key Factors in the Heat Pump vs. Gas Furnace Cost Calculation
A comprehensive cost analysis must consider several factors beyond the initial purchase price.
1. Upfront Costs: Purchase and Installation
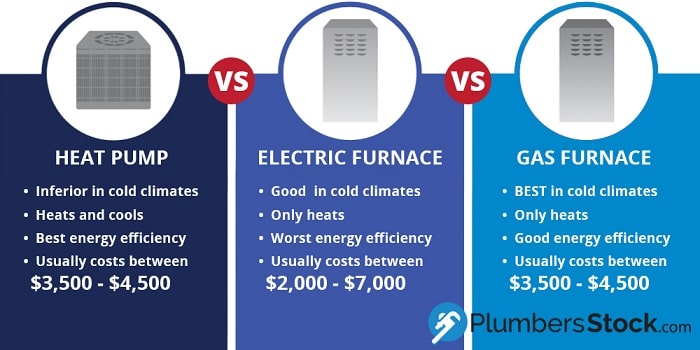
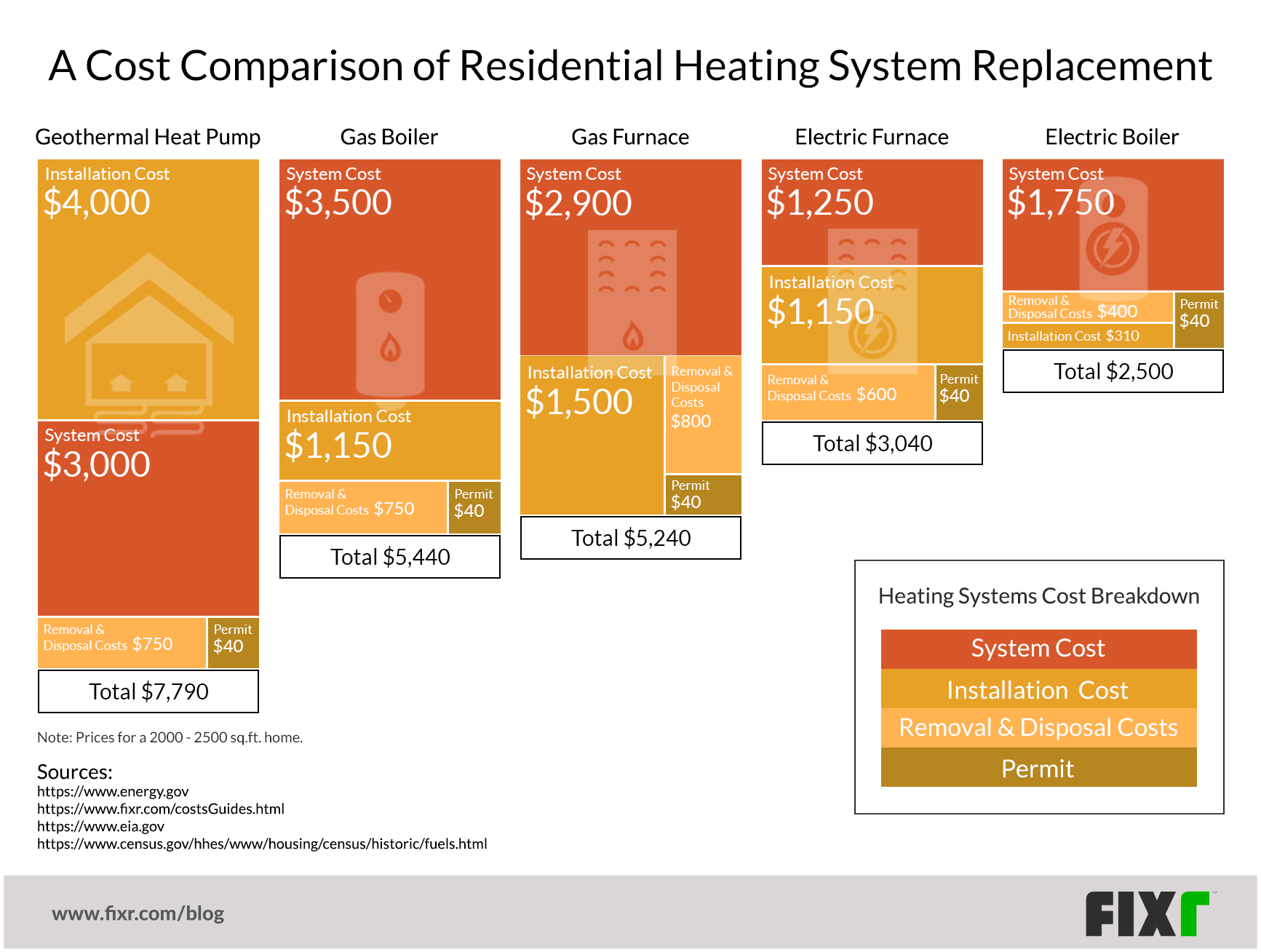
Generally, gas furnaces have a lower upfront cost than heat pumps. However, the cost of installation can vary depending on existing infrastructure. If you already have ductwork in place, installing either system will be more affordable. However, geothermal heat pump installation requires significant excavation, substantially increasing the initial investment. A basic gas furnace installation might range from $4,000 to $8,000, while a heat pump (air-source) can range from $5,000 to $12,000. Geothermal installations can easily exceed $20,000.
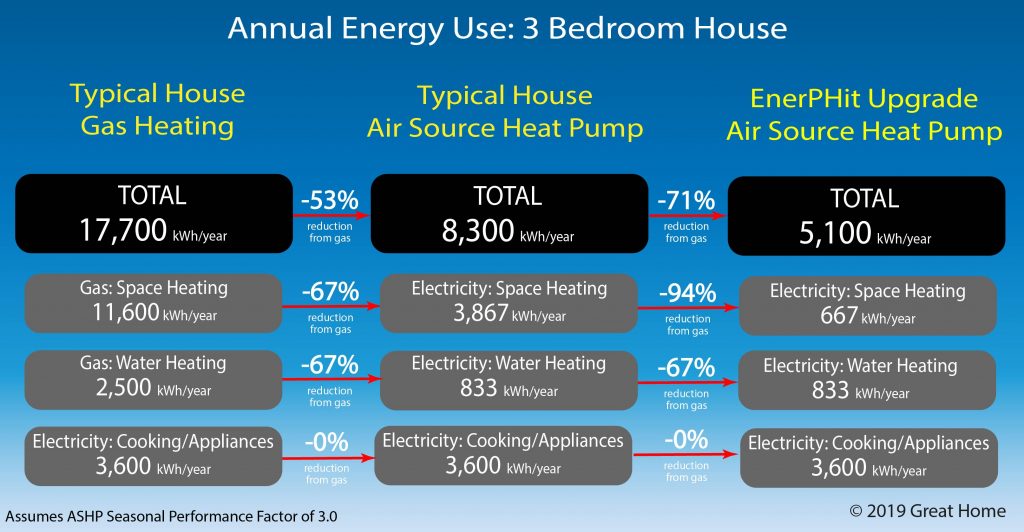
2. Operating Costs: Fuel vs. Electricity
This is where heat pumps often shine. Their high efficiency translates to lower monthly energy bills, especially in moderate climates. Gas furnaces rely on fluctuating fuel prices, which can significantly impact your operating costs. A heat pump can achieve a Coefficient of Performance (COP) of 3 or higher, meaning it delivers three or more units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. Modern, high-efficiency gas furnaces can achieve AFUE ratings of 95% or higher, but they still require constant fuel consumption.
3. Maintenance and Repair Costs
Both systems require regular maintenance, such as filter replacements and professional inspections. Gas furnaces may require more frequent maintenance due to the combustion process, which can lead to wear and tear on components. Heat pumps have more complex components, potentially leading to higher repair costs if something breaks down. However, their lifespan is generally longer, often exceeding 15 years with proper maintenance.
4. Lifespan
A well-maintained gas furnace typically lasts 15-20 years, while a heat pump can last 15-25 years. Geothermal heat pumps can last even longer, up to 50 years for the ground loop component.
5. Climate Considerations
Heat pumps perform optimally in moderate climates with mild winters. In extremely cold climates, their efficiency can decrease significantly, requiring supplemental heating (often electric resistance heat), which negates much of the energy savings. Gas furnaces are more reliable in colder climates, providing consistent heat regardless of the outside temperature. However, advancements in cold-climate heat pump technology are making them increasingly viable in colder regions. Look for models specifically designed for cold weather performance.
6. Government Rebates and Incentives
Many government agencies and utility companies offer rebates and incentives for installing energy-efficient HVAC systems. Heat pumps often qualify for larger rebates due to their higher energy efficiency. Check with your local utility company, state energy office, and the Energy Star website (www.energystar.gov) for available programs. The Inflation Reduction Act has also introduced significant tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements, including heat pumps.
7. Environmental Impact
Heat pumps are generally considered more environmentally friendly than gas furnaces, as they don’t directly burn fossil fuels. However, the electricity used to power them may be generated from fossil fuels, depending on your region's energy mix. Gas furnaces contribute directly to greenhouse gas emissions. If you prioritize sustainability, a heat pump powered by renewable energy sources (like solar panels) is the most environmentally responsible choice.
Using a Heat Pump vs. Gas Furnace Cost Calculator
Online calculators can provide a preliminary estimate of the costs associated with each system. However, it's crucial to use these tools as a starting point and consult with a qualified HVAC contractor for a more accurate assessment. Here’s what a typical calculator considers:
- Location: To account for climate and energy costs in your region.
- Home Size: Square footage to determine the required heating and cooling capacity.
- Fuel Costs: Current prices for natural gas, propane, or electricity.
- System Efficiency: AFUE for gas furnaces and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) and SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) for heat pumps.
- Installation Costs: Estimated costs for purchasing and installing each system.
- Maintenance Costs: Average annual maintenance expenses.
The calculator then projects the total cost of ownership over a specified period (e.g., 5, 10, or 15 years), considering energy savings, rebates, and potential repair costs.
The Smart Home Advantage: Integrating Smart Thermostats and Sensors
Integrating a heat pump or gas furnace with a smart thermostat can significantly enhance energy efficiency and reduce costs. Smart thermostats learn your heating and cooling preferences, automatically adjusting the temperature based on your schedule and occupancy. They can also be controlled remotely via a smartphone app, allowing you to optimize energy usage even when you’re away from home. Features like geofencing (adjusting the temperature based on your location) and energy usage monitoring provide valuable insights into your energy consumption patterns.
Furthermore, consider adding smart sensors to different rooms to create zones within your home. This allows for customized heating and cooling, ensuring that only occupied areas are heated or cooled to your desired temperature. This targeted approach can lead to substantial energy savings.
"Investing in a smart thermostat is like having a personal energy manager working 24/7 to optimize your HVAC system," explains John Smith, a certified HVAC technician.
Making the Right Choice: A Summary
The best choice between a heat pump and a gas furnace depends on your specific circumstances. Here’s a quick summary to help you decide:
- Choose a heat pump if: You live in a moderate climate, prioritize energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, and are willing to invest more upfront for long-term savings.
- Choose a gas furnace if: You live in a cold climate, prioritize lower upfront costs, and prefer a reliable heating system that performs consistently regardless of the outside temperature.
- Consider geothermal if: You have a larger budget, prioritize maximum energy efficiency and sustainability, and plan to stay in your home for a long time to recoup the investment.
Beyond the Calculator: Getting Expert Advice
While a heat pump vs. gas furnace cost calculator provides valuable insights, it’s essential to consult with a qualified HVAC contractor. They can assess your specific needs, evaluate your home’s insulation and ductwork, and recommend the most suitable system for your situation. They can also provide accurate installation estimates and help you navigate available rebates and incentives. Remember to get quotes from multiple contractors and compare their proposals carefully. A reputable contractor will prioritize energy efficiency, proper sizing, and quality installation to ensure your HVAC system performs optimally for years to come.
Ultimately, choosing between a heat pump and a gas furnace is a significant investment. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this article and consulting with experts, you can make an informed decision that saves you money, reduces your environmental impact, and keeps your home comfortable year-round.