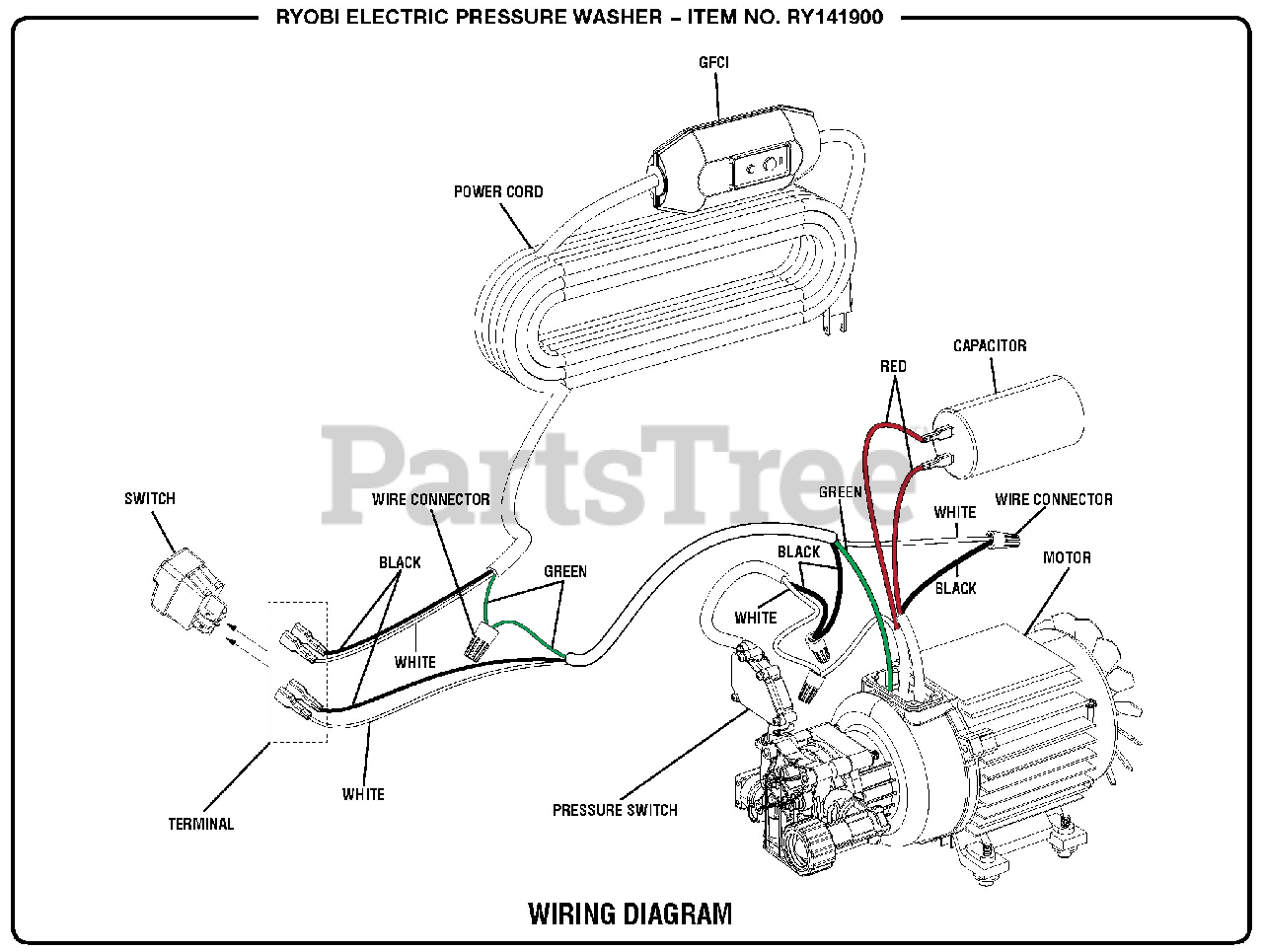
Hot Water Pressure Washer Wiring Diagram

Understanding electrical schematics is a critical skill for HVAC technicians, particularly when dealing with equipment that integrates both heating and high-pressure water systems. Hot water pressure washers, commonly used in industrial cleaning, surface preparation, and even some specialized HVAC applications, are a prime example. Their wiring diagrams, while often appearing complex, are essential for troubleshooting, maintenance, and safe operation.
Decoding the Hot Water Pressure Washer Wiring Diagram: A Technician's Guide
A hot water pressure washer wiring diagram is a visual representation of the electrical components and their connections within the unit. It's a roadmap for tracing circuits, identifying faults, and ensuring that repairs are performed correctly. These diagrams typically include symbols representing various components such as:
- Motors: For driving the water pump and, in some cases, the burner fan.
- Heating Elements/Burners: Responsible for heating the water to the desired temperature.
- Pressure Switches: Monitoring water pressure and controlling the pump motor.
- Temperature Sensors/Thermostats: Regulating the burner and preventing overheating.
- Relays/Contactors: Switching high-voltage circuits for motors and heating elements.
- Transformers: Stepping down voltage for control circuits.
- Fuses/Circuit Breakers: Protecting the electrical system from overloads.
- Wiring: Connecting all the components in a specific configuration.
Navigating these diagrams effectively requires a foundational understanding of electrical principles and component identification. For HVAC technicians, this knowledge is often gained through formal education, apprenticeships, and on-the-job training. Certifications, such as those offered by NATE (North American Technician Excellence), often include sections on electrical troubleshooting and schematic reading.
Understanding Common Components and Circuits
Let's delve into some common circuits found in hot water pressure washers and how they are represented in wiring diagrams:
- Pump Motor Circuit: This circuit typically involves a motor starter (contactor), overload protection, and a pressure switch. The pressure switch acts as a control, starting and stopping the motor based on water pressure. The wiring diagram will show how the switch is wired in series with the motor's power supply.
- Burner Control Circuit: This circuit is more complex and involves a series of safety devices, including flame sensors, high-temperature limit switches, and low-water cutoffs. These devices are wired in series to ensure that the burner only operates under safe conditions. The diagram will illustrate how each safety device interrupts the circuit in case of a fault.
- Heating Element Circuit (for electric models): This circuit includes heating elements, thermostats, and often, a contactor to handle the high current. The thermostat regulates the temperature by cycling the heating elements on and off. The wiring diagram will clearly show the series connection of the thermostat and the heating elements.
When troubleshooting, always refer to the manufacturer's specific wiring diagram for the model you are working on. General diagrams can provide a basic understanding, but each model may have unique features or wiring configurations.
Career Implications and the Job Outlook for HVAC Technicians
The ability to read and interpret electrical schematics, including those for specialized equipment like hot water pressure washers, directly impacts career opportunities and earning potential for HVAC technicians. Employers are increasingly seeking technicians with strong diagnostic skills and a solid understanding of electrical systems.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job outlook for HVAC mechanics and installers is projected to grow 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations. About 38,000 openings for HVAC mechanics and installers are projected each year, on average, over the decade. This growth is driven by factors such as:
- Increased demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems.
- The growing complexity of HVAC equipment.
- The need for technicians to maintain and repair existing systems.
The median annual wage for HVAC mechanics and installers was $59,620 in May 2023. The best-paid 10 percent made more than $87,850. Salary ranges can vary significantly based on experience, location, certifications, and the specific employer.
The Value of Certifications
Obtaining industry-recognized certifications can significantly enhance a technician's career prospects. EPA Section 608 certification is mandatory for technicians who handle refrigerants, but other certifications, such as those offered by NATE, demonstrate a commitment to professionalism and expertise. NATE offers certifications in various specialties, including air conditioning, heat pumps, and gas heating. These certifications often require candidates to pass exams that assess their knowledge of electrical systems, troubleshooting, and schematic reading.
For technicians working with specialized equipment like hot water pressure washers, manufacturer-specific training and certifications can be particularly valuable. These programs provide in-depth knowledge of the equipment's operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting procedures.
Real-World Career Paths
The ability to understand and work with electrical schematics opens doors to various career paths within the HVAC industry. Here are a few examples:
- HVAC Service Technician: Diagnosing and repairing a wide range of HVAC equipment, including hot water pressure washers used in commercial settings.
- Industrial Maintenance Technician: Maintaining and repairing HVAC and other industrial equipment in manufacturing plants, warehouses, and other facilities.
- HVAC Controls Technician: Specializing in the installation, programming, and maintenance of building automation systems (BAS) and other control systems.
- HVAC Project Manager: Overseeing the installation and commissioning of HVAC systems in new construction or renovation projects.
- HVAC Sales Engineer: Providing technical support to customers and selling HVAC equipment and services.
Consider a technician who starts as an apprentice, learns the fundamentals of HVAC systems, and then specializes in industrial maintenance. With experience and additional training, they could become a lead technician responsible for overseeing the maintenance and repair of all HVAC and related equipment in a large manufacturing facility. Their expertise in reading and interpreting electrical schematics would be crucial for diagnosing complex electrical faults and ensuring the reliable operation of critical equipment.
Troubleshooting with Wiring Diagrams: A Practical Approach
When troubleshooting a hot water pressure washer using a wiring diagram, follow these steps:
- Identify the symptom: What is the machine doing (or not doing)? Is it not heating, not pumping, or tripping a circuit breaker?
- Consult the wiring diagram: Locate the relevant circuit based on the symptom. For example, if the machine is not heating, focus on the burner control circuit or the heating element circuit.
- Use a multimeter: Check for voltage and continuity at various points in the circuit. Compare your readings to the expected values based on the diagram.
- Isolate the fault: By systematically checking components and wiring, you can narrow down the source of the problem.
- Replace the faulty component: Once you have identified the faulty component, replace it with a new one of the correct specifications.
- Test the repair: After replacing the component, test the machine to ensure that the problem has been resolved.
Safety is paramount when working with electrical systems. Always disconnect power before working on any electrical components, and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses and insulated gloves. It’s best to consult with a certified electrician if you are not comfortable or are unsure of the process.
Conclusion
Hot water pressure washer wiring diagrams are essential tools for HVAC technicians working with this type of equipment. A solid understanding of these diagrams, combined with strong electrical troubleshooting skills, can lead to rewarding career opportunities and higher earning potential. By investing in education, training, and certifications, technicians can position themselves for success in the growing HVAC industry.
For employers, hiring technicians with these skills ensures that equipment is properly maintained and repaired, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. By providing ongoing training and development opportunities, employers can cultivate a skilled workforce that can meet the challenges of the evolving HVAC landscape. This includes proper training in handling refrigerants in compliance with EPA 608 regulations.