How Do Quartz Heaters Work
Frequently Asked Questions About Quartz Heaters
Quartz heaters are a popular choice for providing supplemental heating in homes, offices, and workshops. They offer several advantages, including quick heating, portability, and energy efficiency. But how do they actually work? This FAQ answers common questions about quartz heater technology, helping you understand how they operate and whether they're the right choice for your heating needs.
Q: What exactly *is* a quartz heater, and how does it differ from other types of heaters?
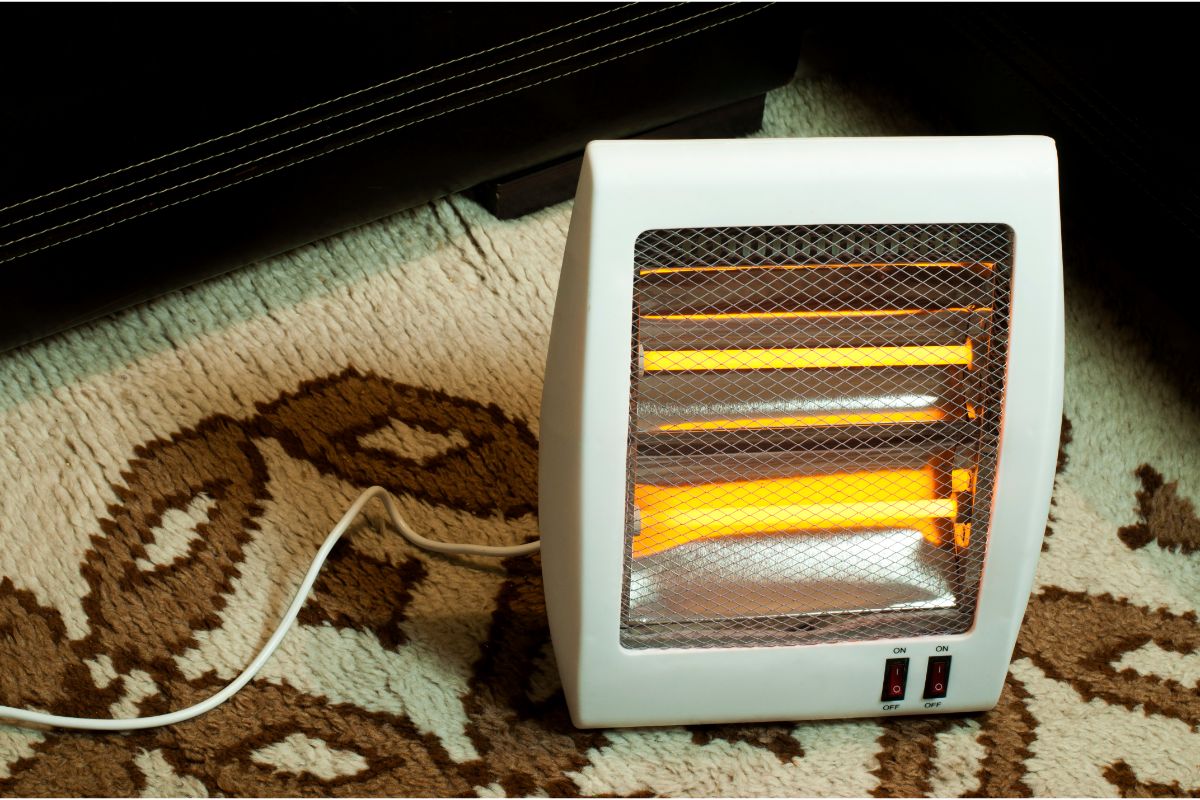
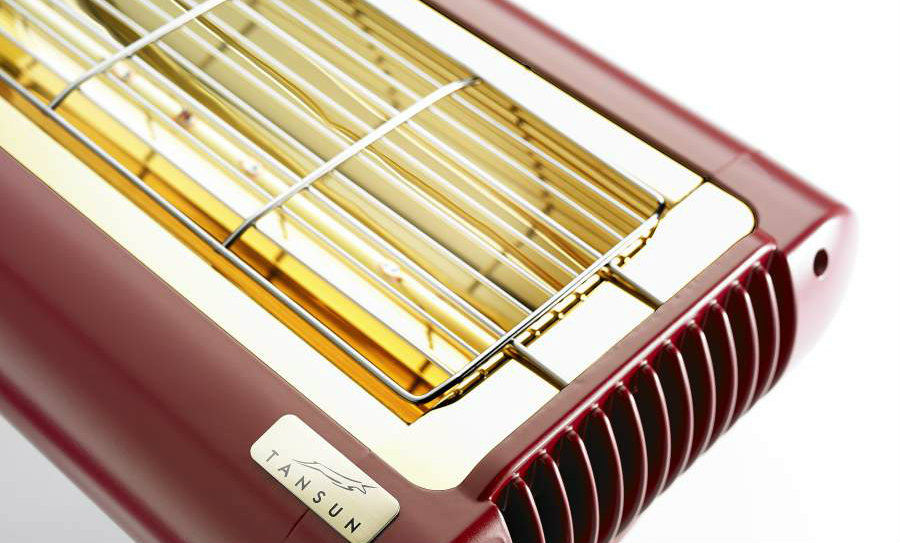
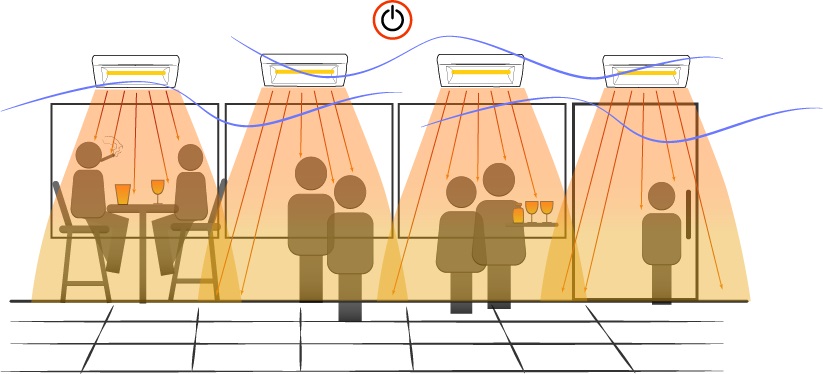
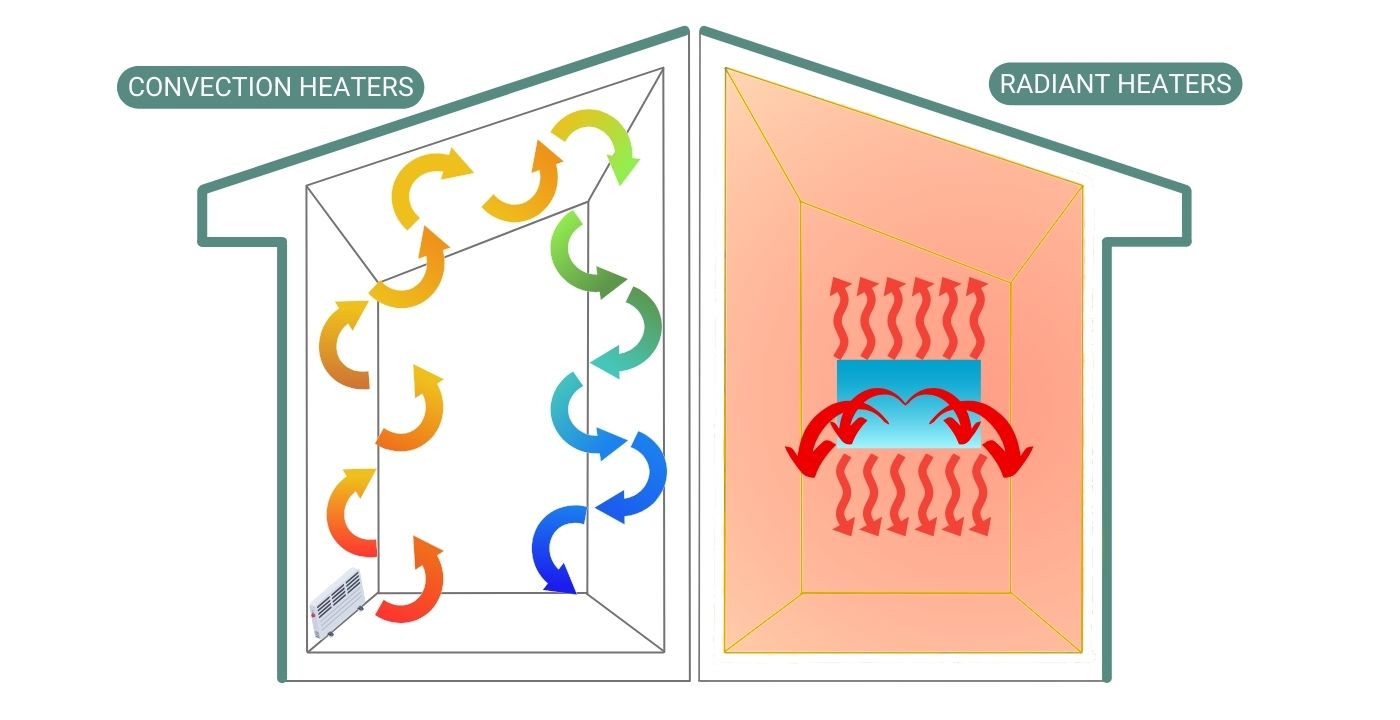
A quartz heater is a type of radiant heater. Unlike convection heaters that warm the air, quartz heaters directly heat objects and people within their line of sight. The core of a quartz heater consists of heating elements encased in quartz glass tubes. When electricity flows through these elements, they heat up and emit infrared radiation. These infrared rays then warm the surfaces they strike, providing a comfortable and efficient heating experience. The key difference lies in how the heat is transferred: directly to objects (radiant) vs. heating the air (convection).
Here's a brief comparison:
- Quartz Heater: Radiant heat, heats objects directly, quick heat-up, efficient for localized heating.
- Convection Heater (e.g., Fan Heater, Oil-Filled Radiator): Heats the air, slower heat-up, effective for heating entire rooms, can dry out the air.
- Ceramic Heater: Can be radiant or convection, generally energy-efficient, good for smaller spaces.
Q: How do the quartz heating elements work? What's special about quartz?
The heating elements inside a quartz heater are typically made of a nichrome (nickel-chromium alloy) or tungsten wire coil. These materials have a high electrical resistance. When electricity passes through them, this resistance causes the wire to heat up intensely. This is similar to how a light bulb filament glows. The wire is designed to withstand high temperatures without melting or degrading quickly.
The quartz glass tube surrounding the heating element plays a crucial role. Quartz is highly transparent to infrared radiation. This means that the heat emitted by the heating element can easily pass through the quartz without being absorbed or blocked. Quartz is also very heat-resistant, capable of withstanding the high temperatures generated by the heating element without cracking or melting. This ensures that the heat is efficiently transmitted outwards, warming the room and objects within it.
In summary:
- Heating Element (Nichrome/Tungsten): Generates heat due to electrical resistance.
- Quartz Tube: Allows infrared radiation to pass through efficiently and withstands high temperatures.
Q: Are quartz heaters energy-efficient? How much will it cost to run one?
Quartz heaters can be quite energy-efficient, especially for localized heating. Because they directly heat objects and people, they don't waste energy heating the entire room if you only need warmth in a specific area. This targeted heating can lead to significant energy savings compared to convection heaters that heat the entire volume of air.
However, the actual cost to run a quartz heater depends on several factors:
- Wattage of the Heater: Higher wattage means more power consumption. Check the heater's label for its wattage rating (e.g., 1500W).
- Electricity Rate: The price you pay per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity varies depending on your location and energy provider. Check your electricity bill for this information.
- Usage Time: How many hours per day do you use the heater?
To calculate the approximate cost per hour, use the following formula:
(Wattage / 1000) x Electricity Rate (per kWh) = Cost per Hour
For example, if you have a 1500W quartz heater and your electricity rate is $0.15 per kWh:
(1500 / 1000) x $0.15 = $0.225 per hour
Therefore, it would cost approximately $0.225 to run the heater for one hour.
To maximize energy efficiency, consider these tips:
- Use the heater only when and where needed.
- Choose a heater with adjustable wattage settings.
- Keep the heater clean to ensure optimal performance.
- Consider using a timer to automatically turn the heater off.
Q: Are quartz heaters safe to use? What safety precautions should I take?
Quartz heaters are generally safe to use when handled correctly and with appropriate precautions. However, like any heating appliance, they can pose safety risks if misused. Always read and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
Here are some essential safety precautions:
- Keep Flammable Materials Away: Never place the heater near flammable materials such as curtains, furniture, bedding, or paper. Maintain a safe distance of at least 3 feet (1 meter) to prevent fires.
- Never Cover the Heater: Covering the heater can cause it to overheat and potentially start a fire.
- Use on a Stable Surface: Place the heater on a level, stable surface to prevent it from tipping over.
- Do Not Use in Wet Areas: Avoid using quartz heaters in bathrooms, laundry rooms, or other damp areas where they could come into contact with water. This poses a serious electrocution risk.
- Unplug When Not in Use: When the heater is not in use, unplug it from the power outlet.
- Inspect the Power Cord: Regularly inspect the power cord for any signs of damage, such as fraying or cracking. If the cord is damaged, do not use the heater and have it repaired or replaced by a qualified technician.
- Keep Away from Children and Pets: Quartz heaters can get very hot to the touch. Keep children and pets away from the heater to prevent burns. Consider using a heater with a safety grill.
- Never Leave Unattended: Do not leave the heater unattended while it is in operation.
- Use a Working Smoke Detector: Ensure that you have a working smoke detector installed in the area where you are using the heater. Test the smoke detector regularly.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Do not plug the heater into the same circuit as other high-wattage appliances. This can overload the circuit and potentially cause a fire.
By following these safety guidelines, you can minimize the risks associated with using a quartz heater and enjoy its benefits safely.
Q: What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a quartz heater?
Like any heating system, quartz heaters have their pros and cons. Understanding these can help you decide if they are the right choice for your needs.
Advantages:
- Rapid Heating: Quartz heaters heat up very quickly, providing almost instant warmth.
- Efficient Localized Heating: They are very effective for heating a specific area or person, making them ideal for spot heating.
- Portability: Many quartz heaters are lightweight and portable, allowing you to easily move them from room to room.
- Relatively Inexpensive: Quartz heaters are generally less expensive to purchase than other types of heating systems.
- Quiet Operation: They operate silently, without the noise of fans or blowers.
- No Air Circulation: Unlike fan-forced heaters, they don't circulate dust or allergens in the air.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Heating Range: They are most effective for heating objects and people directly in front of them. Their heating range is limited.
- Potential Burn Hazard: The surface of the heater can get very hot, posing a burn risk if touched.
- Not Suitable for Large Rooms: They are not ideal for heating large, open spaces as their heating power is localized.
- Can Be Drying: Radiant heat can sometimes feel drying to the skin, although less so than convection heaters.
- Requires Direct Line of Sight: Objects blocking the heater will prevent the heat from reaching you.
Q: How do I maintain my quartz heater to ensure it lasts longer?
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your quartz heater and ensure it operates efficiently. Here are some key maintenance tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Dust and debris can accumulate on the heating elements and reflector, reducing their efficiency. Regularly clean the heater with a soft, dry cloth. Make sure the heater is unplugged and completely cool before cleaning. You can use a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment to remove dust from hard-to-reach areas.
- Check for Damage: Periodically inspect the heater for any signs of damage, such as cracks in the quartz tubes, frayed power cords, or loose connections. If you notice any damage, do not use the heater and have it repaired or replaced by a qualified technician.
- Proper Storage: When storing the heater, keep it in a dry, dust-free place. Avoid storing it in areas where it could be exposed to extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: As mentioned earlier, avoid plugging the heater into the same circuit as other high-wattage appliances. This can strain the electrical system and potentially damage the heater.
- Professional Inspection: Consider having the heater professionally inspected every few years, especially if you use it frequently. A qualified technician can identify and address any potential problems before they become major issues.
- Replacing Heating Elements (If Possible): While not always possible, some quartz heaters allow for the replacement of the heating elements. If your heater stops working and you suspect a faulty element, check the manufacturer's instructions to see if replacement is an option.
By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your quartz heater in good working condition and enjoy its warmth for years to come.