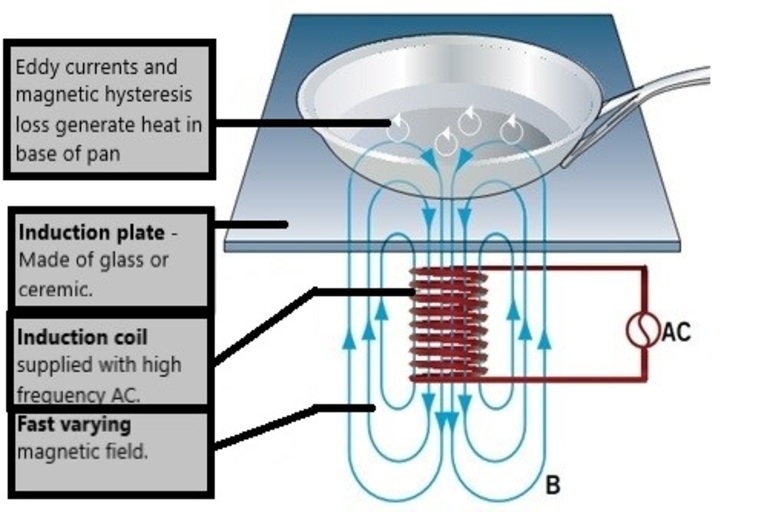
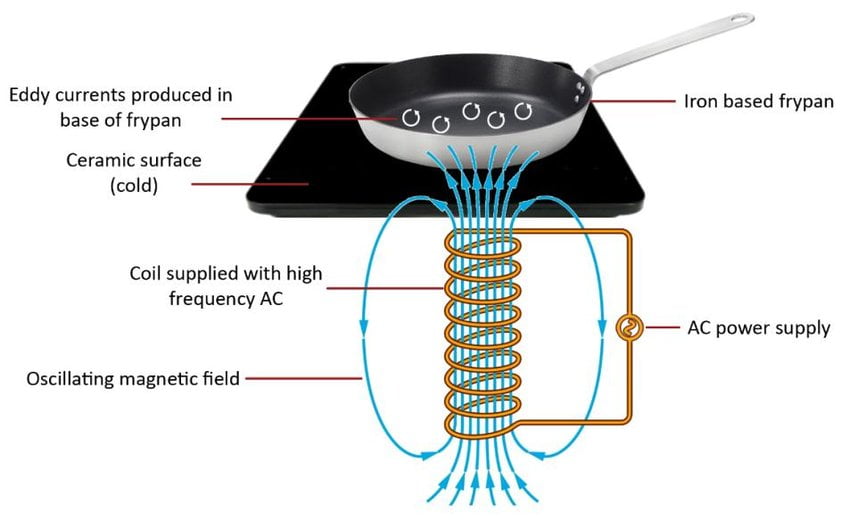
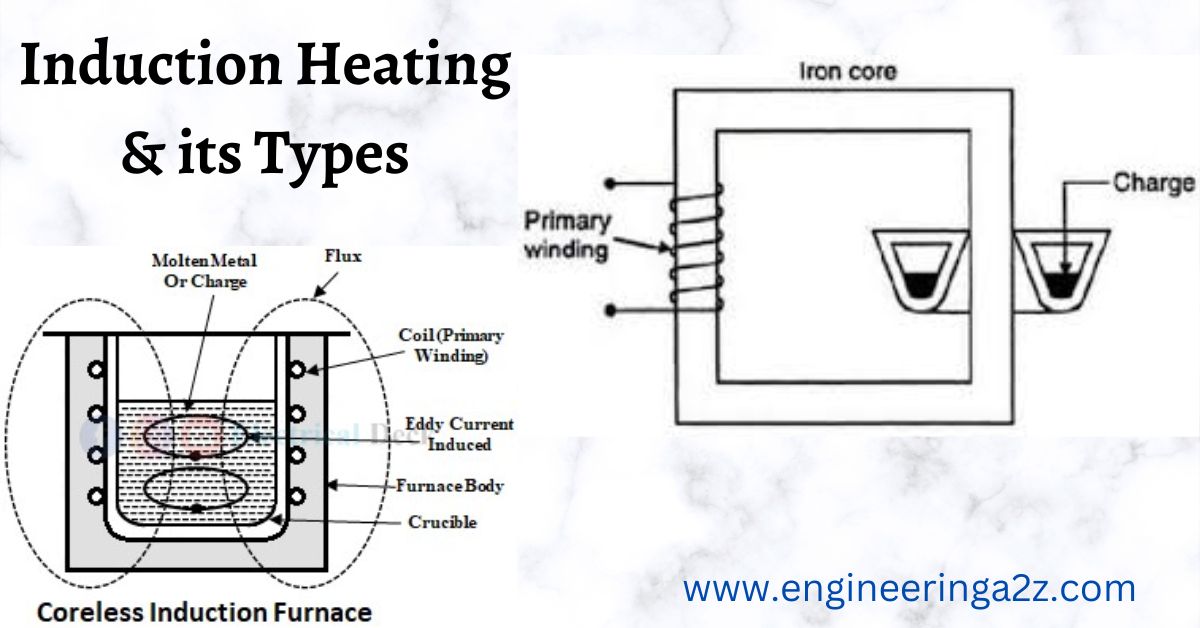
How Does An Induction Fan Work

Understanding Induction Fans in HVAC Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
When considering a new heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system, understanding the various components is crucial. One such component, often overlooked, is the induction fan. While it might not be as prominently discussed as the compressor or heat exchanger, the induction fan plays a vital role in the overall efficiency and performance of your system. This guide will delve into the workings of an induction fan, its pros and cons, and its significance in the context of modern HVAC systems.
What is an Induction Fan?
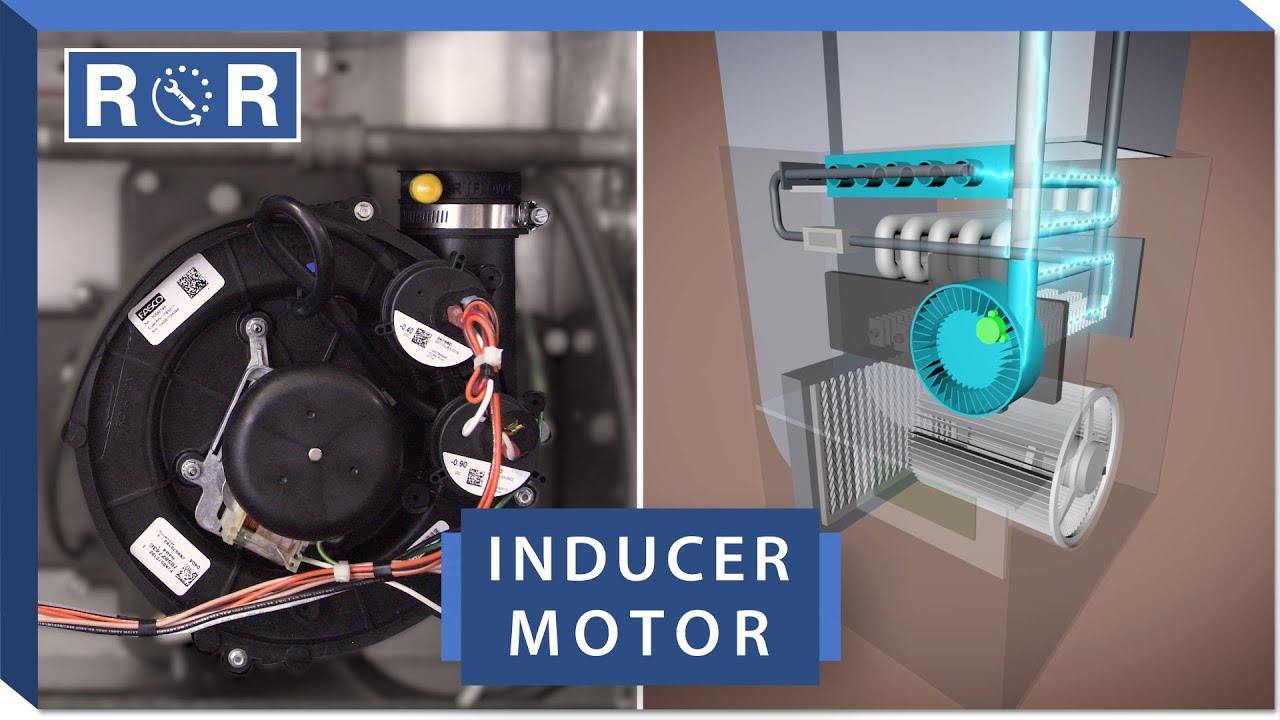
An induction fan, also sometimes referred to as an induced draft fan, is primarily used in heating systems, specifically furnaces. Its primary function is to draw combustion gases out of the heat exchanger and expel them safely through the flue pipe to the outdoors. It ensures that harmful gases like carbon monoxide don't backdraft into your home, maintaining a safe and healthy environment. Think of it as the exhaust system for your furnace.
Unlike older furnaces that relied on natural draft, which depended on the buoyancy of hot gases to rise and exit the flue, modern high-efficiency furnaces utilize induction fans for a more controlled and reliable exhaust process. This controlled process is essential for achieving higher AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) ratings.
How Does an Induction Fan Work?
The functionality of an induction fan is relatively straightforward, though understanding the underlying principles helps appreciate its importance:
- Combustion Process: The furnace initiates the combustion process, burning fuel (natural gas, propane, or oil) to generate heat. This combustion takes place within the heat exchanger.
- Gas Collection: The combustion process produces exhaust gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen. These gases need to be safely removed from the furnace and vented outside.
- Induction Fan Activation: The furnace control board activates the induction fan motor. This usually occurs before the main burner ignites, ensuring the system is properly vented before combustion begins.
- Draft Creation: The induction fan, as its name suggests, *induces* a draft. It creates negative pressure within the heat exchanger, effectively pulling the exhaust gases through the heat exchanger and into the flue pipe.
- Exhaust Venting: The fan forces the exhaust gases through the flue pipe and vents them outside the home, preventing backdrafting and ensuring safe operation.
- Safety Measures: Many systems include pressure switches that monitor the draft created by the induction fan. If the draft is insufficient (indicating a blockage or fan malfunction), the pressure switch will shut down the furnace to prevent the release of harmful gases.
Key Components of an Induction Fan System
- Motor: The electric motor is the heart of the induction fan, providing the rotational force to drive the fan blades. These motors are typically small, but robust, designed for continuous operation during heating cycles.
- Fan Blades: The fan blades are designed to efficiently move air. They are usually made of metal or durable plastic, shaped to maximize airflow and minimize noise.
- Housing: The housing encases the motor and fan blades, providing structural support and directing the airflow.
- Pressure Switch: This crucial safety component monitors the pressure within the exhaust system. If the pressure falls below a certain threshold, the switch shuts down the furnace.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Induction Fans
Like any mechanical component, induction fans have their advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Enhanced Safety: The primary advantage is improved safety by actively preventing backdrafting of combustion gases, particularly carbon monoxide.
- Increased Efficiency: Induction fans are essential for high-efficiency furnaces. By ensuring proper venting, they allow for more complete combustion and heat extraction, leading to higher AFUE ratings.
- Consistent Performance: Unlike natural draft systems, induction fans provide a consistent and reliable draft, regardless of external weather conditions.
- Compact Design: Allows for more compact furnace designs.
Cons:
- Noise: Induction fans can generate noise during operation, although modern designs are significantly quieter than older models.
- Maintenance: Like any mechanical component, induction fans require occasional maintenance, such as cleaning and lubrication.
- Potential for Failure: The motor or fan blades can fail over time, requiring replacement.
- Energy Consumption: Although relatively low, induction fans consume electricity to operate, contributing to overall energy costs.
Induction Fans and HVAC Efficiency Ratings
The presence and proper functioning of an induction fan are directly linked to the efficiency ratings of a furnace. Furnaces with induction fans can achieve higher AFUE ratings because they control the combustion process more precisely. A higher AFUE rating means the furnace converts a greater percentage of fuel into usable heat, resulting in lower energy bills.
While induction fans don't directly impact SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) or HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor), which are metrics for air conditioners and heat pumps respectively, they are a crucial component for achieving high heating efficiency in furnaces that might be paired with these cooling systems.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliable operation of your induction fan. Here are some key maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections by a qualified HVAC technician to check the condition of the fan, motor, and pressure switch.
- Cleaning: Keep the fan blades and housing clean to prevent dust and debris buildup, which can reduce airflow and strain the motor.
- Lubrication: Lubricate the motor bearings as needed, following the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Flue Pipe Inspection: Regularly inspect the flue pipe for any blockages or damage, as these can affect the fan's performance.
Common Troubleshooting Issues
- Noisy Operation: A noisy induction fan can indicate worn bearings, loose blades, or a failing motor.
- Furnace Shut-Down: If the furnace shuts down frequently, it could be due to a faulty pressure switch or a malfunctioning induction fan.
- Visible Rust or Corrosion: Rust or corrosion on the fan or housing can indicate moisture problems and potential failure.
- Weak Draft: A weak draft can be caused by a blocked flue pipe or a failing fan.
If you experience any of these issues, it's best to consult a qualified HVAC technician for diagnosis and repair. Attempting to repair the induction fan yourself can be dangerous and may void your warranty.
Induction Fans in Different HVAC Brands and Models
Virtually all modern, high-efficiency furnaces utilize induction fans. Specific models and brands may vary slightly in design and performance, but the fundamental principle remains the same. When comparing furnace models, focus on the AFUE rating as a primary indicator of heating efficiency.
Here's a brief overview of how induction fans are incorporated in some popular HVAC brands:
- Carrier: Carrier furnaces often feature variable-speed induction fans that adjust their speed based on heating demand, further enhancing efficiency and reducing noise.
- Trane: Trane furnaces are known for their robust construction and reliable induction fan motors.
- Lennox: Lennox offers a range of furnaces with advanced combustion technology, which are complemented by efficient induction fans.
- Goodman: Goodman furnaces provide a cost-effective option with reliable induction fan performance.
When selecting a new furnace, be sure to review the manufacturer's specifications and warranty information for the induction fan and other key components.
Warranties and Maintenance Contracts
Furnace warranties typically cover the induction fan and other components for a specified period. Standard warranties often cover parts for 5-10 years, while extended warranties may offer even longer coverage. Read the warranty terms carefully to understand what is covered and what is not.
Consider purchasing a maintenance contract with a reputable HVAC company. These contracts typically include regular inspections, cleaning, and maintenance services, which can help extend the life of your induction fan and other components.
Cost Considerations
The cost of a new induction fan can vary depending on the brand, model, and complexity of the system. Replacement costs can range from $200 to $600, including parts and labor. Factors influencing the price include the motor type, fan blade material, and installation complexity.
While replacing an induction fan may seem costly, it's important to consider the long-term benefits of a properly functioning system, including improved safety, enhanced efficiency, and reduced energy bills.
Conclusion
The induction fan is a vital component of modern, high-efficiency furnaces. By understanding how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and its maintenance requirements, you can make informed decisions when selecting a new HVAC system. Prioritizing safety, efficiency, and reliability will ensure a comfortable and healthy home environment for years to come.
Remember to consult with a qualified HVAC professional for personalized advice and recommendations tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. They can help you choose the right furnace and induction fan system to optimize your home's heating performance and efficiency.
When comparing HVAC systems, always check the AFUE ratings to find the most efficient and cost-effective option for your home. Don't underestimate the importance of regular maintenance to keep your system running smoothly and safely.