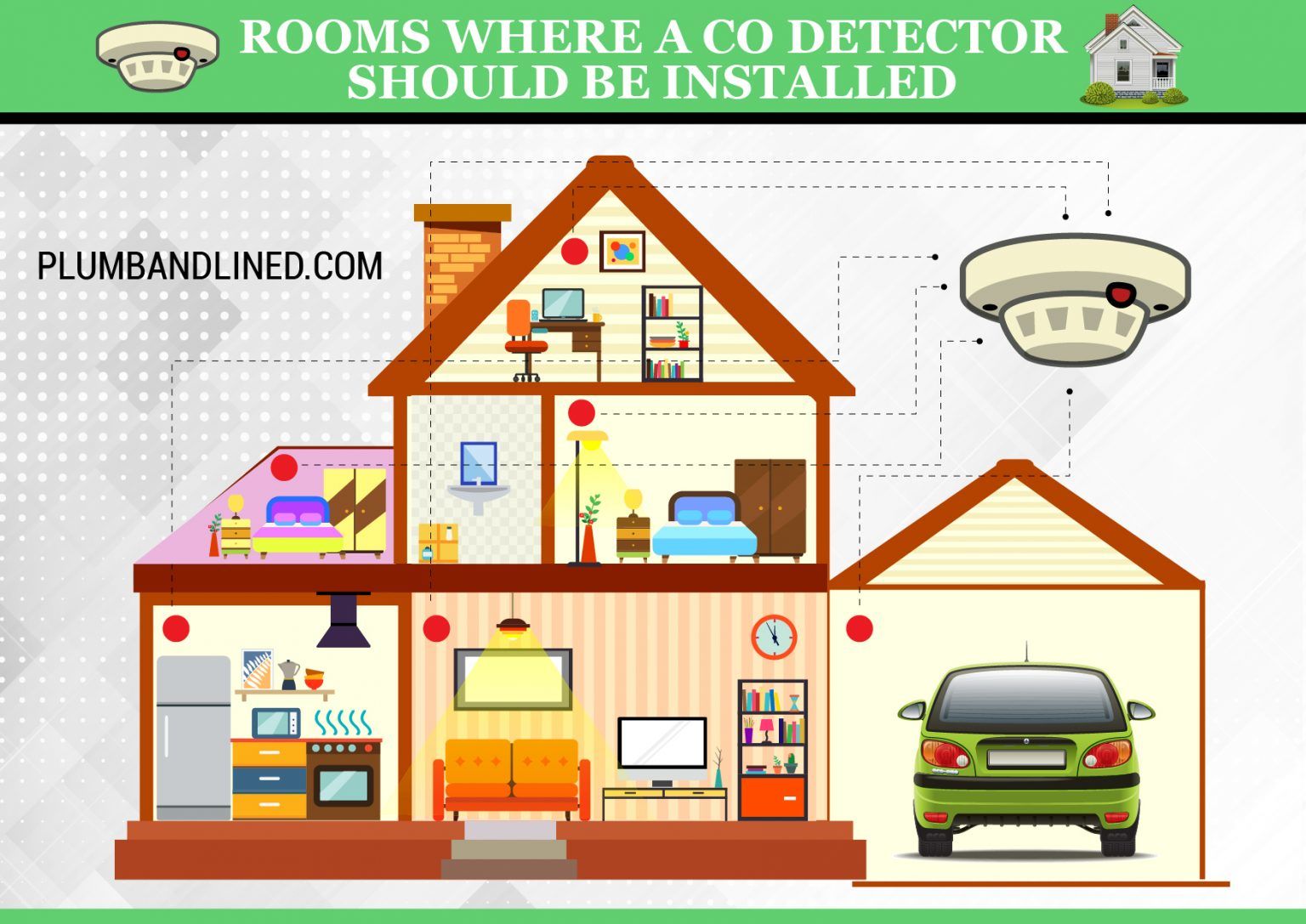
How High Should A Co Detector Be Mounted

Carbon monoxide (CO) is a silent killer. As an HVAC professional, understanding how to advise your clients on proper CO detector placement is not just good service, it's a matter of life and death. Correct installation is paramount, and it’s a topic that comes up frequently, whether you're just starting out, looking to add to your skills, or running an HVAC business. This article will cover the recommended mounting heights, explore the reasons behind them, and touch on related aspects of the HVAC industry, including career paths, certifications, and current trends.
The Importance of Proper CO Detector Placement
Before diving into the specifics, let's reinforce why proper CO detector placement is crucial. CO is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas produced by incomplete combustion. Common sources include furnaces, water heaters, gas stoves, fireplaces, and even vehicles left running in attached garages. Symptoms of CO poisoning can mimic the flu, making it easily overlooked until it’s too late. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), unintentional CO poisoning leads to thousands of emergency room visits and hundreds of deaths annually in the United States. A properly placed CO detector offers an early warning, allowing occupants to evacuate and seek medical attention.
Recommended Mounting Height: Finding the Sweet Spot
The question of how high to mount a CO detector isn’t always straightforward. While some sources recommend installing CO detectors near the ceiling, others advocate for lower placement, at about head height. The answer depends on understanding the dynamics of CO within a room and adhering to manufacturer's instructions.
Why Consider Ceiling Mounting?
Historically, the recommendation for ceiling placement stemmed from the belief that CO is lighter than air and would therefore rise. While this concept persists, it's not entirely accurate. CO has a density very close to that of air, and its movement is more influenced by factors like temperature and air currents.
However, ceiling placement can still be advantageous in certain situations. Specifically:
- Reduced Tampering: Higher placement reduces the likelihood of accidental bumps or tampering, especially in homes with children or pets.
- Avoiding Obstructions: A high location can help prevent the detector from being blocked by furniture or other objects.
Why Consider Lower Mounting (Head Height)?
The more modern and generally accepted recommendation is to install CO detectors at approximately head height, typically between 5 and 6 feet (1.5 to 1.8 meters) from the floor. Here's why:
- Optimal Breathing Zone: CO detectors placed at head height are more likely to detect CO concentrations at the level where people are breathing. This provides the earliest possible warning to occupants.
- Consistent Detection: Because CO mixes relatively evenly with air under most conditions, detectors at head height are effective regardless of whether the CO is rising or falling due to temperature differentials.
- Accessibility: Lower placement makes it easier to test and maintain the detector, including replacing batteries.
The Bottom Line: Follow Manufacturer's Instructions
The most important guidance is always to consult and adhere to the manufacturer's instructions included with the specific CO detector model. Different detectors may have slightly different sensor technologies and therefore different optimal placement recommendations. Some detectors are designed to be placed on the ceiling, while others are specifically intended for wall mounting at head height. Ignoring these instructions can significantly compromise the detector's effectiveness.
Additional Considerations for CO Detector Placement
Beyond the height, several other factors impact the effectiveness of CO detectors:
- Placement Near Sleeping Areas: CO detectors should be installed in or near sleeping areas to ensure occupants are alerted even when asleep.
- Avoidance of Obstructions: Do not place detectors behind curtains, furniture, or other obstructions that could block airflow to the sensor.
- Distance from Fuel-Burning Appliances: Keep detectors at least 10 feet (3 meters) away from fuel-burning appliances like furnaces, water heaters, and stoves. This prevents nuisance alarms caused by temporary CO spikes during appliance startup.
- Avoidance of Humid Areas: Do not install detectors in bathrooms or laundry rooms, where high humidity can damage the sensor.
- Regular Testing and Maintenance: CO detectors should be tested regularly (usually monthly) to ensure they are functioning properly. Batteries should be replaced at least once a year, or as recommended by the manufacturer.
HVAC Career Paths and the Importance of Safety Knowledge
The ability to correctly install and advise on CO detectors is just one aspect of a successful HVAC career. The HVAC industry offers a wide range of career paths, from entry-level technician positions to specialized roles like HVAC design engineers and project managers.
Entry-Level Technicians and Apprenticeships
Many people start their HVAC careers as apprentices, learning the trade under the guidance of experienced technicians. Apprenticeships typically involve on-the-job training combined with classroom instruction. Starting salaries for HVAC apprentices can range from $30,000 to $40,000 per year. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects about 5% growth for HVAC mechanics and installers over the next ten years.
Experienced Technicians and Specialization
As technicians gain experience, they can specialize in specific areas, such as:
- Residential HVAC: Focusing on the installation, maintenance, and repair of HVAC systems in homes.
- Commercial HVAC: Working on larger and more complex HVAC systems in office buildings, hospitals, and other commercial properties.
- Refrigeration: Specializing in the installation and maintenance of refrigeration systems, such as those used in supermarkets and food processing plants.
- Building Automation Systems (BAS): Programming and maintaining the computerized control systems that manage HVAC equipment in large buildings.
Experienced HVAC technicians can earn salaries ranging from $50,000 to $80,000 per year or more, depending on their specialization and location. Highly skilled technicians in high-demand areas can even command six-figure salaries.
Certifications and Professional Development
Certifications are highly valued in the HVAC industry and can significantly enhance career prospects and earning potential. Some of the most common and respected certifications include:
- NATE (North American Technician Excellence): NATE certification demonstrates a technician's knowledge and skills in HVAC installation, maintenance, and repair.
- EPA 608 Certification: Required by the EPA for technicians who handle refrigerants.
- HVAC Excellence: Offers a range of certifications for HVAC technicians at different skill levels.
- Manufacturer-Specific Certifications: Many HVAC equipment manufacturers offer certifications for technicians who are trained on their specific products.
Ongoing professional development is also essential for staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and industry best practices. This can include attending workshops, conferences, and online training courses.
Employers and the Need for Skilled Workers
HVAC employers are constantly seeking skilled and qualified workers to meet the growing demand for HVAC services. Companies value technicians who possess not only technical skills but also strong communication and customer service skills. Employers also prioritize safety knowledge, including the proper installation and maintenance of CO detectors. Investing in employee training and development is crucial for attracting and retaining top talent in the competitive HVAC job market.
Hiring managers often look for candidates who:
- Possess relevant certifications (NATE, EPA 608)
- Have a strong understanding of HVAC systems and components
- Demonstrate excellent troubleshooting and problem-solving skills
- Prioritize safety and adhere to industry best practices
HVAC Industry Trends
The HVAC industry is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as technological advancements, energy efficiency concerns, and changing building codes. Some of the key trends shaping the industry include:
- Smart HVAC Systems: The increasing adoption of smart thermostats, sensors, and connected HVAC equipment that can be controlled remotely and optimized for energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Growing demand for high-efficiency HVAC systems that reduce energy consumption and lower carbon emissions. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar thermal and geothermal.
- Refrigerant Regulations: Phasing out of older refrigerants with high global warming potential (GWP) and the adoption of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
- Indoor Air Quality (IAQ): Increased awareness of the importance of IAQ and the role of HVAC systems in maintaining healthy indoor environments. This includes the use of air purifiers, filters, and ventilation systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the proper mounting height and other considerations for CO detectors is an essential skill for any HVAC professional. By following manufacturer's instructions and adhering to industry best practices, you can help protect your clients from the dangers of CO poisoning. This knowledge, combined with relevant certifications and ongoing professional development, will position you for success in the dynamic and rewarding HVAC industry. Remember, proper CO detector installation isn’t just a job – it's a crucial safety service.