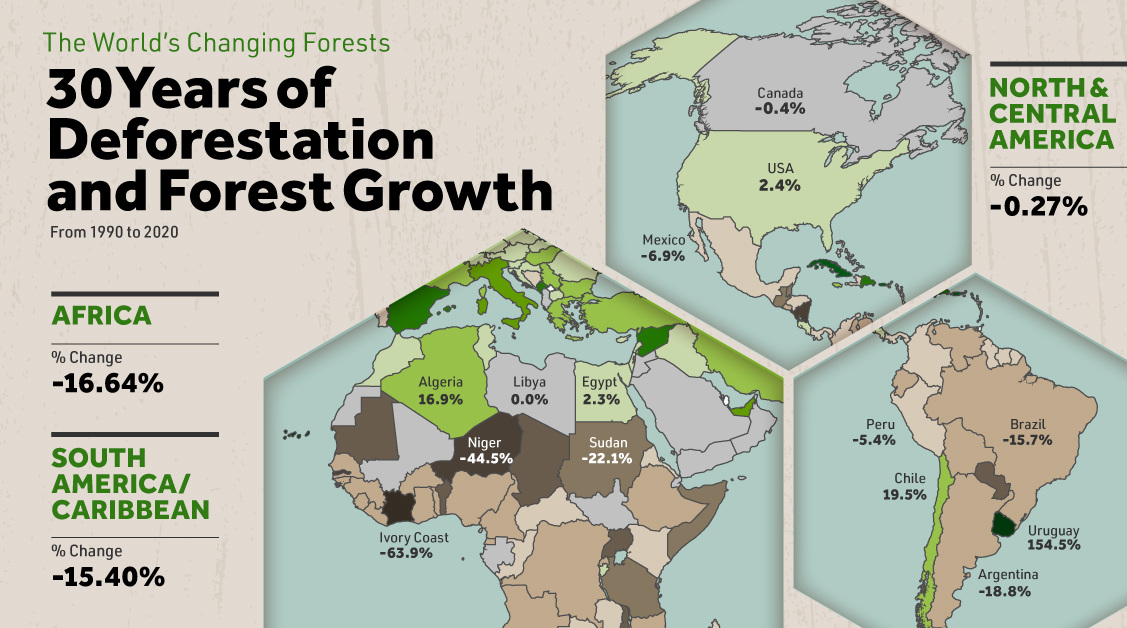
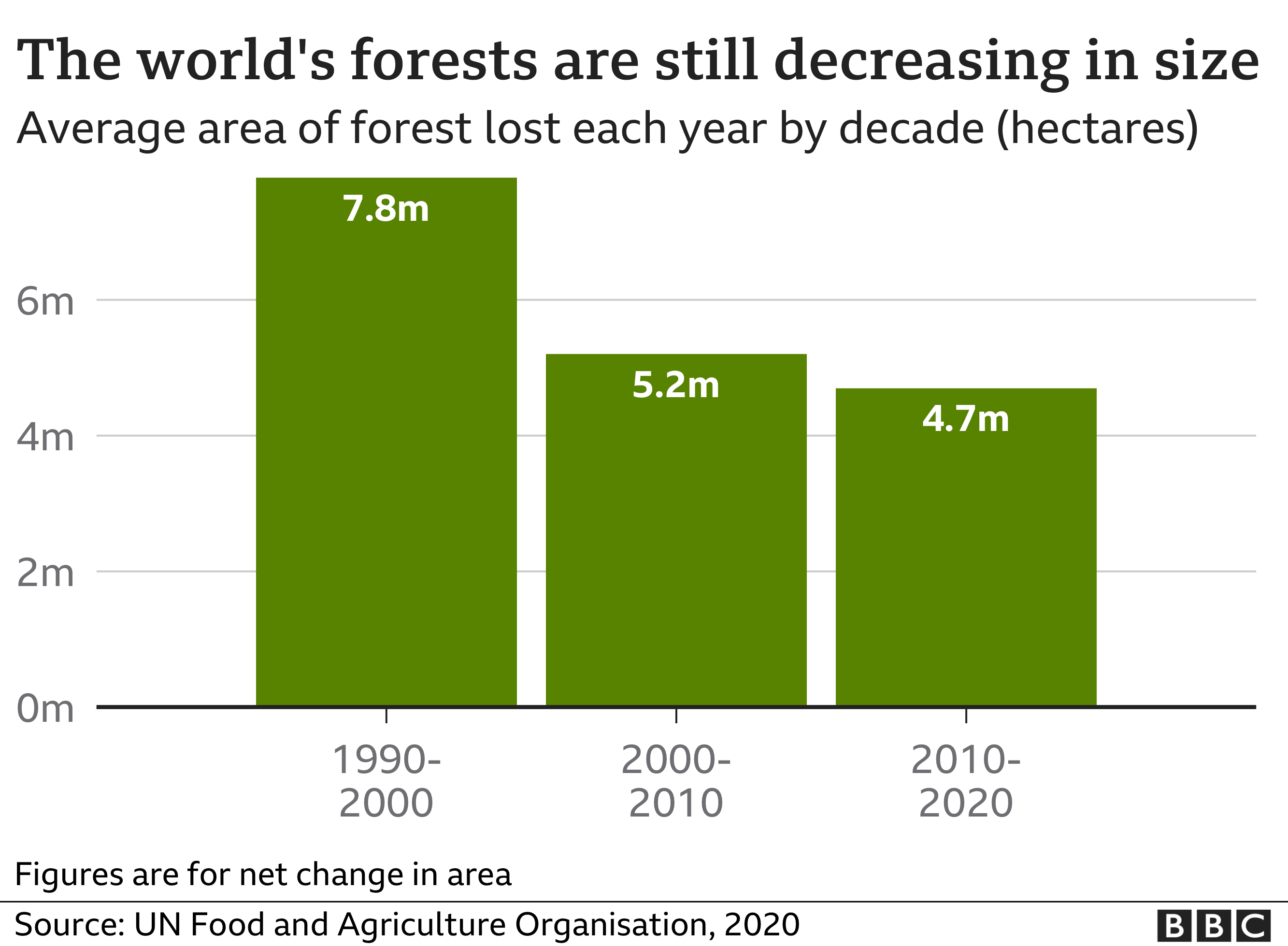
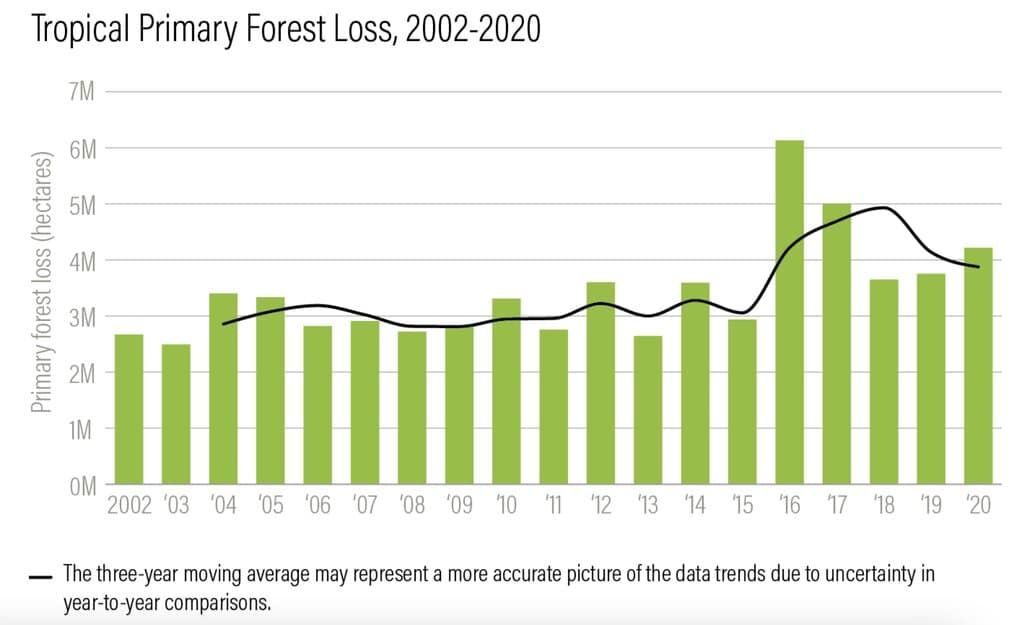
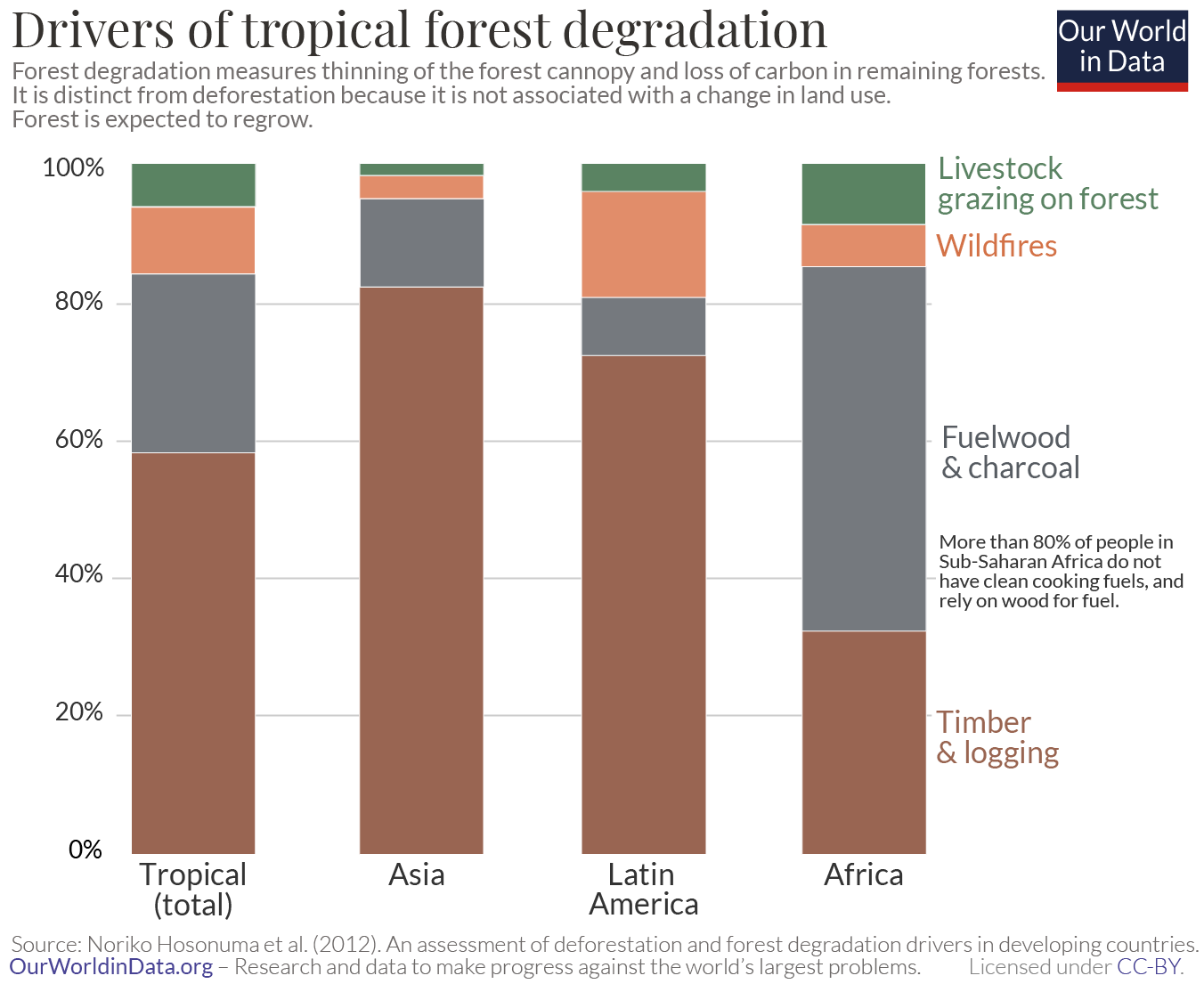
How Is Deforestation Affecting The World

Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses, is a pervasive global issue with far-reaching consequences. It's not just about losing trees; it's about disrupting ecosystems, contributing to climate change, and impacting the livelihoods of millions. Understanding the complexities of deforestation is crucial for making informed decisions and supporting sustainable practices.
What is Deforestation?
Deforestation essentially means the permanent removal of forests to make way for something else. This "something else" can include agriculture (farming and livestock grazing), urbanization (cities and infrastructure), mining, logging, and even the construction of dams. The key is the *permanent* nature of the removal. While sustainable logging practices aim to replant trees and maintain forest cover, deforestation results in a long-term loss.
Think of it like this: Imagine a vibrant city park, full of trees, plants, and animals. Deforestation is like bulldozing that park to build a parking lot. The green space is gone, and the ecological benefits it provided disappear with it.
The Major Drivers of Deforestation
Several factors contribute to deforestation, often working in complex and interconnected ways.
Agriculture: The Primary Culprit
Agriculture is the leading cause of deforestation worldwide. As the global population grows, so does the demand for food. This drives the expansion of farmland, often at the expense of forests. Large-scale agriculture, particularly for commodities like beef, soybeans, palm oil, and coffee, is a major driver.
Consider the Amazon rainforest. Vast swathes of it have been cleared for cattle ranching and soybean cultivation. The pressure to produce more food at lower costs often leads to unsustainable land-use practices.
Logging: For Timber and Paper
The demand for timber for construction, furniture, and paper products contributes significantly to deforestation. Illegal logging, in particular, poses a serious threat, as it often lacks any sustainability considerations.
Think about the wood used to build your house or the paper you use every day. A portion of that likely came from a forest, and if that forest wasn't managed responsibly, it could be a product of deforestation.
Mining: Digging Deep for Resources
Mining operations, especially for minerals and fossil fuels, require clearing large areas of forest to access the underlying resources. The process often involves not only removing trees but also disrupting soil, polluting water sources, and fragmenting habitats.
Imagine a gold mine carved into a mountainside. The scale of such an operation necessitates the removal of vast amounts of vegetation, leaving behind a scarred landscape.
Urbanization: The Expanding Footprint of Cities
As cities grow and populations migrate to urban areas, the demand for land increases. Forests are often cleared to make way for housing, roads, and other infrastructure.
Consider the rapid expansion of cities in developing countries. This expansion often comes at the expense of surrounding forests and agricultural land.
Infrastructure Development: Roads, Dams, and Pipelines
The construction of roads, dams, and pipelines can lead to deforestation, both directly (through clearing land for the infrastructure itself) and indirectly (by opening up previously inaccessible areas to further exploitation).
Think about a new highway cutting through a forest. It not only removes trees directly but also provides access for loggers, farmers, and other developers to enter and exploit the area.
The Environmental Impacts of Deforestation
The environmental consequences of deforestation are numerous and far-reaching. They impact the climate, biodiversity, soil, and water resources.
Climate Change: A Significant Contributor
Forests play a crucial role in regulating the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. Deforestation releases this stored carbon back into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. It's estimated that deforestation accounts for a significant percentage of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Imagine a forest as a giant carbon sink, storing CO2. When you cut down the trees, you're essentially unlocking that carbon and releasing it into the atmosphere, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
Biodiversity Loss: A Crisis of Extinction
Forests are home to a vast array of plant and animal species. Deforestation leads to habitat loss, threatening the survival of countless species and contributing to the ongoing biodiversity crisis. Many species are uniquely adapted to specific forest ecosystems, and when those ecosystems disappear, so do the species that depend on them.
Think about a rainforest teeming with life. When that rainforest is cleared, the animals lose their homes, their food sources, and their ability to survive. This can lead to local extinctions and a decline in overall biodiversity.
Soil Erosion and Degradation: Losing Fertile Ground
Forests protect soil from erosion by providing a canopy cover that intercepts rainfall and a root system that anchors the soil in place. Deforestation removes this protection, leading to increased soil erosion, nutrient depletion, and land degradation. This can reduce the productivity of agricultural land and lead to desertification.
Imagine a hillside covered with trees. The trees' roots hold the soil together, preventing it from being washed away by rain. When the trees are removed, the soil is exposed and easily eroded, leading to landslides and loss of fertile topsoil.
Water Cycle Disruption: Affecting Rainfall and Water Availability
Forests play a vital role in the water cycle by absorbing rainfall, releasing water vapor into the atmosphere through transpiration, and regulating streamflow. Deforestation can disrupt this cycle, leading to reduced rainfall, increased drought, and altered river flows. This can have significant impacts on water availability for agriculture, human consumption, and ecosystem health.
Think about a forest acting like a sponge, absorbing rainfall and slowly releasing it into streams and rivers. When the forest is removed, the water runs off quickly, leading to floods and droughts.
Increased Flooding and Landslides: The Loss of Natural Barriers
The removal of forests, particularly on steep slopes, increases the risk of flooding and landslides. Trees and their root systems help to stabilize the soil and absorb excess water. Without this natural protection, heavy rainfall can lead to devastating landslides and flash floods.
Imagine a mountain slope covered with trees. The trees act as a natural barrier, preventing the soil from sliding down the slope. When the trees are removed, the slope becomes unstable, and heavy rainfall can trigger a landslide.
The Socioeconomic Impacts of Deforestation
Deforestation not only affects the environment but also has significant socioeconomic consequences, particularly for local communities that depend on forests for their livelihoods.
Impact on Indigenous Communities: A Loss of Culture and Livelihoods
Many indigenous communities rely on forests for their sustenance, cultural practices, and traditional knowledge. Deforestation can displace these communities, disrupt their way of life, and threaten their cultural survival. They are often the first and most severely affected by deforestation.
Think about indigenous people living in the Amazon rainforest. Their lives are intimately connected to the forest, and its destruction can lead to the loss of their homes, their food sources, and their cultural identity.
Loss of Livelihoods: Reduced Access to Forest Resources
Forests provide a wide range of resources that support local livelihoods, including timber, fuelwood, medicinal plants, and non-timber forest products. Deforestation reduces access to these resources, impacting the income and well-being of forest-dependent communities.
Imagine a village that relies on a nearby forest for firewood, building materials, and food. When the forest is cleared, the villagers lose access to these essential resources, forcing them to find alternative sources of income.
Economic Costs: Loss of Ecosystem Services
Forests provide valuable ecosystem services, such as water purification, climate regulation, and pollination, that contribute to economic productivity. Deforestation degrades these services, leading to economic losses in sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and fisheries.
Think about a forest that filters water, providing clean drinking water for a nearby city. When the forest is cleared, the water becomes polluted, requiring expensive treatment before it can be used. This illustrates the economic cost of losing ecosystem services.
What Can Be Done to Combat Deforestation?
Combating deforestation requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the underlying drivers, promotes sustainable land management, and empowers local communities.
Sustainable Agriculture: Reducing the Pressure on Forests
Promoting sustainable agricultural practices can reduce the need to clear forests for farmland. This includes improving crop yields, adopting agroforestry techniques, and reducing food waste.
Instead of clearing more forest to grow more food, farmers can use more efficient farming methods to produce more food on existing land. This reduces the pressure on forests and helps to ensure food security.
Sustainable Forestry: Managing Forests Responsibly
Implementing sustainable forestry practices can ensure that forests are managed in a way that maintains their ecological integrity and provides long-term economic benefits. This includes selective logging, replanting trees, and protecting biodiversity.
Think about a logging company that carefully selects which trees to cut down, replants trees after harvesting, and protects areas of high biodiversity. This is an example of sustainable forestry.
Protecting Existing Forests: Establishing Protected Areas
Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, can help to conserve forests and protect biodiversity. These areas can serve as refuges for endangered species and provide valuable ecosystem services.
Imagine a national park that protects a vast area of forest from logging, mining, and other destructive activities. This park serves as a haven for wildlife and helps to maintain the ecological integrity of the forest.
Promoting Reforestation and Afforestation: Restoring Degraded Lands
Reforestation (replanting trees in deforested areas) and afforestation (planting trees in areas that were not previously forested) can help to restore degraded lands and increase carbon sequestration.
Think about a community that plants trees on a degraded hillside to prevent soil erosion and restore the forest. This is an example of reforestation.
Strengthening Governance and Law Enforcement: Combating Illegal Logging
Strengthening governance and law enforcement can help to combat illegal logging and other illegal activities that contribute to deforestation. This includes improving monitoring and enforcement capacity, prosecuting offenders, and promoting transparency and accountability.
Imagine a government agency that actively monitors forests for illegal logging, investigates and prosecutes offenders, and works to promote transparency and accountability in the forestry sector. This is an example of good governance.
Consumer Choices: Supporting Sustainable Products
Consumers can play a role in combating deforestation by making informed purchasing decisions and supporting products that are produced sustainably. This includes choosing products that are certified by organizations such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and avoiding products that are linked to deforestation.
When you buy wood or paper products, look for the FSC label. This indicates that the product comes from a sustainably managed forest. By choosing FSC-certified products, you can help to support sustainable forestry practices.
In conclusion, deforestation is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant environmental, social, and economic consequences. By understanding the drivers of deforestation and the impacts it has, we can make informed decisions and support sustainable practices that protect our forests for future generations. It's a collective responsibility that requires action from individuals, governments, and businesses alike. The future of our planet depends on it.