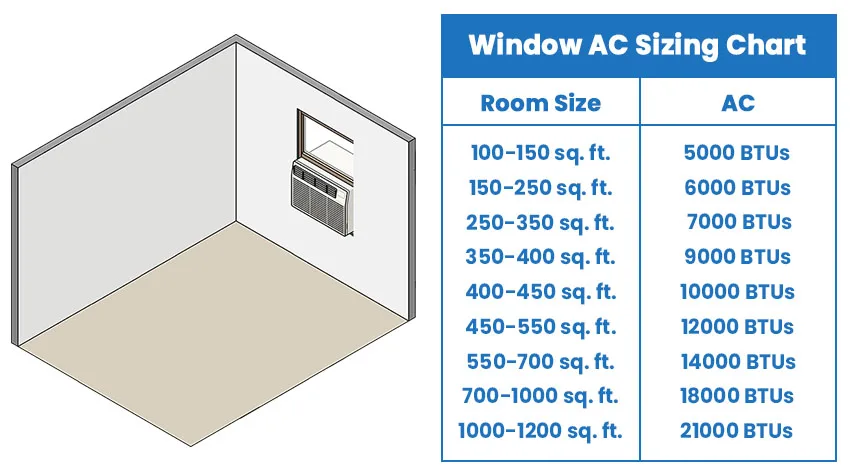
How Many Square Feet Does 9000 Btu Cover

Understanding the coverage area of an air conditioner or heat pump is crucial for efficient climate control. A common question among homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers is: "How many square feet does a 9000 BTU unit cover?" The answer, while seemingly straightforward, depends on several factors. This article will delve into these variables, providing a comprehensive guide to determine the appropriate BTU rating for your specific needs.
Understanding BTU and Its Significance
BTU stands for British Thermal Unit. It's a measurement of energy – specifically, the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In the context of HVAC systems, BTU indicates the cooling or heating capacity of the unit. A higher BTU rating signifies a more powerful system capable of removing or adding more heat per hour.
Think of it this way: a 9000 BTU air conditioner can remove 9000 BTUs of heat from a room every hour. This heat removal process cools the air and makes the space more comfortable. However, a 9000 BTU unit isn't a magic bullet. Its effectiveness is significantly affected by the room's characteristics.
The Rule of Thumb: 400 Square Feet
A general rule of thumb suggests that a 9000 BTU air conditioner is suitable for cooling approximately 400 square feet. This is a good starting point, but it's essential to consider several other factors that can increase or decrease the required BTU capacity.
Factors Influencing BTU Requirements
While the 400 square feet rule provides a baseline, several environmental and structural elements can significantly impact the cooling or heating load of a room. Accounting for these factors ensures you select the right sized unit, preventing energy waste and discomfort.
Climate and Insulation
The climate in which you live plays a crucial role. In hotter climates with longer summers, you'll likely need a higher BTU rating per square foot compared to cooler regions. Proper insulation is also paramount. Well-insulated walls, ceilings, and floors minimize heat transfer, reducing the load on the HVAC system. If your home has poor insulation, you'll need a more powerful unit to compensate for the heat gain (in summer) or heat loss (in winter). Consider the R-value of your insulation. Higher R-values indicate better insulation performance.
Sun Exposure
Rooms with significant sun exposure, particularly those facing south or west, will require more cooling power. Direct sunlight increases the heat load on the space, necessitating a higher BTU rating. The number and size of windows, as well as whether they are energy-efficient (low-E glass), also impact heat gain. Blinds, curtains, or window films can help mitigate this effect.
Ceiling Height
The standard square footage calculation assumes a ceiling height of around 8 feet. If your ceilings are higher, you have a larger volume of air to cool or heat, requiring a more powerful unit. For example, a room that's 400 sqft with 10ft ceilings needs more BTUs compared to 400sqft room with 8ft ceilings.
Number of Occupants
Each person in a room generates heat. A room regularly occupied by multiple people will require a higher BTU rating than a room typically occupied by just one or two individuals. Consider the average number of occupants when determining the appropriate BTU capacity.
Heat-Generating Appliances
Appliances like computers, ovens, stoves, and lighting fixtures generate heat, adding to the cooling load of a room. If you have a room with numerous heat-generating appliances, you'll need a unit with a higher BTU rating. A kitchen, for example, will typically require more cooling power than a bedroom of the same size.
Airflow and Ventilation
Proper airflow and ventilation are crucial for distributing cooled or heated air evenly throughout the space. Obstructions to airflow, such as furniture blocking vents, can reduce the effectiveness of the unit. Consider adding fans to assist in air circulation and ensure proper ventilation to prevent stale air.
Calculating Your Specific BTU Needs
To determine the specific BTU requirements for your space, consider using a BTU calculator available online. These calculators typically ask for information about the square footage, climate, insulation, sun exposure, number of occupants, and heat-generating appliances. Alternatively, you can consult with an HVAC professional who can conduct a load calculation to determine the precise BTU needs of your space.
A simplified calculation method involves starting with the 400 sq ft rule of thumb for 9000 BTU. Then, make adjustments based on the following factors:
- Poor Insulation: Add 10% to the BTU requirement.
- Direct Sunlight: Add 10% to 15% to the BTU requirement.
- More than 2 Occupants: Add 600 BTU per additional person.
- Heat-Generating Appliances: Add 400 BTU per appliance.
For example, if you have a 400 sq ft room with poor insulation and direct sunlight, your adjusted BTU requirement would be: 9000 + (9000 * 0.10) + (9000 * 0.10) = 10,800 BTU. Therefore, a 9000 BTU unit might be insufficient.
The Consequences of Oversizing or Undersizing
Choosing the right size HVAC unit is critical for optimal performance and energy efficiency. Oversizing or undersizing can lead to several problems.
Oversizing
An oversized unit cools or heats the space too quickly, leading to short cycling. Short cycling is when the unit turns on and off frequently, failing to run long enough to dehumidify the air properly. This can result in a clammy, uncomfortable environment and increased energy consumption. Furthermore, short cycling puts extra strain on the components, potentially shortening the lifespan of the unit. The initial cost might be higher, and you will be wasting energy.
Undersizing
An undersized unit struggles to maintain the desired temperature, especially during peak cooling or heating periods. It will run continuously, consuming excessive energy and potentially overworking the compressor, leading to premature failure. You'll experience inconsistent temperatures and discomfort. Simply put, it's working harder, consuming more energy, and still not properly conditioning the space.
Cost, Efficiency, and Lifespan Considerations
Beyond BTU capacity, several other factors influence the cost, efficiency, and lifespan of HVAC systems.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
Look for units with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings for cooling and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings for heating. Higher SEER and HSPF ratings indicate better energy efficiency, translating to lower energy bills. Energy Star certified units meet specific efficiency guidelines set by the EPA.
Types of Systems
Consider different types of HVAC systems, such as window units, portable air conditioners, mini-split systems, and central air conditioning. Window units and portable air conditioners are typically less expensive but less efficient than mini-split or central air conditioning systems. Mini-split systems offer zoning capabilities, allowing you to control the temperature in individual rooms. Central air conditioning provides whole-house cooling but requires ductwork installation.
Lifespan
The lifespan of an HVAC system depends on various factors, including the quality of the unit, maintenance practices, and usage patterns. Properly maintained HVAC systems can last for 10-15 years or longer. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters and coils, can significantly extend the lifespan of the unit.
Cost
The cost of an HVAC system varies depending on the type, size, efficiency, and installation complexity. Window units and portable air conditioners are generally the least expensive, while central air conditioning systems are the most costly. Consider the long-term costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, when making your decision.
Working with HVAC Professionals
Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional is highly recommended, especially when selecting a new HVAC system or replacing an existing one. A professional can perform a load calculation to determine the precise BTU needs of your space and recommend the most appropriate system for your specific requirements. They can also ensure proper installation, which is critical for optimal performance and longevity.
Professional HVAC contractors will assess your home's unique characteristics and provide tailored recommendations, factoring in things like existing ductwork (if applicable), building materials, and regional climate data. Getting multiple quotes from different contractors is advisable to ensure you're getting a fair price and comprehensive service.
Conclusion
While a 9000 BTU air conditioner can effectively cool approximately 400 square feet under ideal conditions, understanding the numerous factors that influence cooling and heating loads is crucial for accurate sizing. By considering climate, insulation, sun exposure, ceiling height, occupancy, heat-generating appliances, and airflow, you can determine the appropriate BTU rating for your specific needs. Remember to consult with an HVAC professional for personalized recommendations and ensure proper installation for optimal performance, energy efficiency, and long-term cost savings. Selecting the right sized unit makes a big difference in your comfort and wallet.

/air-conditioning-chart-1152654_final-01-5c522db7c9e77c0001d7671e.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/air-conditioning-chart-1152654_final-02-c37c8b4fdf08432baf378e8f0cb9d8e0.jpg)