How Many Watts In An Air Conditioner
Understanding Air Conditioner Wattage: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the wattage of an air conditioner is crucial for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers alike. It's not just about understanding your energy bill; it's about selecting the right unit for your needs, ensuring efficient operation, and preventing electrical overloads. This article provides a detailed breakdown of air conditioner wattage, how it relates to cooling capacity, and the factors that influence energy consumption.
What is Wattage and Why Does it Matter?
Wattage is the unit of measurement for electrical power. Simply put, it tells you how much electricity an appliance consumes. In the context of air conditioning, the wattage indicates the amount of power the unit requires to operate. Higher wattage generally means higher energy consumption, but it can also indicate a more powerful cooling capacity.
Understanding wattage is vital for several reasons:
- Calculating Energy Costs: Wattage is a key factor in determining your air conditioning energy bill. You can estimate the running cost by multiplying the wattage by the number of hours the unit operates and then multiplying that by the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) charged by your electricity provider.
- Sizing the Unit Correctly: Choosing an air conditioner with the appropriate wattage is essential for efficient cooling. An undersized unit will struggle to cool the space, running continuously and consuming excessive energy. Conversely, an oversized unit will cycle on and off frequently, leading to uneven temperatures, increased wear and tear, and wasted energy.
- Preventing Electrical Overloads: Knowing the wattage helps you ensure that your electrical circuits can handle the load. Overloading circuits can trip breakers, create fire hazards, and damage appliances.
- Comparing Energy Efficiency: Wattage, along with other efficiency ratings like EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) and SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), helps you compare the energy efficiency of different air conditioner models.
Watts vs. Cooling Capacity (BTU)
While wattage measures electrical power consumption, BTU (British Thermal Unit) measures the cooling capacity of an air conditioner. A BTU is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. Air conditioners are rated based on how many BTUs of heat they can remove from a room per hour (BTU/h).
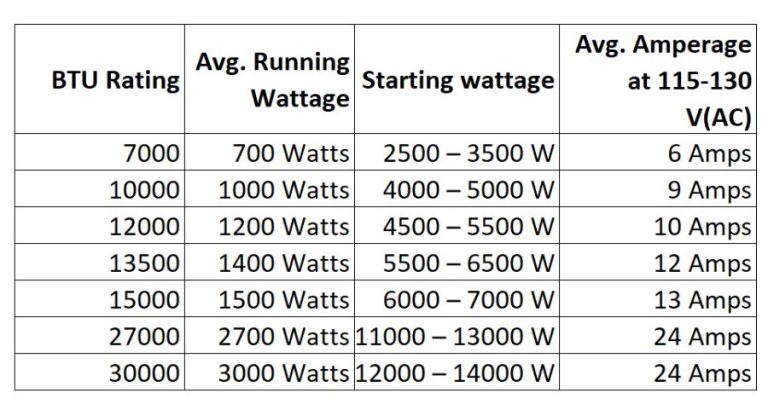
The relationship between wattage and BTU is not always straightforward, but generally, higher BTU units consume more watts. A rough estimate is that a 12,000 BTU air conditioner (1 ton) will draw around 1000-1500 watts. However, this is just a ballpark figure, and the actual wattage will vary depending on the unit's efficiency.
Example: A window air conditioner with a cooling capacity of 5,000 BTU might consume around 450-550 watts, while a larger 18,000 BTU unit could consume 1400-1800 watts.
It is crucial to consider both wattage and BTU when selecting an air conditioner. A high-BTU unit with low wattage indicates higher energy efficiency.
Factors Affecting Air Conditioner Wattage
Several factors influence the wattage of an air conditioner:
- Cooling Capacity (BTU): As mentioned earlier, higher BTU units generally require more power.
- Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER): EER is the ratio of cooling output (BTU) to power input (watts) at a specific operating point. A higher EER indicates greater energy efficiency. Modern air conditioners are increasingly focusing on improved EER ratings.
- Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER): SEER is a more comprehensive measure of energy efficiency than EER. It takes into account the cooling performance over an entire cooling season. Higher SEER ratings indicate better energy efficiency and lower energy bills. Look for units with a SEER rating of 14 or higher.
- Type of Air Conditioner: Different types of air conditioners (window, portable, central) have varying wattage requirements.
- Compressor Type: Compressors are the heart of the air conditioning system. More efficient compressor technologies, such as variable-speed compressors, can significantly reduce wattage consumption.
- Fan Speed: Air conditioners typically have multiple fan speeds. Higher fan speeds require more power.
- Age and Condition of the Unit: Older air conditioners tend to be less efficient and consume more power than newer models. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the coils and changing the filters, can help maintain efficiency.
- Insulation and Room Size: Poor insulation forces the unit to work harder and consume more power to maintain the set temperature.
Typical Wattage Ranges for Different Types of Air Conditioners
Here's a general overview of the wattage ranges you can expect for different types of air conditioners:
- Window Air Conditioners:
- 5,000 BTU: 450-550 watts
- 6,000 BTU: 500-600 watts
- 8,000 BTU: 700-800 watts
- 10,000 BTU: 800-1000 watts
- 12,000 BTU: 1000-1200 watts
- Portable Air Conditioners:
- 8,000 BTU: 800-1000 watts
- 10,000 BTU: 900-1200 watts
- 12,000 BTU: 1100-1400 watts
- 14,000 BTU: 1300-1600 watts
- Central Air Conditioners: These are measured in tons. 1 ton = 12,000 BTU.
- 1.5 ton (18,000 BTU): 1500-2000 watts
- 2 ton (24,000 BTU): 2000-2500 watts
- 2.5 ton (30,000 BTU): 2500-3000 watts
- 3 ton (36,000 BTU): 3000-3500 watts
- 4 ton (48,000 BTU): 4000-5000 watts
- 5 ton (60,000 BTU): 5000-6000 watts
Note: These are estimated ranges. Always refer to the manufacturer's specifications for the exact wattage of a particular model.
Calculating Your Air Conditioning Costs
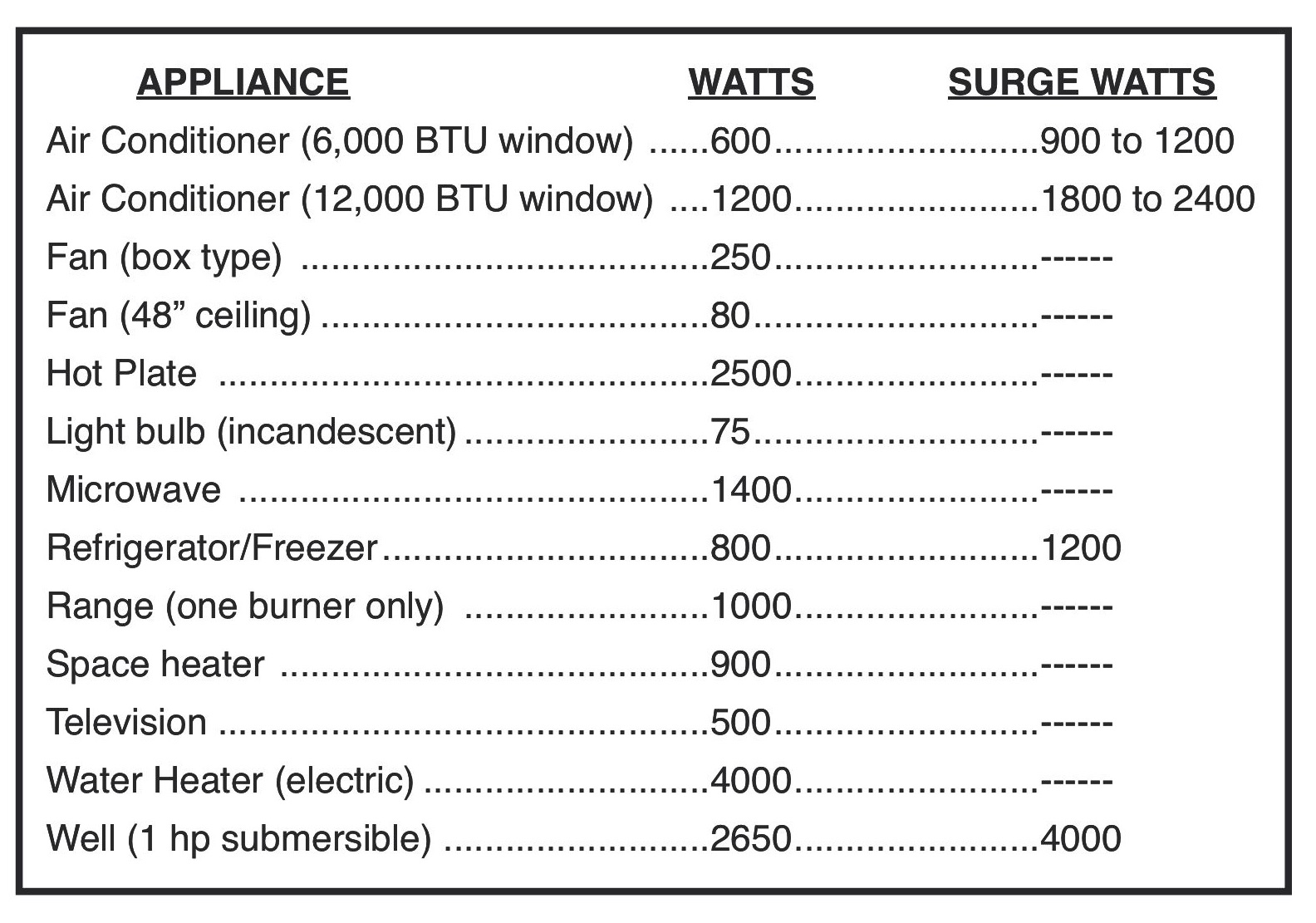
To estimate your air conditioning costs, you'll need the following information:
- Air conditioner wattage (from the unit's label or manual)
- Hours of operation per day
- Days of operation per month
- Electricity cost per kWh (from your electricity bill)
Here's the formula:
(Wattage / 1000) x Hours of Operation x Days of Operation x Cost per kWh = Monthly Cost
Example:
Let's say you have a 1000-watt air conditioner that runs for 8 hours a day, 30 days a month, and your electricity cost is $0.15 per kWh.
(1000 / 1000) x 8 x 30 x $0.15 = $36 per month
Tips for Reducing Air Conditioner Wattage Consumption
Here are some tips to help you reduce your air conditioning energy consumption and lower your electricity bills:
- Choose an Energy-Efficient Model: Look for air conditioners with high EER and SEER ratings. ENERGY STAR certified models are a good choice.
- Size the Unit Correctly: Don't oversize your air conditioner. Consult with an HVAC professional to determine the appropriate size for your space.
- Use a Programmable Thermostat: Program your thermostat to raise the temperature when you're away or asleep.
- Maintain Your Air Conditioner: Regularly clean the coils and change the filters.
- Improve Insulation: Proper insulation helps keep your home cool and reduces the workload on your air conditioner.
- Seal Air Leaks: Seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings.
- Use Fans: Ceiling fans and portable fans can help circulate air and reduce the need for air conditioning.
- Close Curtains and Blinds: During the hottest part of the day, close curtains and blinds to block out sunlight.
- Consider a Ductless Mini-Split System: For targeted cooling, ductless mini-split systems can be a very efficient alternative to central air.
Conclusion
Understanding air conditioner wattage is essential for making informed decisions about your cooling needs. By considering wattage, BTU, EER, SEER, and other factors, you can choose the right unit for your home or building, optimize energy efficiency, and save money on your electricity bills. Regular maintenance and energy-saving practices can further reduce your energy consumption and extend the lifespan of your air conditioning system. Whether you're a homeowner, HVAC technician, or facility manager, a solid grasp of air conditioner wattage will empower you to create a comfortable and energy-efficient environment.