How Much Does It Cost To Put Central Air

Central Air Installation: A Comprehensive Cost Guide for Homeowners
Central air conditioning is a significant investment for any home, offering unparalleled comfort and boosting property value. However, understanding the costs involved is crucial before making a decision. This guide breaks down the various factors that influence the price of installing or replacing a central air system, helping you make an informed choice.
Understanding the Base Costs: System Components
The most significant portion of your central air installation cost lies in the equipment itself. A complete central air system typically includes:
- Outdoor Condenser Unit: This component houses the compressor and fan, responsible for cooling the refrigerant.
- Indoor Evaporator Coil: Located inside your furnace or air handler, the evaporator coil absorbs heat from the air.
- Air Handler: This unit circulates air throughout your ductwork. If you already have a forced-air furnace, it can often be used with the new AC system.
- Refrigerant Lines: These insulated copper pipes connect the outdoor and indoor units, carrying the refrigerant.
- Thermostat: Controls the system's operation and temperature settings.
The price of these components varies based on several factors:
- Size (BTU): Measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs), the size of your AC system needs to match your home's square footage and climate. Larger homes require higher BTU ratings, leading to higher costs. Undersized units will struggle to cool effectively, while oversized units can lead to humidity problems and energy waste.
- Efficiency (SEER Rating): The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measures the cooling efficiency of an AC unit. Higher SEER ratings mean lower energy bills, but also a higher initial purchase price. Current minimum SEER ratings are mandated by federal regulations.
- Brand and Model: Different brands offer varying levels of quality, features, and price points. Premium brands like Carrier and Trane often come with advanced features and longer warranties, but at a higher cost compared to budget-friendly options like Goodman.
Expect to pay anywhere from $3,000 to $7,000+ for the equipment alone, depending on the factors mentioned above.
Installation Costs: Labor and Additional Expenses
Installation is another significant cost factor. This includes:
- Labor: Hiring a qualified HVAC technician is crucial for proper installation. Labor costs vary based on location, complexity of the job, and the contractor's rates.
- Ductwork: If your home doesn't have existing ductwork or if the existing ductwork is inadequate, you'll need to factor in the cost of installing new or modifying existing ducts. This can significantly increase the overall project cost.
- Electrical Work: The electrical system needs to be properly wired to handle the new AC unit's power requirements. This may involve upgrading your electrical panel or running new wiring.
- Permits and Inspections: Most municipalities require permits for HVAC installations, and inspections to ensure the work meets building codes.
- Refrigerant: The cost of the refrigerant itself (e.g., R-410A) can vary, and may be a separate charge.
- Disposal of Old Unit: Many installers include disposal of your old AC unit in their quote, but it's important to confirm.
Installation costs can range from $1,500 to $5,000+, depending on the complexity of the job.
Total Cost Breakdown: Putting it All Together
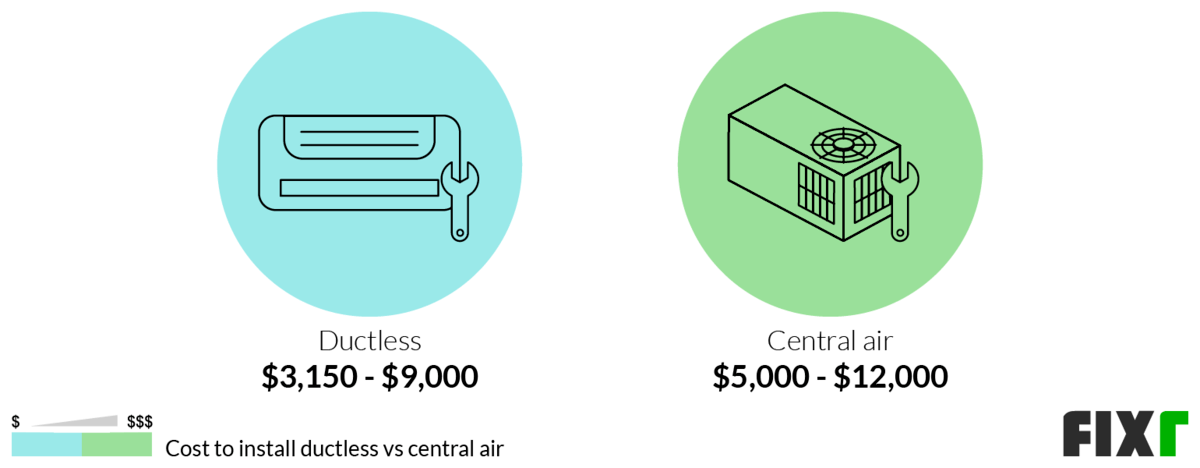
Therefore, the total cost to install central air can range from $4,500 to $12,000+, depending on the factors outlined above. Here's a general estimate based on system size and complexity:
- Small Home (1,000 - 1,500 sq ft): $4,500 - $8,000
- Medium Home (1,500 - 2,000 sq ft): $6,000 - $10,000
- Large Home (2,000+ sq ft): $8,000 - $12,000+
It's essential to get multiple quotes from different HVAC contractors to compare prices and services. Be sure to ask for a detailed breakdown of the costs, including equipment, labor, permits, and any potential additional expenses.
Factors Affecting Cost: Beyond the Basics
Several other factors can influence the cost of your central air installation:
- Home Location: Labor costs and permit fees vary significantly by region. Areas with higher costs of living generally have higher HVAC installation prices.
- System Complexity: Homes with difficult-to-access attics or crawl spaces may require more labor and specialized equipment, increasing the installation cost. Also, homes requiring extensive ductwork modifications will see higher costs.
- Technology: Smart thermostats, zoning systems, and variable-speed air conditioners can add to the initial cost but offer enhanced comfort and energy savings.
- Time of Year: HVAC contractors are often busier during peak seasons (summer and winter). You may be able to negotiate a better price during the off-season (spring and fall).
Popular HVAC Brands and Models: A Comparison
Choosing the right brand and model is critical. Here's a brief overview of some popular options:
- Carrier: Known for their high-quality and energy-efficient systems, Carrier offers a wide range of models to suit different needs and budgets. Their Infinity series boasts some of the highest SEER ratings available.
- Trane: Another top-tier brand, Trane is renowned for its durability and reliability. Their XR and XV series are popular choices.
- Lennox: Lennox offers innovative technology and energy-efficient designs. Their Dave Lennox Signature Collection is their premium line.
- Goodman: Goodman provides more affordable options without sacrificing quality. They're a good choice for budget-conscious homeowners.
- Rheem: Rheem offers a balance of performance and value. Their Prestige series provides high-efficiency options.
When comparing models, pay attention to the SEER rating, the warranty offered, and any special features that may be important to you, such as noise levels or smart home integration.
Understanding Efficiency Ratings: SEER, AFUE, and HSPF
When selecting an HVAC system, understanding efficiency ratings is crucial for making an informed decision. These ratings help you compare the energy performance of different models and estimate your potential energy savings.
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): As mentioned previously, SEER measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit. Current minimum standards vary depending on the region you live in.
- AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): While this applies primarily to furnaces, it's important if you're considering a combined heating and cooling system. AFUE measures the heating efficiency of a furnace. A higher AFUE rating indicates that more of the fuel is converted into heat, resulting in lower heating bills.
- HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): This rating applies to heat pumps and measures their heating efficiency. Similar to SEER, a higher HSPF rating indicates better heating performance.
Warranties and Maintenance: Protecting Your Investment
A good warranty is essential for protecting your investment in a new central air system. Most manufacturers offer a base warranty on their products, typically covering parts for 5-10 years. Some manufacturers also offer extended warranties that cover labor costs.
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your AC system. Regular maintenance tasks include:
- Changing Air Filters: Dirty air filters restrict airflow and reduce efficiency. Change your air filters every 1-3 months, depending on usage.
- Cleaning the Condenser Coils: The outdoor condenser coils can become dirty, reducing their ability to dissipate heat. Clean the coils regularly with a garden hose.
- Inspecting Ductwork: Check your ductwork for leaks and damage. Seal any leaks with duct tape or mastic.
- Professional Maintenance: Schedule an annual maintenance check with a qualified HVAC technician. They can inspect the system, clean the coils, check the refrigerant levels, and identify any potential problems.
Financing Options and Rebates: Making it Affordable
Installing central air can be a significant expense, but several financing options and rebates can help make it more affordable:
- HVAC Financing: Many HVAC contractors offer financing options through third-party lenders.
- Manufacturer Rebates: Some manufacturers offer rebates on qualifying energy-efficient models.
- Utility Rebates: Your local utility company may offer rebates for installing energy-efficient HVAC systems.
- Government Tax Credits: Check for federal and state tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Installing central air is a major decision, but by understanding the costs involved, considering your specific needs, and choosing the right equipment and contractor, you can enjoy a comfortable and energy-efficient home for years to come. Remember to prioritize factors like SEER ratings, warranty coverage, and professional installation to maximize your investment.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CentralAC-51a9e6136f9c470e8390d9b4d9362a60.jpg)





