How To Calculate Cfm In A Room

Imagine this: it’s a sweltering summer day, and your air conditioner suddenly stops blowing cold air. Instead, it's just circulating warm air, making the problem worse. Before you call a repair technician, there are a few simple checks you can perform yourself. Understanding how to calculate the required airflow (CFM - Cubic Feet per Minute) for a room can also help you diagnose if the AC unit is even adequately sized for your space, which could be the root cause of the issue. This article will guide you through basic AC troubleshooting and how to calculate CFM requirements for your rooms.
Troubleshooting a Malfunctioning Air Conditioner
Safety First!
Before you start any troubleshooting, always disconnect the power to your AC unit. Locate the breaker in your electrical panel labeled for the AC and switch it to the 'off' position. For window units, unplug them from the wall. Safety is paramount!
Step 1: Check the Power Supply
The most common cause of a sudden AC failure is a loss of power. Follow these steps:
- Verify the Breaker: Go to your electrical panel and ensure the breaker for the AC unit hasn't tripped. If it has, switch it completely off, then back on.
- Inspect the Power Cord (Window Units): Check for any visible damage to the power cord, such as cuts or fraying. A damaged cord needs replacing. Do not attempt to repair a damaged cord yourself.
- Test the Outlet (Window Units): Plug another appliance into the same outlet to see if it's working. If the outlet isn't working, you may have a tripped breaker or a faulty outlet.
Step 2: Examine the Thermostat Settings
Sometimes, the problem is simply incorrect thermostat settings.
- Mode: Make sure the thermostat is set to 'Cool' and not 'Heat' or 'Fan Only'.
- Temperature: Ensure the set temperature is lower than the current room temperature. Don't set it excessively low; a difference of 10-15 degrees is usually sufficient.
- Fan Setting: Try setting the fan to 'Auto' instead of 'On'. 'On' will run the fan continuously, even when the compressor isn't cooling.
- Check Batteries: Some thermostats require batteries. Replace them if they are old.
Step 3: Clean the Air Filter
A dirty air filter restricts airflow, causing the AC unit to work harder and less efficiently. It’s one of the most common issues.
- Locate the Filter: The air filter is usually located in the indoor unit, behind a removable panel. Consult your AC unit's manual for specific instructions.
- Remove the Filter: Carefully remove the filter.
- Clean or Replace: If the filter is washable, clean it with water and mild detergent, let it dry completely, and then reinstall it. If it's a disposable filter, replace it with a new one of the same size and type. Never operate the AC without a filter.
Step 4: Check the Outdoor Unit (If Applicable)
If you have a central AC system, the outdoor unit (condenser) needs to be clear of obstructions.
- Clear Debris: Remove any leaves, branches, grass clippings, or other debris that may be blocking the unit.
- Ensure Proper Airflow: Make sure there's at least 2 feet of clear space around the unit.
Step 5: Inspect the Condensate Drain Line
A clogged condensate drain line can cause the AC to shut down or leak water.
- Locate the Drain Line: The drain line is usually a PVC pipe that exits the indoor unit and drains outside or into a floor drain.
- Check for Clogs: Look for any visible clogs or obstructions in the drain line.
- Clear the Drain Line: You can try using a wet/dry vacuum to suck out any debris from the drain line. Alternatively, you can use a stiff wire or pipe cleaner to break up the clog.
- Pour a Cup of Bleach: After clearing the clog, pour a cup of diluted bleach into the drain line to prevent future clogs.
When to Call a Professional
If you've tried these basic troubleshooting steps and your AC unit is still not working, it's time to call a qualified HVAC technician. Do not attempt to repair complex components like the compressor, refrigerant lines, or electrical components yourself. These repairs require specialized tools, knowledge, and licensing.
Specifically, call a professional if:
- You suspect a refrigerant leak. Refrigerant is a hazardous substance that requires special handling.
- The compressor is not running or making unusual noises.
- You are uncomfortable working with electrical components.
- The unit is still under warranty. Attempting repairs yourself may void the warranty.
How to Calculate CFM in a Room: Understanding Airflow Needs
CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute, measures the volume of air moving in or out of a space per minute. Knowing the appropriate CFM for a room is crucial for ensuring proper ventilation, heating, and cooling. An undersized AC unit will struggle to cool the room effectively, while an oversized unit can lead to short cycling (frequent on/off cycles), which wastes energy and reduces the unit's lifespan.
Why Calculate CFM?
- Proper Ventilation: Adequate airflow removes stale air, pollutants, and odors, creating a healthier indoor environment.
- Efficient Heating and Cooling: Matching the AC unit or furnace's CFM to the room's needs ensures optimal temperature control and energy efficiency.
- Preventing Mold and Mildew: Proper ventilation helps control humidity levels, reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth.
- Balanced Air Pressure: Correct CFM ensures balanced air pressure throughout the house, preventing drafts and uncomfortable temperature variations.
Methods for Calculating CFM
There are several methods for calculating CFM, each with varying degrees of accuracy. Here are three common approaches:
Method 1: Using Room Volume and Air Changes per Hour (ACH)
This is a commonly used method that considers the size of the room and how frequently the air needs to be replaced.
- Calculate Room Volume: Measure the length, width, and height of the room in feet. Multiply these three measurements together to get the room volume in cubic feet.
- Example: Length = 12 feet, Width = 10 feet, Height = 8 feet. Volume = 12 ft x 10 ft x 8 ft = 960 cubic feet.
- Determine Air Changes per Hour (ACH): ACH is the number of times the air in a room is completely replaced in one hour. The required ACH depends on the room's purpose. Here are some typical ACH values:
- Bedrooms: 4-6 ACH
- Living Rooms: 4-6 ACH
- Kitchens: 6-8 ACH (more if heavy cooking is involved)
- Bathrooms: 8-10 ACH
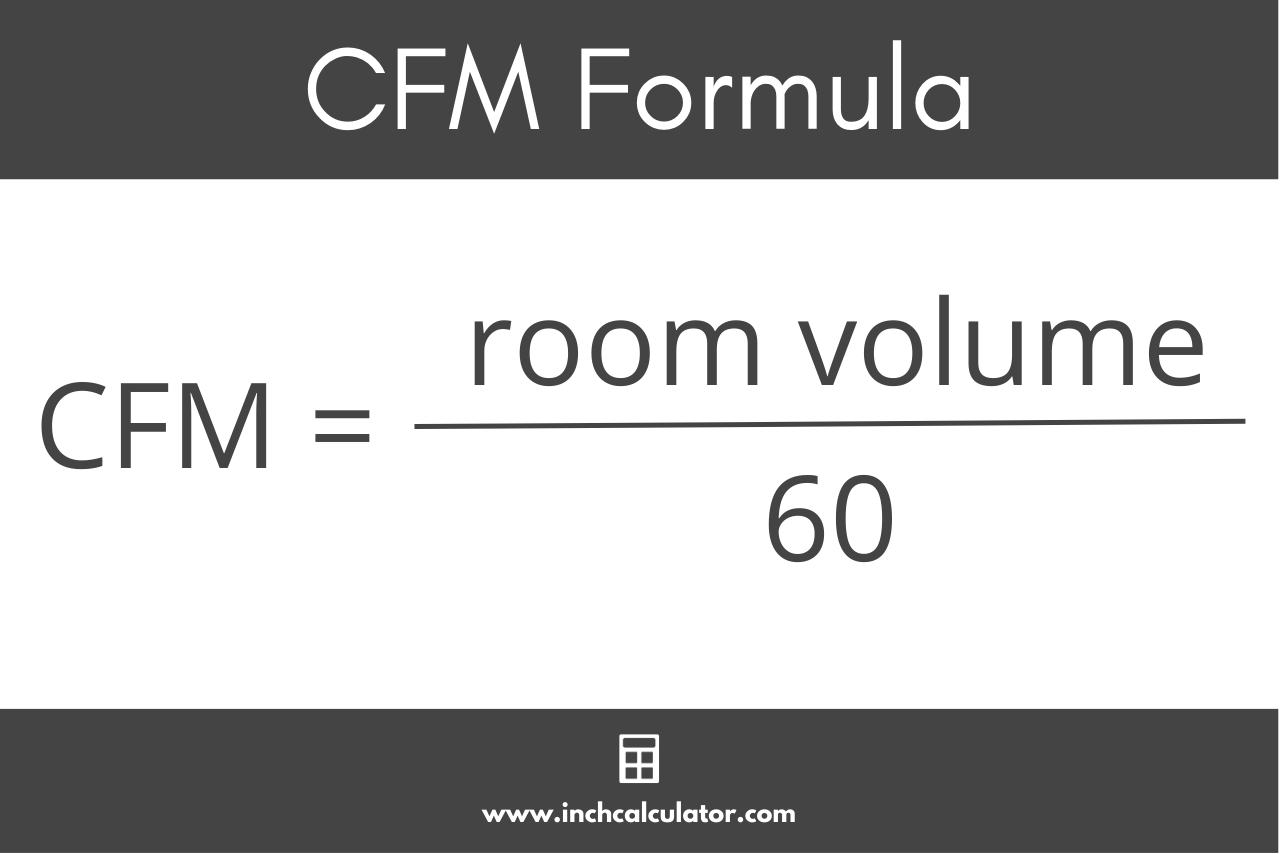
- Calculate Required CFM: Use the following formula:
CFM = (Room Volume x ACH) / 60
(Divide by 60 to convert air changes per hour to air changes per minute)- Example: Room Volume = 960 cubic feet, ACH = 6. CFM = (960 x 6) / 60 = 96 CFM.
Therefore, for this example bedroom, you would need an air handling system capable of moving approximately 96 CFM.
Method 2: Using Room Square Footage and Cooling Load (BTU/hr)
This method is more specific to air conditioning and considers the cooling load of the room, measured in British Thermal Units per hour (BTU/hr).
- Calculate Room Square Footage: Measure the length and width of the room in feet. Multiply these two measurements together to get the room square footage.
- Example: Length = 12 feet, Width = 10 feet. Area = 12 ft x 10 ft = 120 square feet.
- Determine the Cooling Load (BTU/hr): A general rule of thumb is to use 20 BTU per square foot. However, this can vary depending on factors like insulation, window size, and sun exposure.
- Example: Using the 20 BTU per square foot rule: 120 square feet * 20 BTU/sq ft = 2400 BTU.
- Calculate Required CFM: Use the following formula:
CFM = BTU / (1.08 x Temperature Difference)
*Where:* * BTU is the cooling load in BTU/hr. * 1.08 is a constant that accounts for the specific heat of air and air density. * Temperature Difference is the desired temperature difference between the supply air and the return air (typically between 15-20 degrees Fahrenheit).- Example: BTU = 2400, Temperature Difference = 20 degrees Fahrenheit. CFM = 2400 / (1.08 x 20) = 111.11 CFM.
Method 3: Using Online CFM Calculators
Several online CFM calculators are available. These calculators typically require you to input the room's dimensions, purpose, and other factors like climate and insulation levels. While convenient, remember that these calculators provide estimates, and their accuracy may vary depending on the calculator's algorithms and the information you provide.
Factors Affecting CFM Requirements
Several factors can influence the CFM requirements for a room. Consider these factors when calculating CFM:
- Room Size: Larger rooms require more CFM to maintain proper ventilation and temperature control.
- Room Purpose: Rooms with different purposes have different ventilation needs. Kitchens and bathrooms, for example, require higher CFM due to cooking fumes and moisture.
- Climate: Hotter and more humid climates may require higher CFM for effective cooling.
- Insulation: Well-insulated rooms require less CFM than poorly insulated rooms.
- Window Size and Orientation: Large windows and windows facing south or west can increase the room's cooling load, requiring higher CFM.
- Occupancy: Rooms with more occupants require higher CFM to provide adequate ventilation.
- Heat-Generating Appliances: Rooms with appliances that generate heat, such as computers or stoves, may require higher CFM for cooling.
Final Thoughts
By understanding these troubleshooting steps and calculation methods, you can take a more proactive approach to home maintenance and ensure a comfortable and healthy living environment. Remember to prioritize safety and call a professional when dealing with potentially hazardous repairs. Calculating the correct CFM will help in selecting the properly sized ventilation or cooling systems for your specific needs.