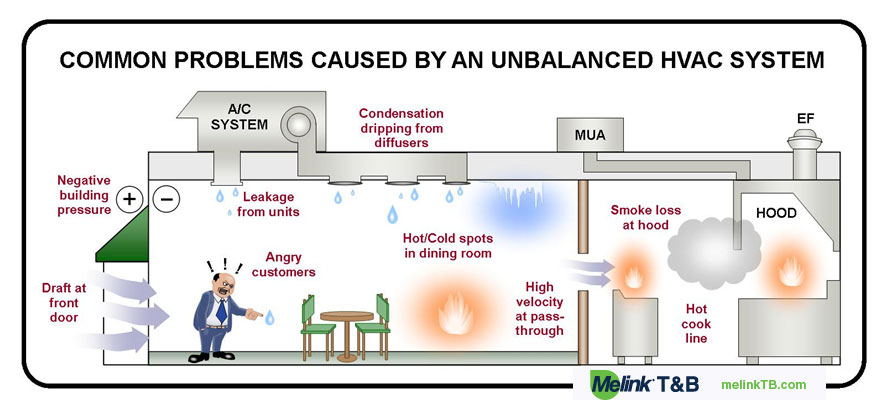
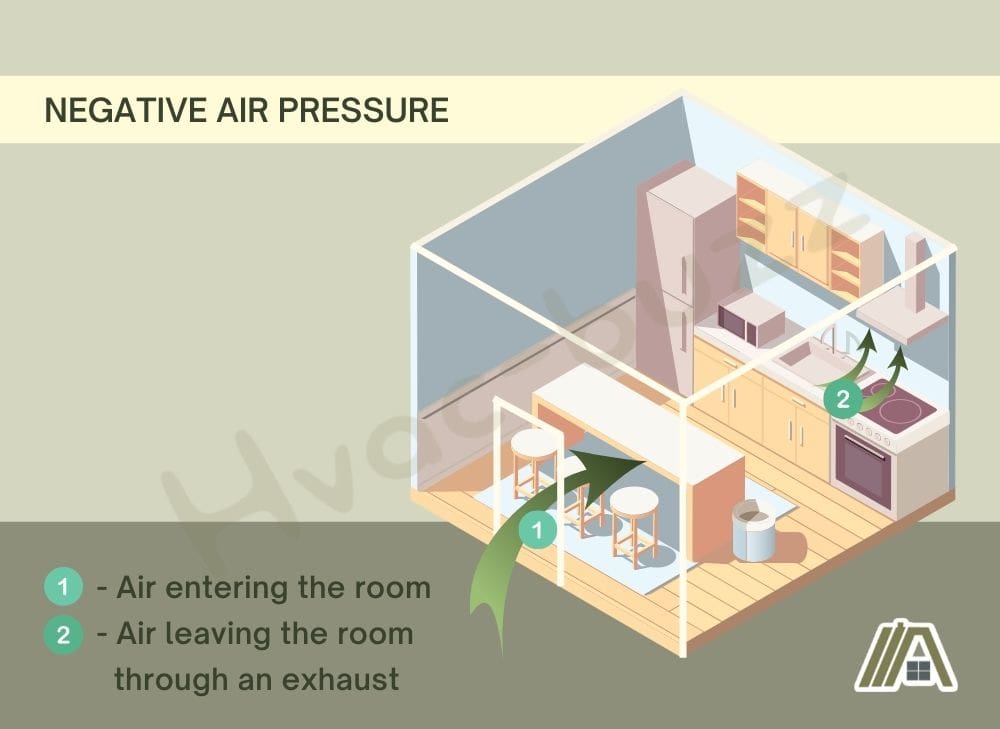
How To Fix Negative Air Pressure In House
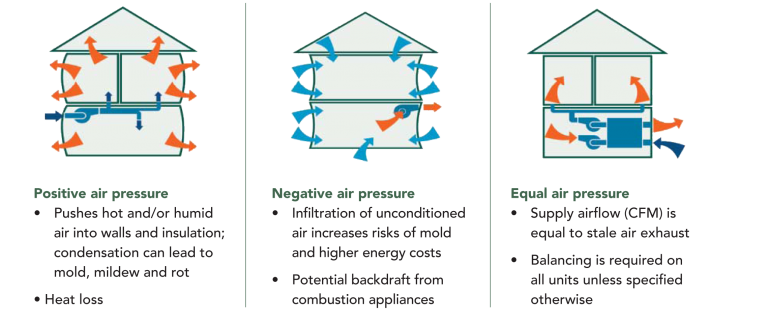
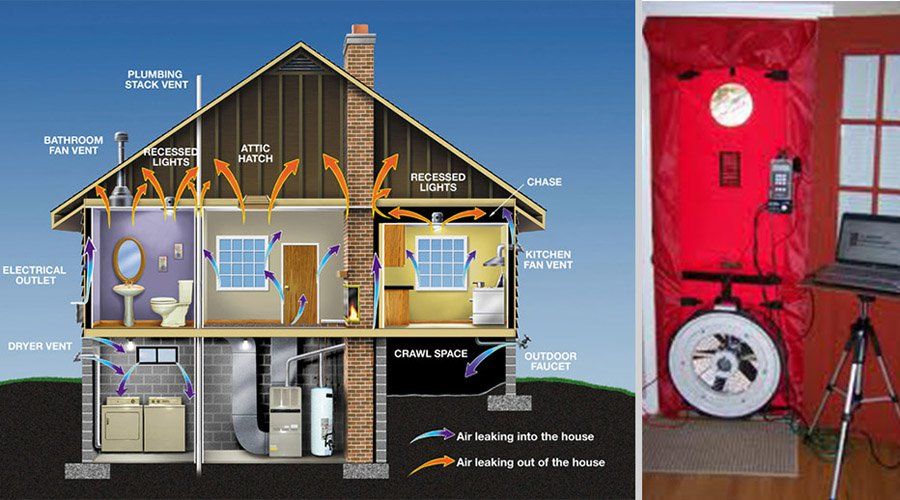
Negative air pressure in a house, also known as a pressure imbalance, occurs when more air is being exhausted from a building than is being supplied. This imbalance forces outside air to be drawn in through various leaks and openings, such as gaps around doors and windows, electrical outlets, and even the foundation. While a slight negative pressure is often unavoidable, excessive negative pressure can lead to increased energy bills, uncomfortable drafts, and even potential health issues by drawing in pollutants and allergens.
Understanding the Causes of Negative Air Pressure
Identifying the root cause of negative air pressure is the first step toward resolving the problem. Common culprits include:
- Exhaust Fans: Kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans are designed to remove moisture and odors, but they can significantly contribute to negative pressure if they are used excessively or if the home is not adequately ventilated. For example, running a high-powered kitchen exhaust hood for extended periods while cooking can exhaust a substantial amount of air.
- Clothes Dryers: Clothes dryers vent large volumes of air to the outside. In tightly sealed homes, this can create a significant pressure imbalance.
- Fireplaces and Wood Stoves: These appliances require combustion air, which is often drawn from inside the house. A fireplace damper that isn't sealing properly can also contribute to air leakage even when the fireplace isn't in use.
- HVAC Systems: Malfunctioning or improperly sized HVAC systems can also contribute to negative pressure. An undersized return duct system, for instance, may not be able to supply enough air to the furnace or air handler, causing it to draw air from other areas of the house.
- Building Tightness: In highly energy-efficient homes, the lack of natural air infiltration can exacerbate negative pressure issues caused by exhaust fans and appliances. Newer homes built to stricter energy codes are particularly susceptible.
Diagnosing Negative Air Pressure
Several methods can be used to diagnose negative air pressure:
- The Door Test: Close all windows and exterior doors. Open an interior door slightly (about an inch or two). Hold a thin piece of tissue paper near the crack. If the paper is pulled toward the interior of the house, it indicates negative pressure.
- Smoke Test: Use a smoke pencil or incense stick near windows, doors, and other potential air leaks. Observe the direction of the smoke. If the smoke is drawn into the house, it confirms air infiltration due to negative pressure.
- Manometer Test: A manometer is a device that measures air pressure differences. A professional HVAC technician can use a manometer to measure the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the house. A negative reading indicates negative pressure.
Solutions for Fixing Negative Air Pressure
Addressing negative air pressure requires a multi-faceted approach, often involving a combination of the following strategies:
1. Supply Air to Combustion Appliances
Ensure that combustion appliances, such as furnaces, water heaters, and fireplaces, have an adequate supply of combustion air. This can be achieved through:
- Dedicated Air Ducts: Install dedicated air ducts that bring outside air directly to the appliance. This prevents the appliance from drawing air from inside the house.
- Openings to the Outdoors: Create permanent openings to the outdoors, such as louvers or vents, near the appliance. The size of the opening should be based on the appliance's BTU input rating and local building codes.
- Power-Vented Appliances: Consider replacing naturally drafted appliances with power-vented models. Power-vented appliances use a fan to exhaust combustion gases, reducing their reliance on indoor air.
2. Balance Exhaust and Supply Air
Ensure that the amount of air being exhausted from the house is balanced by an equal amount of supply air. This can be accomplished by:
- Using Kitchen and Bathroom Exhaust Fans Sparingly: Limit the use of exhaust fans to only when they are needed and for the shortest possible duration.
- Installing a Makeup Air System: A makeup air system introduces fresh air into the house to compensate for the air being exhausted. These systems can be interlocked with exhaust fans to automatically activate when the fans are turned on.
- Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) and Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs): ERVs and HRVs are ventilation systems that exchange stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while recovering energy in the process. They help to maintain balanced air pressure while improving indoor air quality and reducing energy consumption. ERVs are better suited for humid climates, while HRVs are more effective in colder climates. The cost for these systems can range from $800 to $3,000 installed, depending on the size and complexity of the system.
3. Seal Air Leaks
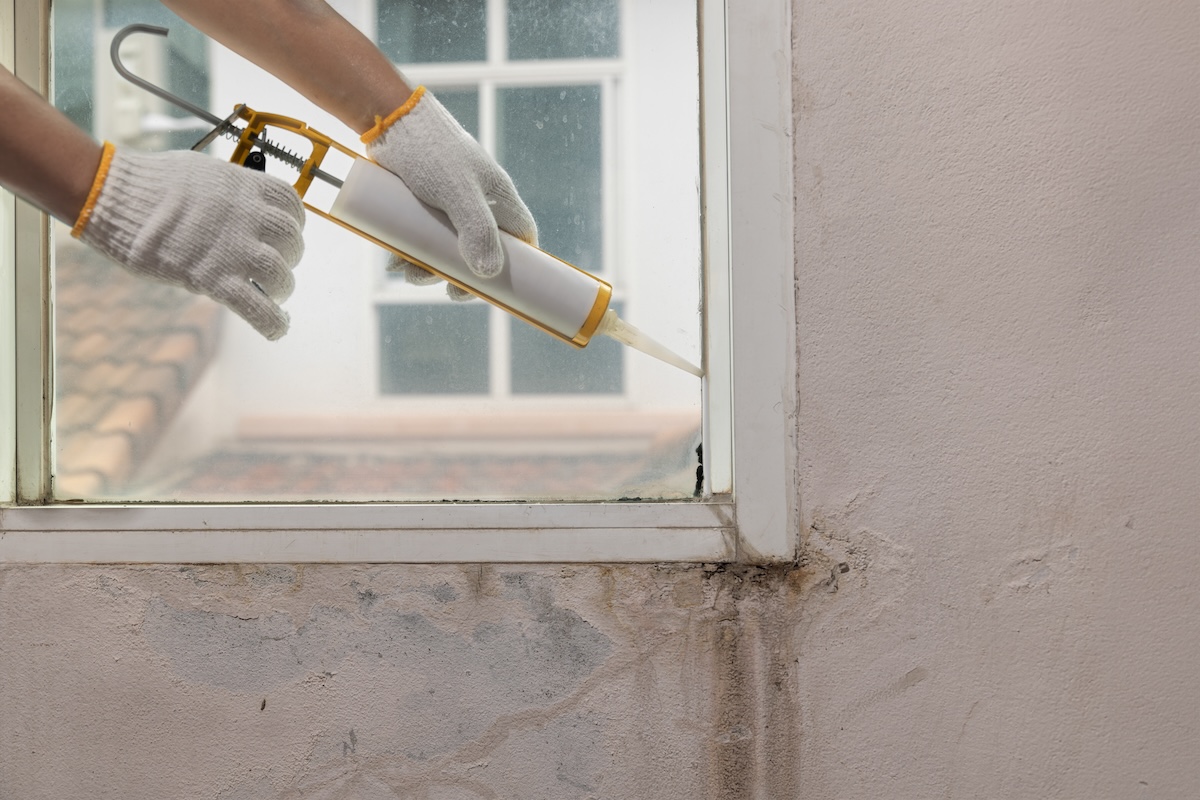
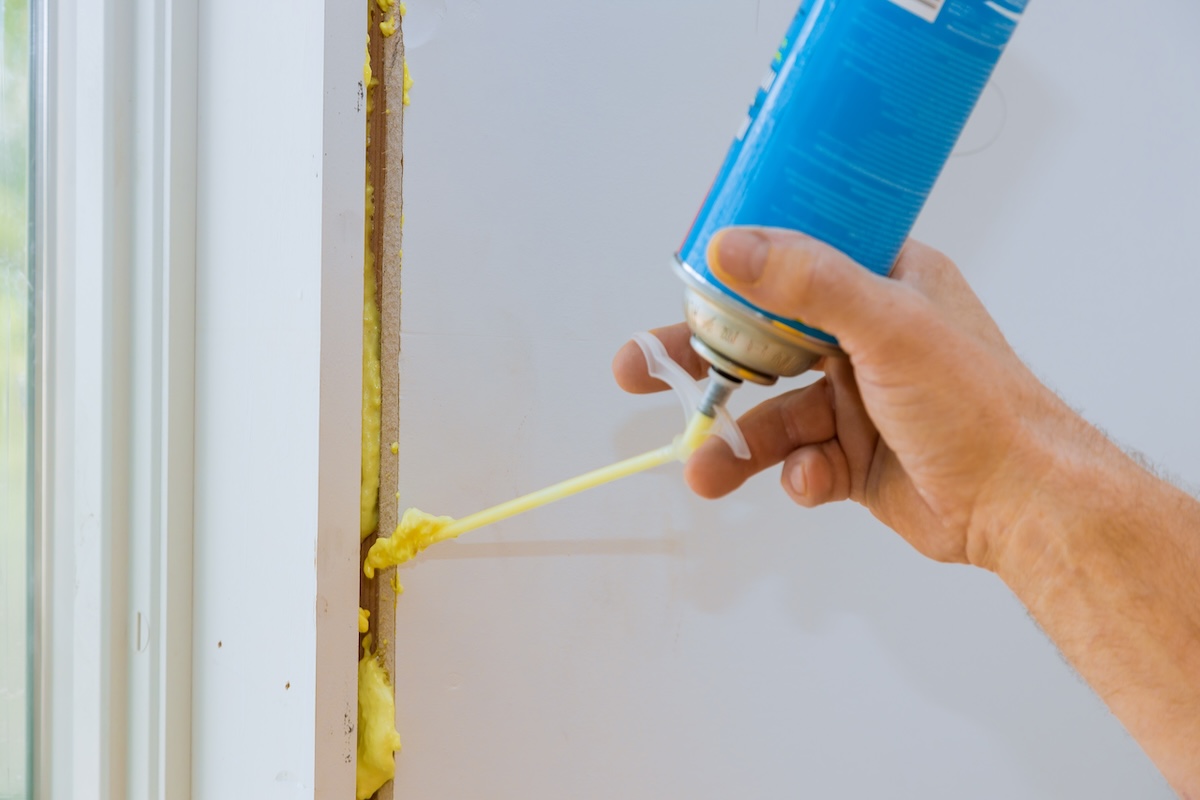
Reducing air leakage is a crucial step in addressing negative air pressure. This involves sealing gaps and cracks around windows, doors, pipes, and electrical outlets. Common methods include:
- Caulking: Use caulk to seal gaps around windows, doors, and pipes.
- Weatherstripping: Install weatherstripping around doors and windows to create a tighter seal.
- Expanding Foam: Use expanding foam to seal larger gaps and cracks, such as around pipes and electrical outlets.
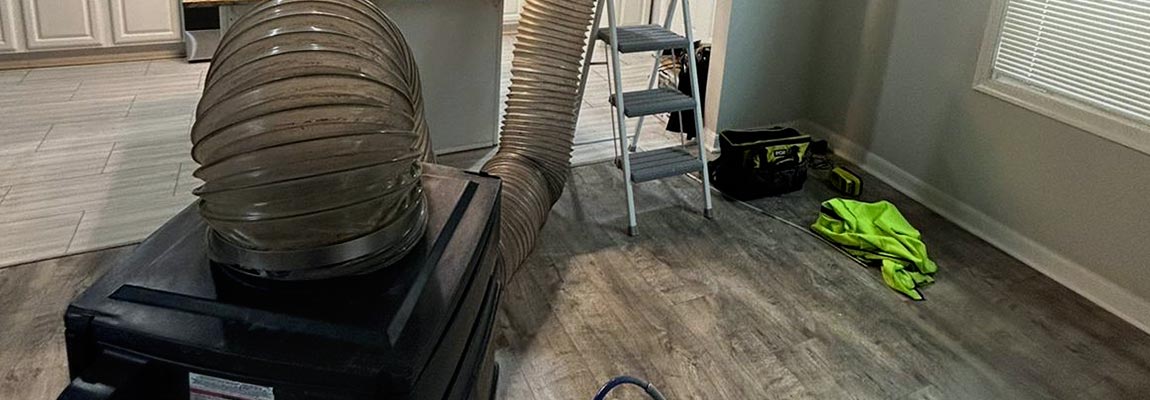
- Professional Air Sealing: Consider hiring a professional contractor to perform a comprehensive air sealing of your home. This typically involves using a blower door test to identify air leaks and then sealing them with appropriate materials. The cost of professional air sealing can range from $500 to $2,000, depending on the size and complexity of the project.
4. Optimize HVAC System Performance
Ensure that your HVAC system is properly sized and functioning correctly. This includes:
- Proper Duct Sizing: Ensure that the ductwork is properly sized and installed. Undersized return ducts can restrict airflow and contribute to negative pressure.
- Regular Filter Changes: Regularly change the air filter to maintain proper airflow. A dirty air filter can restrict airflow and reduce the efficiency of your HVAC system.
- Professional HVAC Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your HVAC system to ensure that it is functioning properly. A qualified HVAC technician can identify and address any issues that may be contributing to negative pressure.
5. Fireplace Considerations
Fireplaces, while aesthetically pleasing, can be significant contributors to negative air pressure. To mitigate this:
- Ensure a Tight-Sealing Damper: Make sure your fireplace damper seals tightly when not in use. A leaky damper can allow a significant amount of air to escape from the house.
- Install a Fireplace Insert: Consider installing a fireplace insert, which is a self-contained unit that fits inside the existing fireplace opening. Fireplace inserts are more efficient and less likely to contribute to negative pressure.
- Supply Outside Air to the Fireplace: Some fireplaces are designed with an outside air intake, which allows them to draw combustion air from the outdoors rather than from inside the house.
Cost Considerations
The cost of fixing negative air pressure can vary widely depending on the severity of the problem and the solutions implemented. Simple fixes, such as sealing air leaks and using exhaust fans sparingly, may cost only a few dollars. More complex solutions, such as installing a makeup air system or replacing an HVAC system, can cost several thousand dollars.
Here is a general overview of potential costs:
- DIY Air Sealing: $50 - $200 (materials)
- Professional Air Sealing: $500 - $2,000
- Makeup Air System: $500 - $1,500 (installed)
- ERV/HRV System: $800 - $3,000 (installed)
- HVAC System Repair or Replacement: Varies widely depending on the system and the extent of the work required.
Conclusion
Addressing negative air pressure is essential for maintaining a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient home. By understanding the causes of negative pressure, diagnosing the problem accurately, and implementing appropriate solutions, homeowners can significantly improve their indoor air quality and reduce their energy bills. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional can provide valuable insights and ensure that the chosen solutions are tailored to the specific needs of the home.