How To Fix Your Gas Fireplace

Troubleshooting Your Gas Fireplace: A Homeowner's Guide
A gas fireplace offers the ambiance of a traditional wood-burning fireplace without the mess and hassle. However, like any appliance, issues can arise. This guide provides homeowners, real estate investors, and contractors with a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and fixing common gas fireplace problems. Remember, safety is paramount. If you're uncomfortable working with gas lines or electrical components, always consult a qualified HVAC technician.
Common Gas Fireplace Issues and Solutions
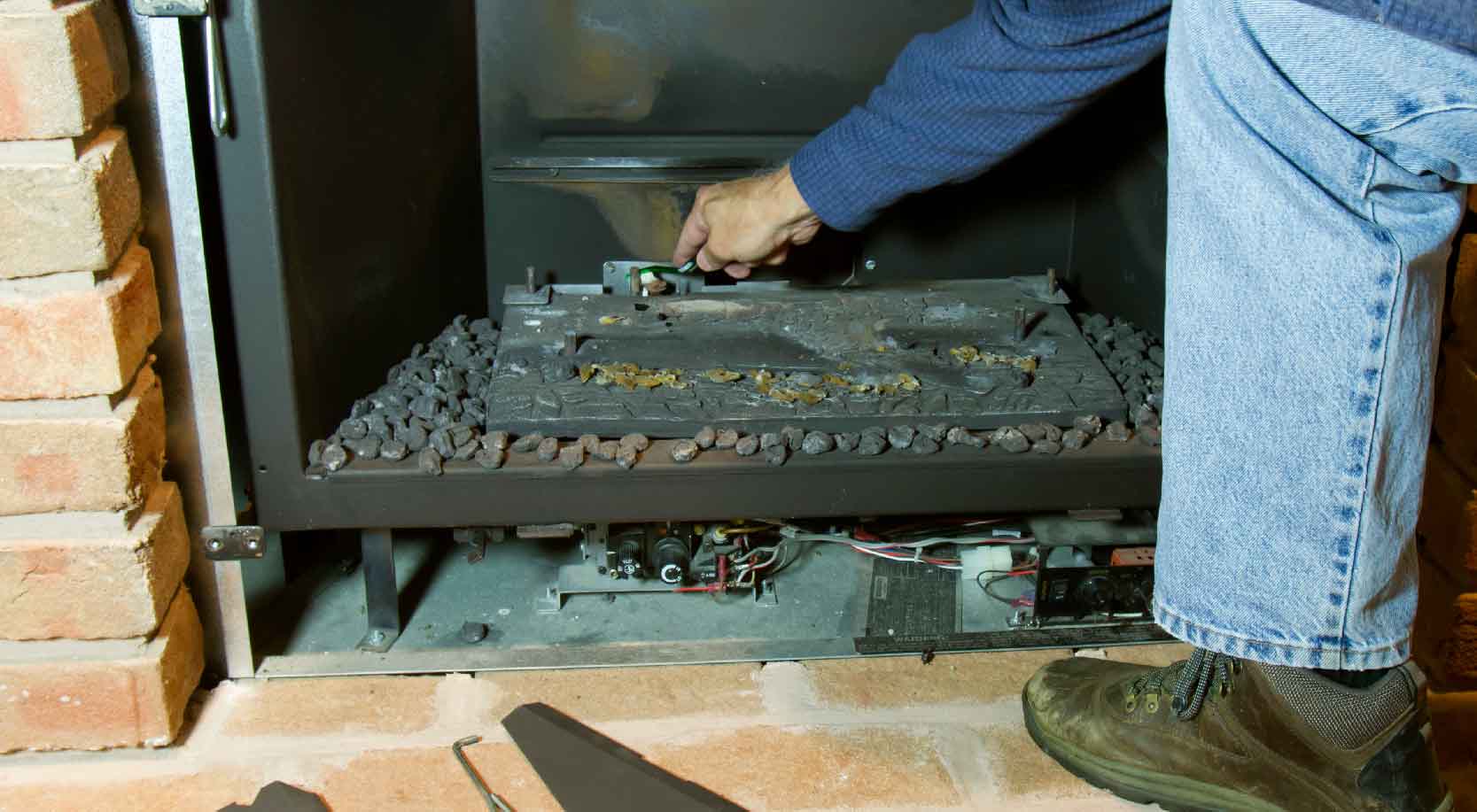
1. Pilot Light Problems
A malfunctioning pilot light is one of the most frequent issues encountered. A pilot light is a small, continuous flame that ignites the main burner when heat is called for. Problems can include:
- Pilot Light Won't Light:
- Possible Cause: Gas supply is off.
- Solution: Check the main gas valve to the fireplace and ensure it's open. Also, verify that your home's gas supply is active.
- Possible Cause: Air in the gas line.
- Solution: Hold down the pilot button for an extended period (up to a minute) to purge air from the line.
- Possible Cause: Clogged pilot orifice.
- Solution: Carefully clean the pilot orifice with a thin wire or compressed air. Refer to your owner's manual for specific instructions.
- Possible Cause: Faulty thermocouple or thermopile.
- Solution: These safety devices sense the pilot flame and allow gas to flow to the main burner. If they fail, the pilot light will extinguish when you release the pilot button. A multimeter can test the voltage output. Replacement is often the best solution.
- Pilot Light Lights But Goes Out:
- Possible Cause: Dirty pilot assembly.
- Solution: Clean the pilot assembly thoroughly. Use a small brush and compressed air.
- Possible Cause: Weak thermocouple or thermopile.
- Solution: As mentioned above, these may need replacement. A weak signal can cause the pilot to extinguish.
- Possible Cause: Drafts.
- Solution: Ensure there are no drafts affecting the pilot flame. Check for open windows or doors nearby.
- Pilot Light is Yellow or Orange:
- Possible Cause: Improper air-to-fuel mixture or dirty burner.
- Solution: Check the air shutter on the burner. Adjust it to provide a blue flame with minimal yellow. Clean the burner to remove any debris.
2. Main Burner Issues
Problems with the main burner can prevent the fireplace from producing heat.
- Main Burner Won't Light:
- Possible Cause: Faulty igniter or spark module.
- Solution: Check the igniter for spark while attempting to light the fireplace. If no spark is present, replace the igniter or spark module.
- Possible Cause: Faulty gas valve.
- Solution: The gas valve controls the flow of gas to the main burner. If it's not opening, the burner won't light. Testing requires a multimeter and knowledge of electrical circuits. Replacement is usually necessary.
- Possible Cause: Obstruction in the burner ports.
- Solution: Clean the burner ports with a wire brush to remove any debris that may be blocking the gas flow.
- Main Burner Lights But Shuts Off:
- Possible Cause: Flame sensor issue (if equipped).
- Solution: Some fireplaces use a flame sensor to ensure the burner stays lit. If the sensor doesn't detect a flame, it will shut off the gas. Clean the flame sensor with fine steel wool.
- Possible Cause: Overheating.
- Solution: Some fireplaces have a safety switch that shuts off the unit if it overheats. Ensure proper ventilation around the fireplace.
- Uneven Flame or Low Heat:
- Possible Cause: Partially clogged burner ports.
- Solution: Carefully clean all burner ports.
- Possible Cause: Low gas pressure.
- Solution: This could indicate a problem with your home's gas supply. Contact your gas company.
3. Odors
Any gas odor should be addressed immediately.
- Gas Odor:
- Possible Cause: Gas leak.
- Solution: Evacuate the premises immediately. Do not use any electrical switches or phones. Call your gas company from a safe location.
- Burning Smell:
- Possible Cause: Dust or debris burning off.
- Solution: Clean the fireplace thoroughly, including the logs and burner area. This is common after periods of inactivity.
4. Blower Malfunctions (If Equipped)
Some gas fireplaces have blowers to circulate warm air.
- Blower Not Working:
- Possible Cause: Power switch is off.
- Solution: Ensure the blower switch is turned on.
- Possible Cause: Blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker.
- Solution: Check the fuse or circuit breaker and replace or reset as needed.
- Possible Cause: Faulty blower motor.
- Solution: If the motor is humming but not turning, it may be seized or faulty. Replacement is usually necessary.
- Blower is Noisy:
- Possible Cause: Dirty blower fan.
- Solution: Clean the blower fan blades.
- Possible Cause: Loose blower motor.
- Solution: Tighten the blower motor mounting screws.
Maintenance for Longevity
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing problems and extending the life of your gas fireplace.
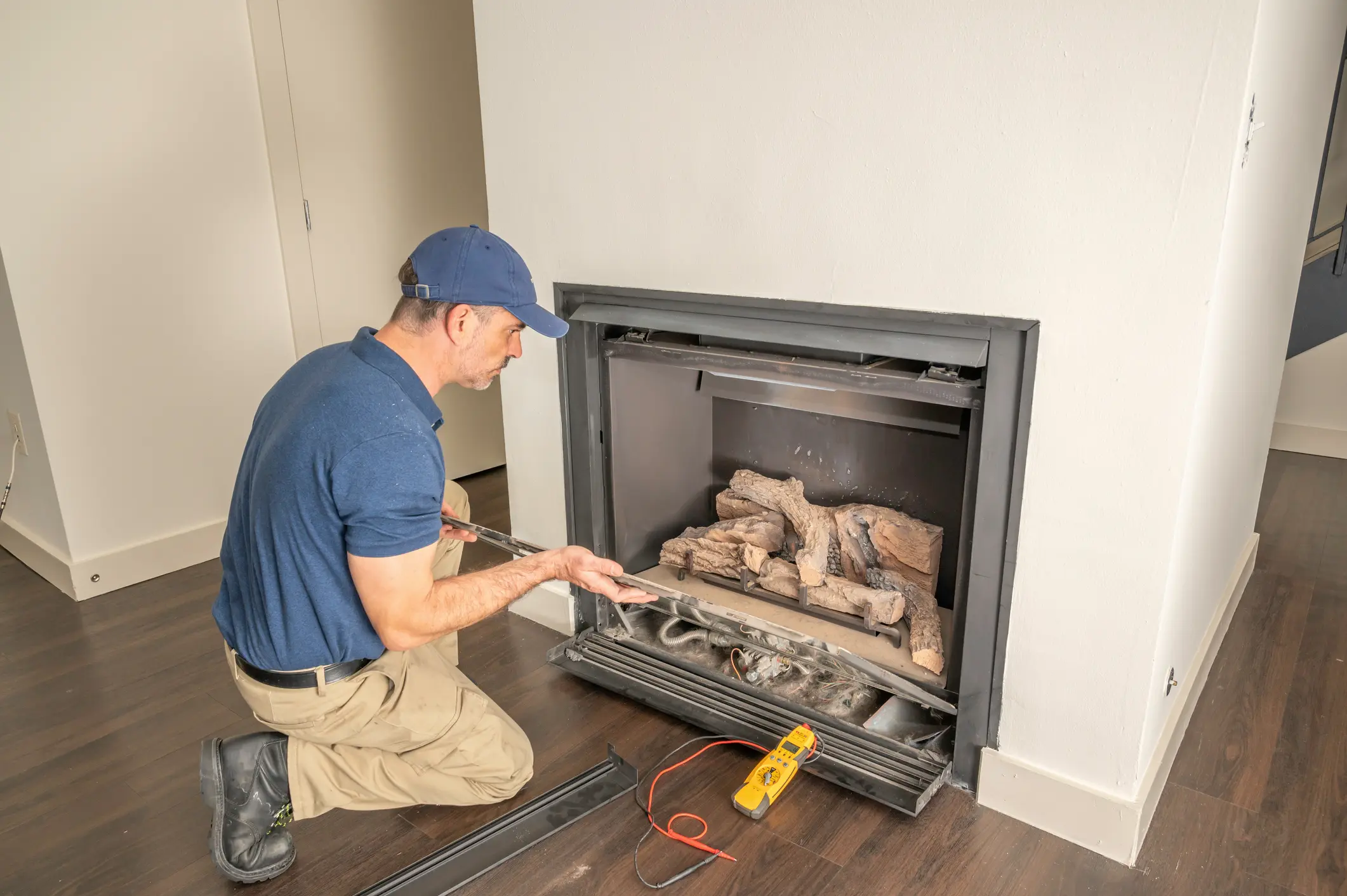
- Annual Inspection: Have your fireplace professionally inspected and cleaned annually by a qualified HVAC technician.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the glass, logs, and burner area to remove dust and debris.
- Log Placement: Ensure the logs are positioned correctly according to the manufacturer's instructions. Incorrect placement can affect the flame pattern and efficiency.
- Vent Inspection: Inspect the venting system regularly for blockages or damage. A blocked vent can lead to carbon monoxide buildup.
Safety First!
Working with gas appliances can be dangerous. If you are not comfortable performing any of these repairs, consult a qualified HVAC technician. Always turn off the gas supply before attempting any repairs. Ensure adequate ventilation when working on your fireplace.
Gas Fireplace Brands and Features to Consider
When considering a new gas fireplace, several brands offer a range of features and styles. Some popular brands include Napoleon, Heat & Glo, and Majestic. Features to consider include:
- Direct Vent vs. Vent-Free: Direct vent fireplaces vent exhaust gases outside, while vent-free models do not. Direct vent models are generally safer and more efficient.
- Ignition Type: Options include standing pilot, electronic ignition, and intermittent pilot ignition (IPI). Electronic ignition and IPI are more energy-efficient.
- Heat Output: Choose a fireplace with the appropriate BTU (British Thermal Unit) rating for the size of your space.
- Aesthetics: Gas fireplaces come in a variety of styles, including traditional, contemporary, and linear.
Warranties
Gas fireplace warranties vary by manufacturer and model. Be sure to read the warranty carefully before purchasing. Common warranty coverage includes:
- Parts: Coverage for defective parts.
- Labor: Coverage for the cost of labor to repair or replace defective parts.
- Burner: Often carries a longer warranty period than other components.
Energy Efficiency
While gas fireplaces are primarily for ambiance, some models offer reasonable energy efficiency. Look for models with features like sealed combustion and programmable thermostats. Some models are also rated with an AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) rating, although this is less common than with furnaces.
Cost Considerations
The cost of a gas fireplace can vary widely depending on the brand, features, and installation requirements. Expect to pay anywhere from $2,000 to $10,000 or more, including installation. Venting can significantly add to the cost. Remember to factor in annual maintenance costs as well.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting your gas fireplace can save you time and money. By understanding the common issues and solutions, you can keep your fireplace running smoothly and safely. However, remember that safety is always the top priority. When in doubt, consult a qualified HVAC professional.