How To Read Heating Oil Tank Gauge

Understanding how to read your heating oil tank gauge is crucial for managing your home's heating fuel supply. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, enabling you to accurately determine your tank's oil level and avoid unexpected run-outs, saving you time, money, and potential discomfort.
Locating Your Heating Oil Tank Gauge
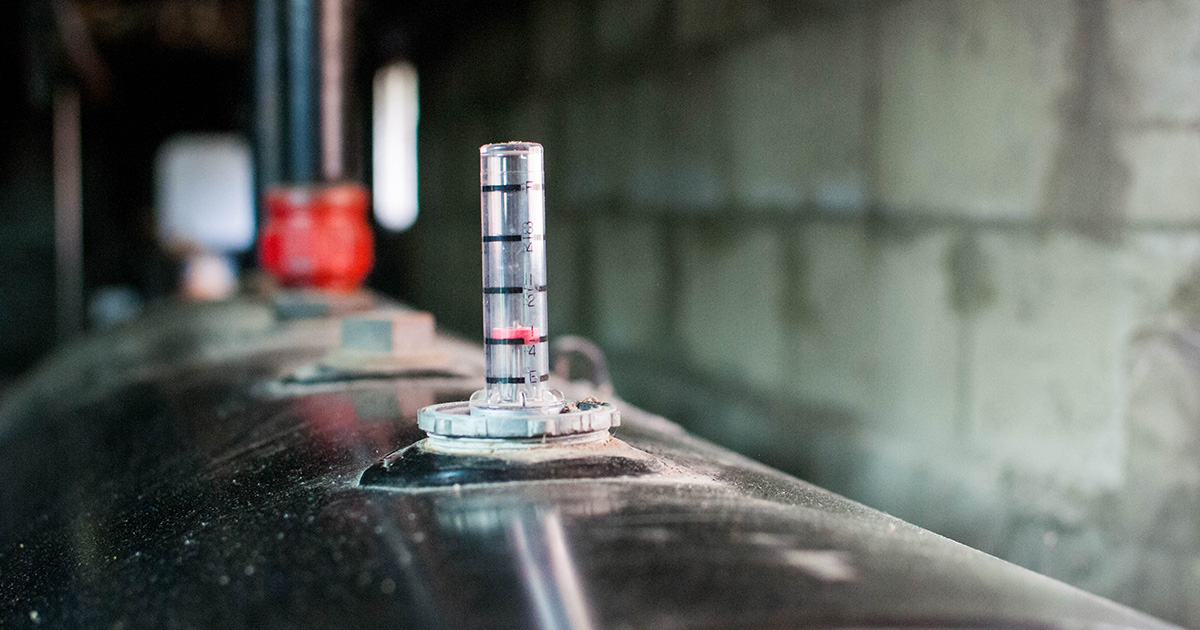
The first step is finding the gauge. It's usually located on top of your heating oil tank. Most tanks are situated in your basement, garage, or outside near the foundation of your house. Look for a small, clear plastic or glass tube sticking out of the top of the tank. This is where the gauge is housed.
Important Safety Note: Before approaching your oil tank, ensure the area is well-ventilated. If you smell a strong odor of oil, evacuate the area immediately and contact your heating oil supplier or a qualified technician.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Heating Oil Tank Gauge
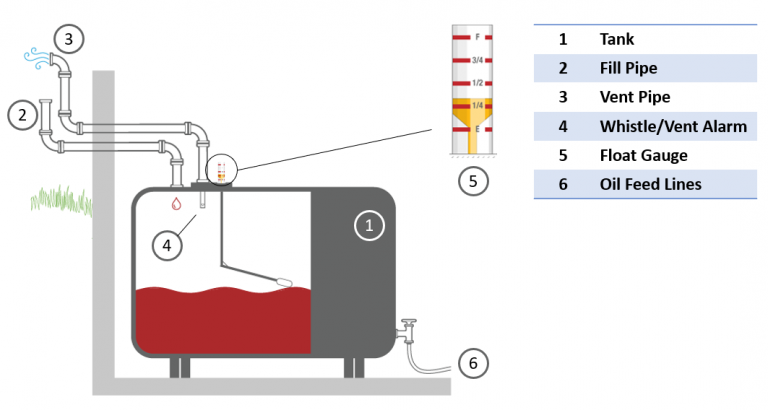
A typical heating oil tank gauge is a relatively simple device. It consists of several key components:
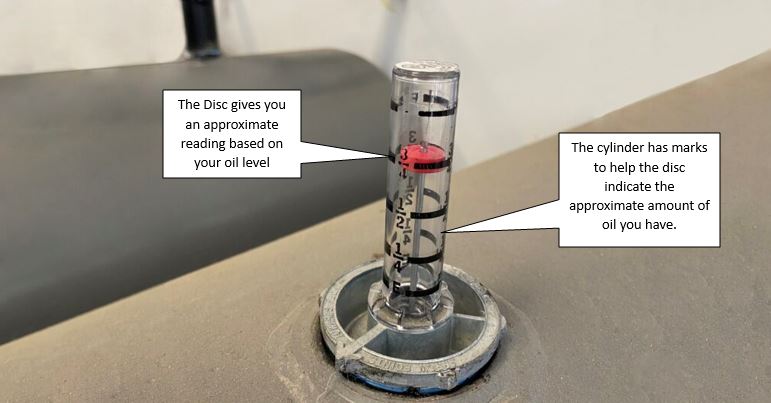
- The Float: This is a buoyant object (usually plastic or foam) that floats on the surface of the oil inside the tank. Think of it like a bobber on a fishing line – it rises and falls with the oil level.
- The Indicator Arm: This arm is connected to the float. As the float rises and falls, the arm moves accordingly.
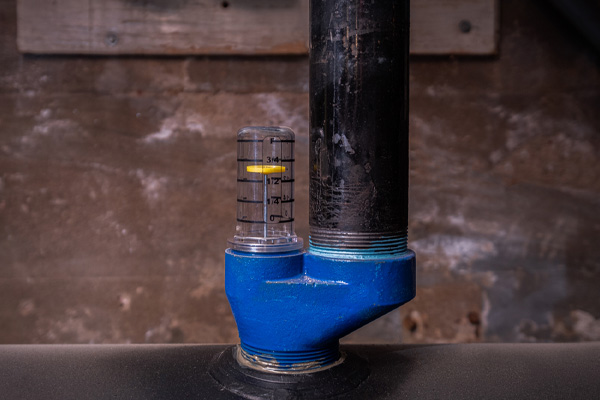
- The Gauge Face: This is the part you read. It's marked with numbers and/or fractions that indicate the level of oil in the tank. The markings typically range from empty (0) to full (1 or 100%).
Some gauges also have a small vent or cap on top. This allows air to escape as the tank is filled and prevents pressure from building up inside. Never attempt to remove this vent cap yourself, as you could damage the gauge or create a safety hazard.
Reading the Gauge: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you know where the gauge is and what it looks like, here's how to read it:
- Visually Inspect the Gauge: Before you even try to read the level, take a moment to inspect the gauge for any signs of damage. Look for cracks in the plastic housing, a broken or detached indicator arm, or any other visible problems. If the gauge appears damaged, do not attempt to read it. Contact a qualified technician to repair or replace the gauge.
- Gently Tap the Gauge (If Necessary): Sometimes, the float can get stuck, especially in older tanks. A gentle tap on the gauge housing might dislodge it and allow it to move freely. Don't hit it hard – a light tap is all that's needed.
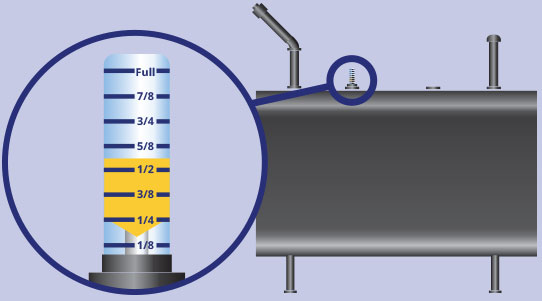
- Read the Number or Fraction: The gauge face will display a number or fraction indicating the oil level. Common markings include:
- Fractions: 1/4, 1/2, 3/4, Full. These fractions represent the percentage of the tank that is full. For example, 1/2 means the tank is half full.
- Numbers: 0 to 1 or 0 to 100%. These numbers represent the percentage of the tank that is full. For example, 0.5 or 50% means the tank is half full.
- Interpret the Reading: Once you've read the number or fraction, you need to understand what it means in terms of actual oil volume. This requires knowing the capacity of your tank.
Calculating Your Remaining Oil Volume
Knowing your tank's capacity is key to determining how much oil you actually have left. Tank capacity is typically measured in gallons. Common residential heating oil tank sizes include 275 gallons, 330 gallons, and 500 gallons.
Finding Your Tank's Capacity:
- Check the Tank Label: The tank's capacity is often printed on a label affixed to the tank itself. Look for a number followed by "gallons" or "gal."
- Check Your Homeowner's Records: If you can't find a label, check your homeowner's insurance policy, home inspection report, or previous oil delivery invoices. These documents may contain information about your tank size.
- Measure the Tank (If Necessary): As a last resort, you can estimate the tank's capacity by measuring its dimensions (length, width, and height) and using a tank volume calculator available online. Be extremely careful if you attempt to measure the tank yourself, and always prioritize safety.
Calculating Remaining Oil:
Once you know your tank's capacity and the gauge reading, you can calculate the approximate amount of oil remaining in your tank. Here's how:
Example:
- Tank Capacity: 275 gallons
- Gauge Reading: 1/4
- Calculation: (1/4) * 275 gallons = 68.75 gallons
This means you have approximately 68.75 gallons of oil remaining in your tank.
Troubleshooting Common Gauge Problems
Sometimes, your heating oil tank gauge might not work correctly. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
- Gauge Reads Empty Even Though You Just Had a Delivery: This could indicate a stuck float, a damaged gauge, or a leak in the tank or fuel lines. Contact a qualified technician immediately.
- Gauge Reads Full All the Time: This usually indicates a stuck float. A gentle tap on the gauge might dislodge it. If not, you'll need to have the gauge repaired or replaced.
- Gauge is Difficult to Read: Clean the gauge face with a damp cloth. If the markings are faded or damaged, consider replacing the gauge.
- Gauge is Leaking Oil: This is a serious problem. Turn off the oil burner immediately and contact your heating oil supplier or a qualified technician.
Why Regular Monitoring is Important
Regularly checking your heating oil tank gauge is essential for several reasons:
- Preventing Run-Outs: Running out of heating oil can be a major inconvenience, especially during cold weather. It can also damage your heating system and require a costly restart.
- Budgeting for Oil Deliveries: By monitoring your oil consumption, you can better predict when you'll need to order more oil and budget accordingly.
- Detecting Potential Problems: A sudden drop in oil level could indicate a leak in your tank or fuel lines. Early detection can prevent costly repairs and environmental damage.
Tips for Conserving Heating Oil
Besides monitoring your oil level, there are several steps you can take to conserve heating oil and save money on your energy bills:
- Insulate Your Home: Proper insulation can significantly reduce heat loss and lower your heating oil consumption. Focus on insulating your attic, walls, and floors.
- Seal Drafts: Seal any cracks or gaps around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent drafts.
- Lower Your Thermostat: Even a few degrees can make a difference. Consider using a programmable thermostat to automatically lower the temperature when you're away or asleep.
- Maintain Your Heating System: Regular maintenance, including cleaning and tuning, can ensure that your heating system is operating efficiently. Think of it like tuning your car engine - it helps it run smoother and more efficiently.
- Consider Upgrading to a More Efficient Heating System: If your heating system is old and inefficient, consider upgrading to a newer, more efficient model. While the initial cost may be higher, the long-term savings on your energy bills can be significant.
When to Order Heating Oil
A good rule of thumb is to order heating oil when your tank reaches 1/4 full. This gives you ample time to schedule a delivery and avoid running out of oil, especially during peak heating season. Some companies offer automatic delivery services, where they monitor your oil consumption and schedule deliveries automatically, ensuring that you never run out.
Professional Assistance
While reading your heating oil tank gauge is a relatively simple task, it's always a good idea to consult with a qualified heating technician if you have any concerns or questions. A technician can inspect your tank and gauge for any potential problems and provide expert advice on maintaining your heating system.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently read your heating oil tank gauge, manage your fuel supply effectively, and ensure a warm and comfortable home throughout the heating season. Regular monitoring and proactive maintenance are key to preventing problems and saving money on your heating bills.