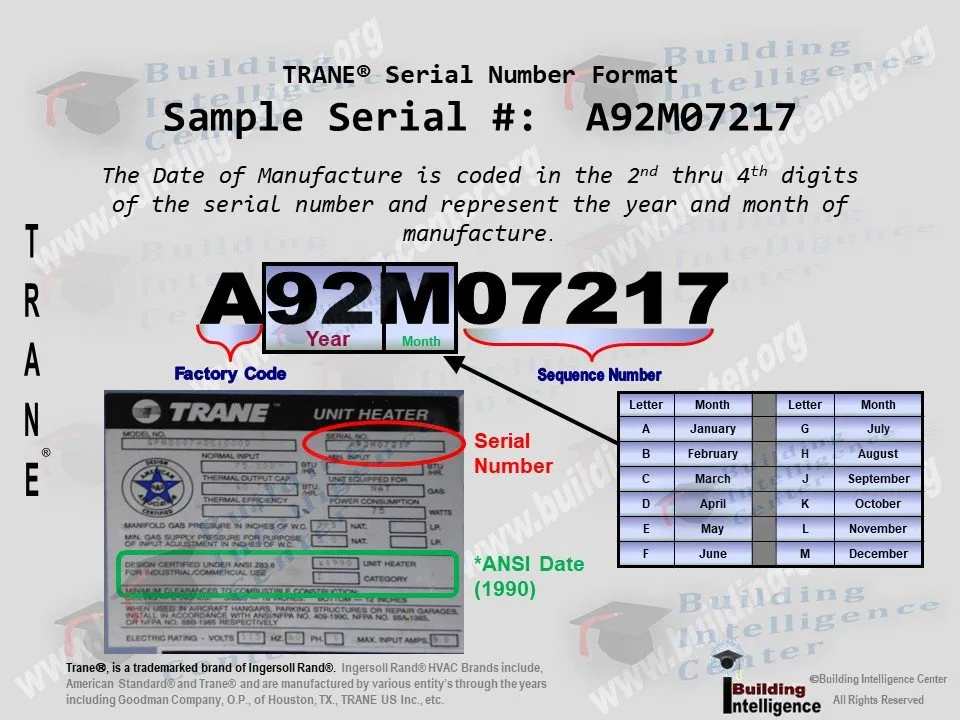
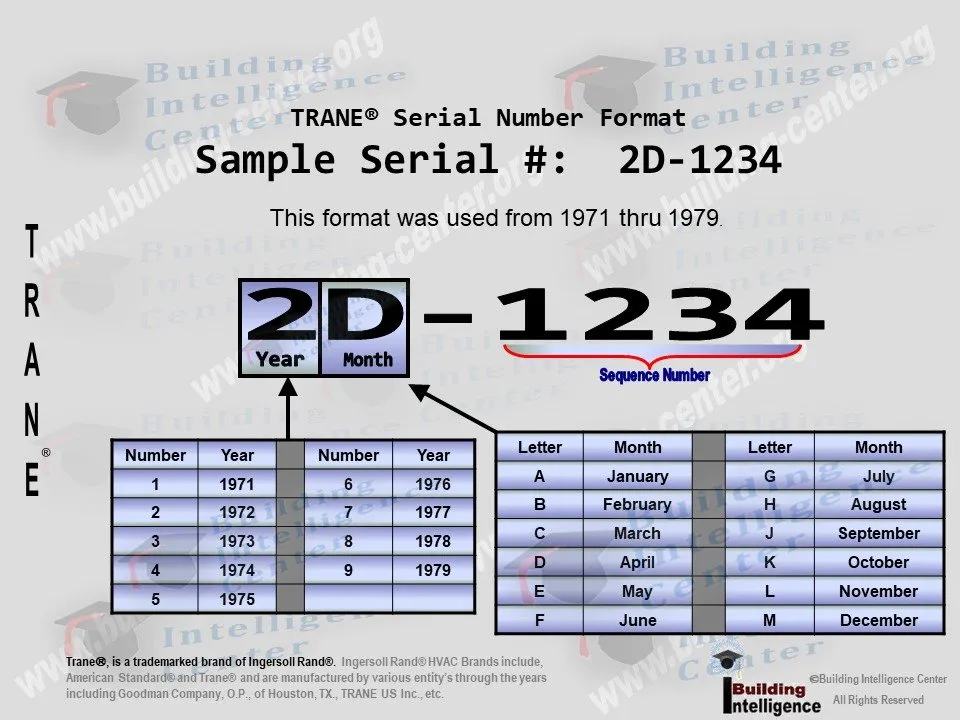
How To Read Trane Model Numbers
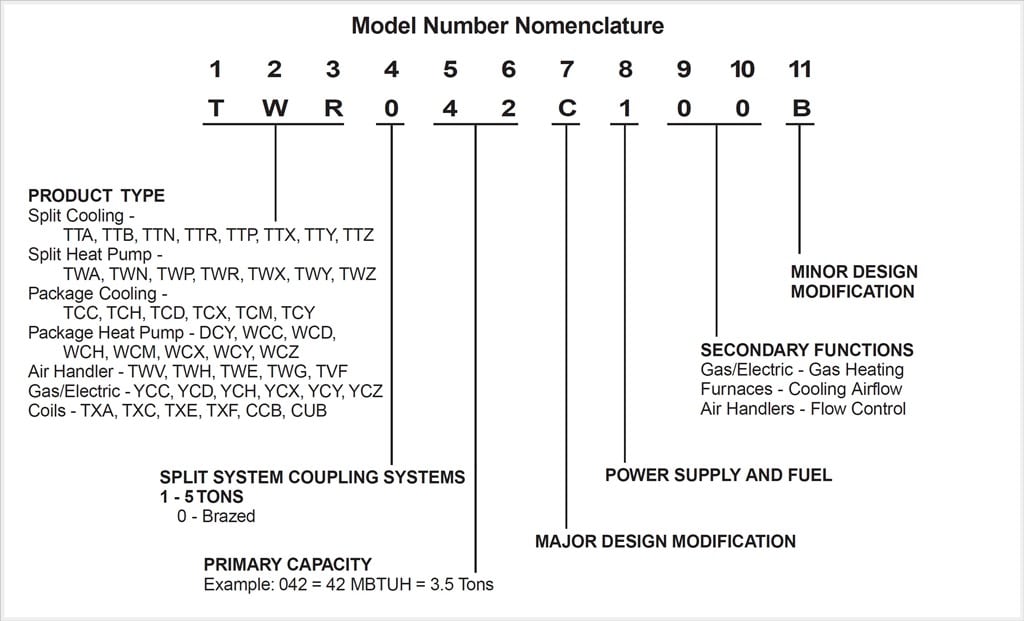
Understanding Trane model numbers might seem daunting, but it's a powerful tool for deciphering the capabilities and specifications of their HVAC systems. By breaking down the seemingly complex code, you can gain valuable insights into the unit's efficiency, size, features, and more. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently read and interpret Trane model numbers, helping you make informed decisions when purchasing or maintaining your HVAC equipment.
Decoding the Trane Model Number: A Step-by-Step Guide
Trane model numbers are generally a string of letters and numbers, each segment representing a specific characteristic of the unit. While the exact format can vary slightly depending on the type of equipment (e.g., air conditioner, heat pump, furnace), the underlying principles remain consistent. Let's dissect the most common elements:
1. Identifying the Product Type
The first few characters typically indicate the type of HVAC equipment. Common abbreviations include:
* XR: This often signifies a reliable, mid-range model, balancing performance and affordability. * XL: Denotes a higher-end, premium model with advanced features and enhanced efficiency. * XV: Indicates a variable-speed system, offering superior comfort and energy savings. Think of variable speed like a car's cruise control, adjusting the output to maintain a consistent temperature instead of simply turning on and off. * 4TTR: This is commonly used for air conditioner outdoor units. * 4TWX: Often used for heat pump outdoor units. * S: Frequently found in furnace model numbers.These prefixes help you quickly understand the basic category and performance level of the equipment.
2. Nominal Cooling Capacity (BTU/h)
Following the product type, you'll usually find a number indicating the nominal cooling capacity of the air conditioner or heat pump, measured in British Thermal Units per hour (BTU/h). This number represents the amount of heat the unit can remove from a space in one hour. However, this number is usually not the exact BTU rating. Instead, it is typically divided by 1000.
For example, a number like "024" represents approximately 24,000 BTU/h, which is equivalent to a 2-ton unit (since 1 ton = 12,000 BTU/h). Similarly, "036" corresponds to 36,000 BTU/h or a 3-ton unit, and "048" signifies 48,000 BTU/h or a 4-ton unit. "060" represents 60,000 BTU/h or a 5-ton unit. It’s vital to choose the right size for your space. An undersized unit will struggle to cool effectively, while an oversized unit can lead to short cycling and humidity issues.
Important Note: This is a *nominal* rating. The actual cooling capacity may vary slightly depending on operating conditions and other factors. Always consult the unit's official specifications for precise performance data.
3. Series or Version Number
Often located after the capacity indicator, this section usually consists of numbers and/or letters that define the specific series or version of the model. This is essential for identifying compatible components and finding accurate service information. This portion of the model number helps distinguish between different generations or variations of the same basic unit.
For instance, a suffix like "A" or "B" might indicate a revision with improved features or updated components. This number is particularly helpful for service technicians when ordering replacement parts or troubleshooting issues.
4. Efficiency Rating (SEER/HSPF/AFUE)
A critical element in the model number relates to the unit's energy efficiency. The way this is represented varies depending on the equipment type:
* SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): Primarily used for air conditioners and heat pumps, SEER measures the cooling efficiency over an entire cooling season. A higher SEER rating indicates greater energy savings. Modern air conditioners typically have SEER ratings ranging from 13 to 28. In some older models, this may be implicitly indicated by the model series (e.g., XL15i implies a higher SEER than XR13). New models now include this value as part of the model number. * HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor): Used for heat pumps, HSPF measures the heating efficiency over an entire heating season. A higher HSPF rating signifies better heating performance and lower energy costs. Look for models with an HSPF of 8 or higher. * AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency): Used for furnaces, AFUE represents the percentage of fuel that is converted into usable heat. A higher AFUE rating means less wasted energy and lower heating bills. Modern furnaces can have AFUE ratings ranging from 80% to over 98%.Understanding these ratings is crucial for evaluating the long-term cost-effectiveness of the equipment. A more efficient unit might have a higher upfront cost, but it can save you significant money on energy bills over its lifespan.
5. Refrigerant Type
The model number might also contain an indication of the refrigerant type used in the system. Think of refrigerant as the 'blood' of your AC system, carrying heat from inside to outside. The refrigerant type is increasingly important due to environmental regulations. Older systems often used R-22, which is now being phased out. Newer systems typically use R-410A or R-32, which are more environmentally friendly.
The presence of "410A" or similar designations confirms that the unit uses the newer, more sustainable refrigerant. Using the correct refrigerant is critical for the proper operation and longevity of the equipment.
6. Voltage and Phase
For larger commercial or industrial units, the model number might include information about the voltage and phase requirements. This is essential for ensuring compatibility with the electrical system. Examples might include "208/230-1" for single-phase 208/230-volt power or "460-3" for three-phase 460-volt power. Incorrect voltage can damage the equipment and pose a safety hazard.
7. Other Features and Options
Depending on the specific model, other codes might indicate additional features or options, such as: * i: Units with this denotation are often equipped with Trane’s communicating technology (eComfort/Nexia). * Variable-speed fan motor: This means the unit can adjust its airflow based on demand, providing more consistent temperatures and quieter operation. * Two-stage operation: This allows the unit to operate at two different levels of capacity, improving efficiency and comfort. * Sound insulation: This reduces the noise level of the unit, making it quieter to operate. * Coastal protection: This adds an extra layer of protection to the unit, protecting from corrosive elements.
Consult the manufacturer's documentation or contact a qualified HVAC technician for a complete explanation of all the codes in the model number.
Example: Decoding a Sample Trane Model Number
Let's take a hypothetical Trane model number: 4TTR4036M1000AA. Here's how we can break it down:
* 4TTR: Indicates an air conditioner outdoor unit. * 4: Series number. * 036: Approximately 36,000 BTU/h (3-ton) cooling capacity. * M: Is part of the series identification, but the specific meaning would require looking at the manufacturer's information for the precise model. * 100: Nominal SEER. * 0AA: Indicates the build series of the unit.By understanding these segments, you can quickly grasp the key specifications of this particular air conditioner.
Why Understanding Model Numbers Matters
Decoding Trane model numbers provides several benefits:
* Informed Purchasing Decisions: You can compare different models based on their efficiency, capacity, and features, ensuring you choose the best unit for your needs and budget. * Accurate Maintenance and Repairs: Technicians can use the model number to identify the correct replacement parts and access specific service information. * Troubleshooting Assistance: Knowing the model number allows you to find online resources and support forums specific to your equipment. * Warranty Claims: The model number is essential for registering your equipment and filing warranty claims. * Equipment Evaluation: When buying a home, understanding the age and efficiency of the existing HVAC system helps you assess potential future costs.Where to Find the Model Number
The model number is typically located on a nameplate affixed to the unit. For outdoor units (air conditioners and heat pumps), the nameplate is usually on the side or back of the unit. For indoor units (furnaces and air handlers), the nameplate is typically inside the unit, often accessible by removing a panel. The nameplate will also include the serial number. It's a good idea to take a picture of the nameplate and keep it for your records.
Final Thoughts
While Trane model numbers can seem complex at first, understanding the basic components empowers you to make informed decisions about your HVAC equipment. By using this guide as a reference, you can confidently navigate the world of Trane model numbers and ensure you are getting the right system for your home or business. Remember, when in doubt, consult a qualified HVAC professional for expert advice.