How To Wire Furnace To Generator

Connecting a furnace to a generator can be a crucial skill, especially during power outages. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to wire a furnace to a generator, focusing on safety, compliance, and best practices for HVAC professionals. It also touches on relevant career paths, certifications, and industry trends.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Wiring
A furnace is a critical component of a home's heating system, and ensuring its reliable operation during a power outage requires careful planning and execution. Improper wiring can lead to dangerous situations, including electrical fires, damage to the furnace or generator, and even carbon monoxide poisoning. Safety is paramount when dealing with electricity and gas-powered appliances.
Safety First: Disconnect Power and Follow Local Codes
Before you even think about touching any wires, disconnect the main power supply to your furnace. This is non-negotiable. Locate the circuit breaker that controls the furnace and switch it off. Then, verify that the power is indeed off using a non-contact voltage tester. Also, always consult your local electrical codes. These codes are in place for a reason and must be followed to ensure safety and compliance. Ignoring local codes can lead to fines and, more importantly, create hazardous conditions.
Essential Tools and Materials
Gather the necessary tools and materials before starting the wiring process. This will make the job smoother and more efficient. Here’s a list of essentials:
- Generator: Choose a generator with sufficient wattage to power your furnace. Check the furnace's nameplate for its power requirements (in watts or amps). Add a safety margin of at least 20% to ensure the generator can handle the load.
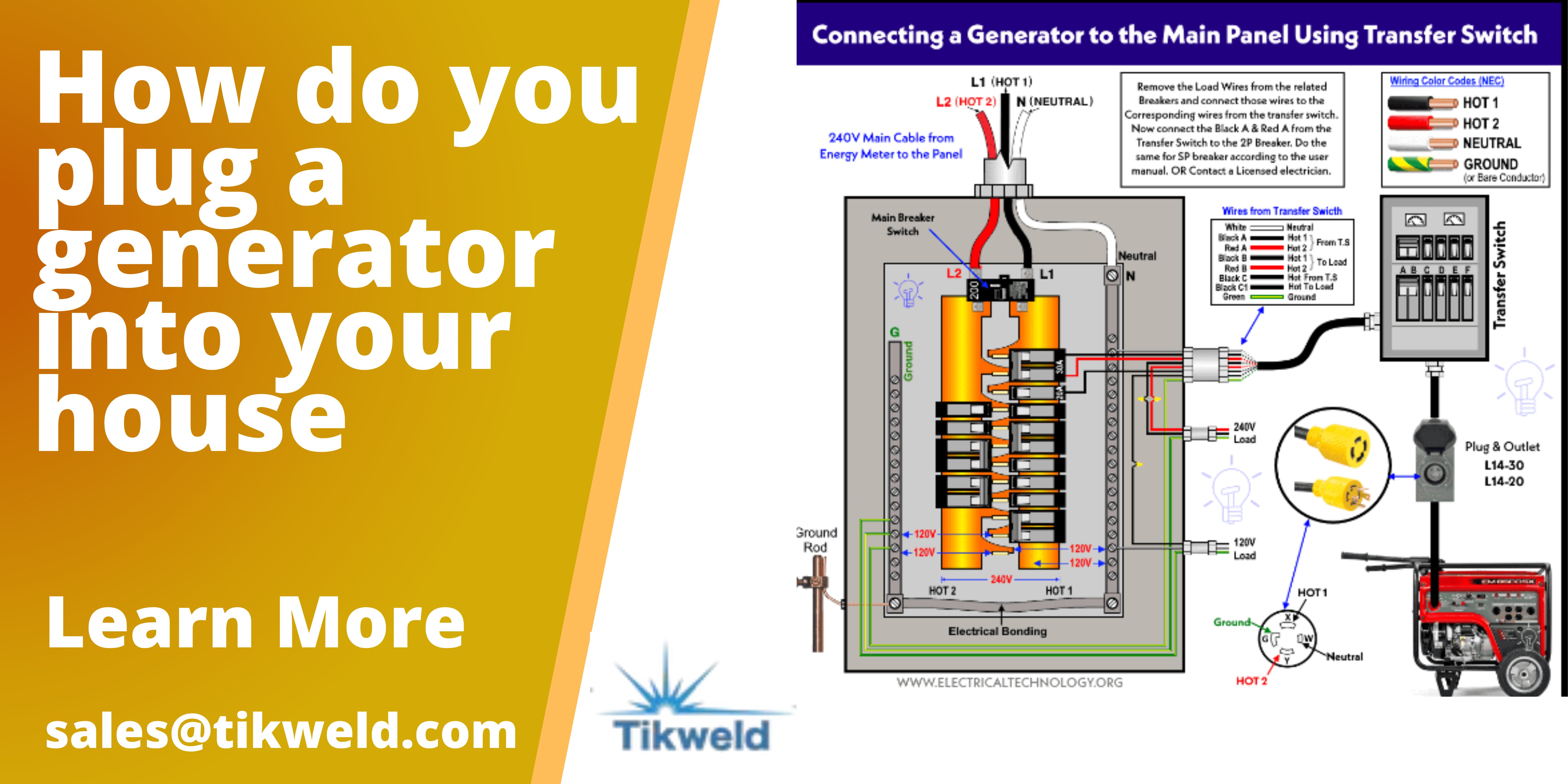
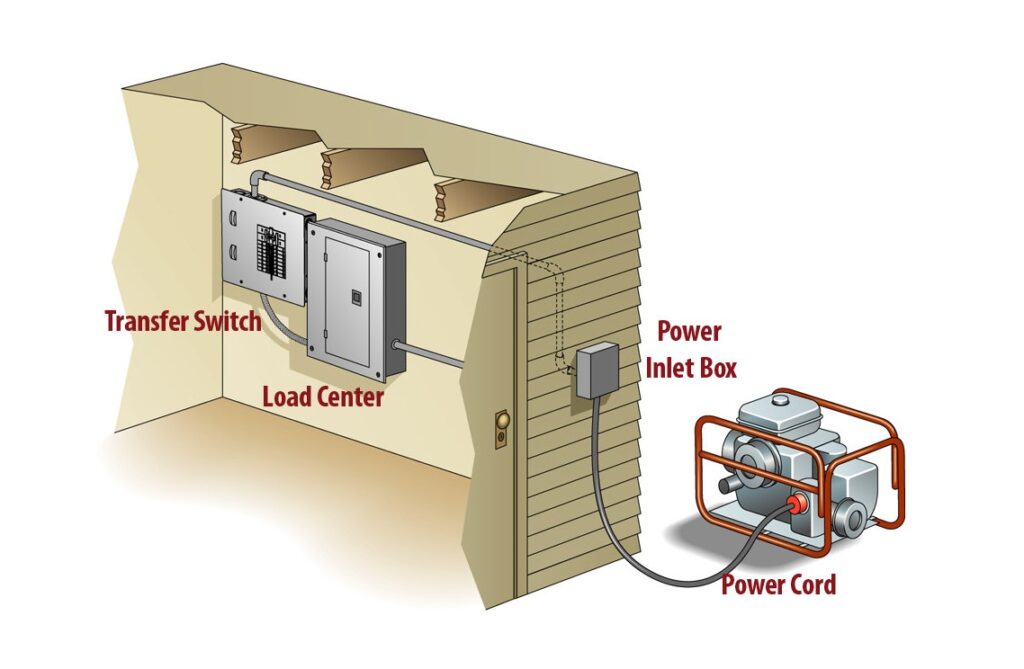
- Transfer Switch: A manual or automatic transfer switch is critical. It isolates the furnace circuit from the utility grid during generator operation, preventing backfeeding and potential harm to utility workers. This is a crucial safety component and often legally required.
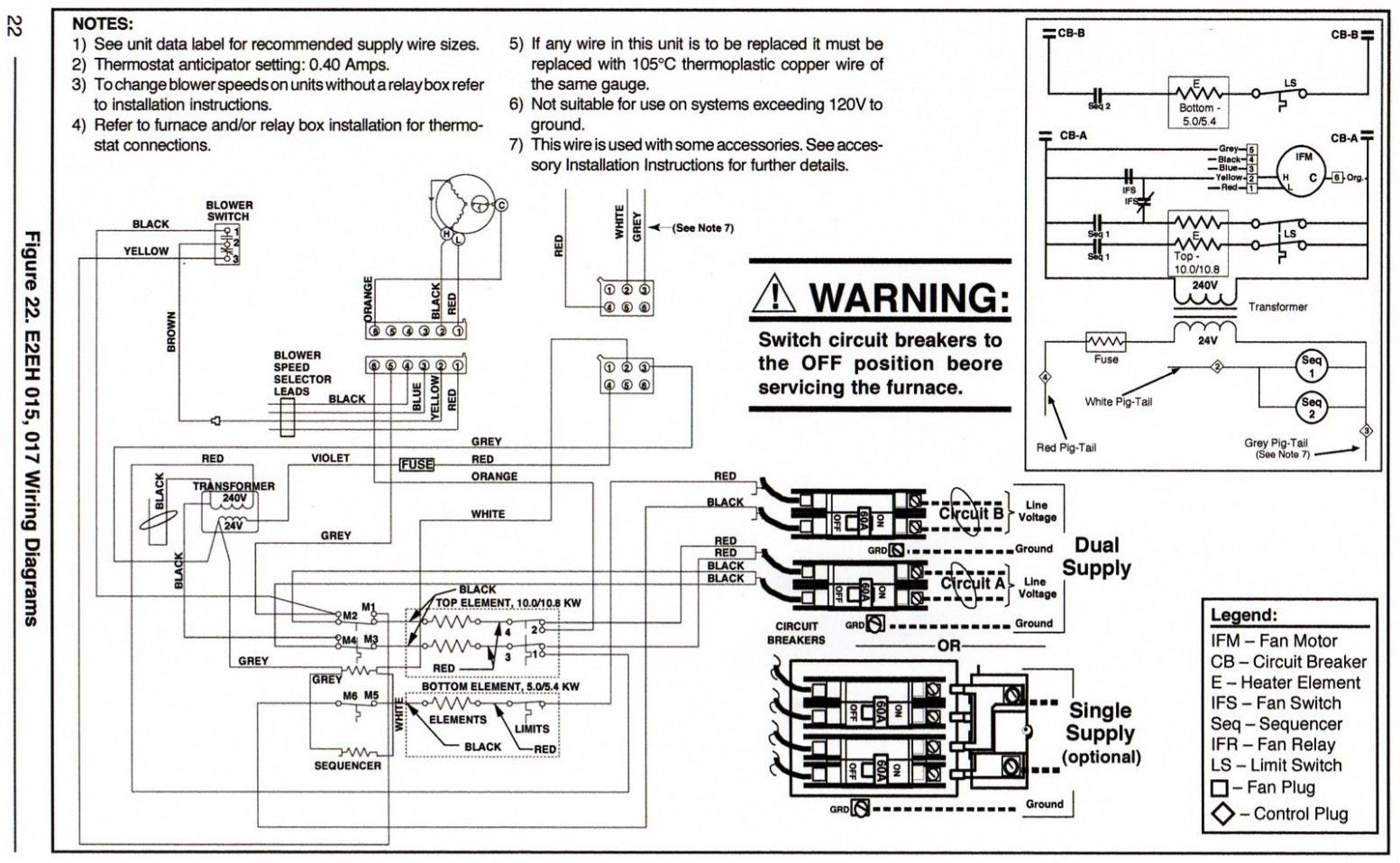
- Wiring: Use appropriately sized wiring (gauge) for the amperage of the furnace circuit. Consult an electrical chart to determine the correct wire gauge for your specific setup. Common types include THHN or NM-B cable.
- Conduit: Protect wiring with conduit, especially in exposed areas or where required by local codes. Rigid or flexible metal conduit (RMC or FMC) are common choices.
- Connectors and Fittings: Use appropriate connectors and fittings to ensure secure and weatherproof connections.
- Tools: Include wire strippers, wire connectors, screwdrivers, pliers, a multimeter, a voltage tester, and a drill.
Step-by-Step Wiring Guide Using a Transfer Switch
This guide outlines the general process. Always refer to the specific instructions provided with your generator and transfer switch, and consult a qualified electrician if you’re unsure about any step.
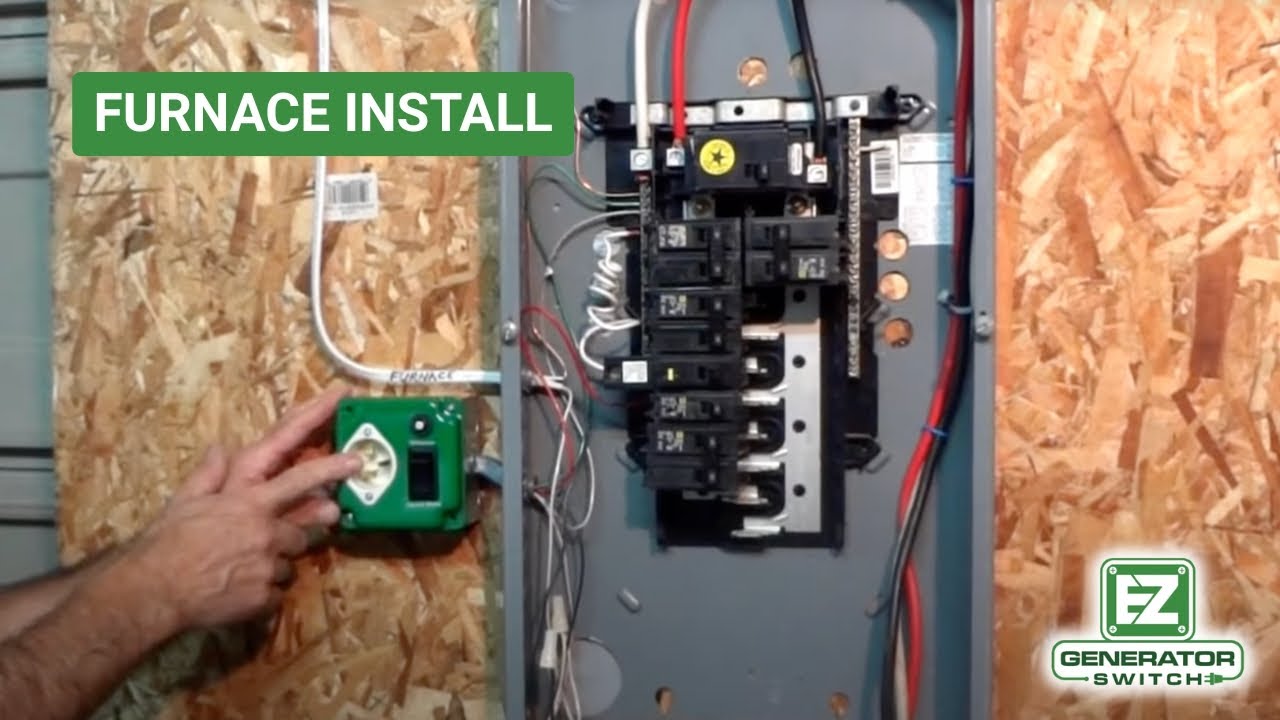
- Install the Transfer Switch: Mount the transfer switch near the main electrical panel. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for installation.
- Connect the Utility Power: Disconnect the main power supply to your home. Connect the utility power wires to the appropriate terminals on the transfer switch.
- Connect the Generator Power: Connect the generator power wires to the designated terminals on the transfer switch.
- Connect the Furnace Circuit: Identify the circuit breaker for the furnace in your main electrical panel. Disconnect the wire from the breaker and connect it to the transfer switch. Run a new wire from the transfer switch to the circuit breaker.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of the generator, transfer switch, and furnace. This is crucial for safety and preventing electrical shock. Connect all grounding wires to a common grounding point.
- Testing: After completing the wiring, test the system. Start the generator and switch the transfer switch to the generator power position. Verify that the furnace is operating correctly. Check voltage and amperage readings with a multimeter to ensure proper operation.
Transfer Switch Types: Manual vs. Automatic
Choosing the right transfer switch depends on your needs and budget. A manual transfer switch requires you to manually switch between utility power and generator power. This is a more affordable option but requires someone to be present during a power outage to switch over. An automatic transfer switch (ATS) automatically switches to generator power when it detects a power outage and switches back to utility power when it returns. This is a more convenient option but also more expensive.
Generator Sizing for Furnaces
Proper generator sizing is crucial to ensure the furnace operates correctly and to avoid overloading the generator. Furnaces require a significant amount of power to start up, known as the inrush current. To determine the appropriate generator size, follow these steps:
- Check the Furnace Nameplate: Locate the nameplate on the furnace, which lists the electrical specifications, including voltage, amperage, and wattage.
- Calculate Total Wattage: If the nameplate lists amperage, multiply it by the voltage to calculate the wattage. For example, if the furnace requires 10 amps at 120 volts, the wattage is 10 x 120 = 1200 watts.
- Account for Inrush Current: Multiply the running wattage by a factor of 2 to 3 to account for the inrush current. For example, if the running wattage is 1200 watts, the inrush wattage could be 2400 to 3600 watts.
- Add a Safety Margin: Add a safety margin of at least 20% to the inrush wattage to ensure the generator can handle the load without being overloaded.
Example: A furnace requires 1200 running watts and has an inrush current three times the running wattage (3600 watts). Adding a 20% safety margin (3600 x 0.20 = 720 watts) brings the total required generator wattage to 3600 + 720 = 4320 watts. Therefore, you would need a generator with a continuous output of at least 4320 watts.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful planning and execution, issues can arise. Here are some common problems and potential solutions:
- Furnace Not Starting: Check the generator’s output voltage and frequency. Ensure the transfer switch is properly engaged. Verify that the furnace's circuit breaker is not tripped.
- Generator Overload: The generator may be undersized for the furnace's load. Reduce the load on the generator or upgrade to a larger generator.
- Wiring Issues: Check for loose connections, damaged wires, or incorrect wiring. Use a multimeter to verify continuity and voltage levels.
Career Paths in HVAC and Electrical Work
The ability to wire a furnace to a generator is a valuable skill that can open doors to various career paths in the HVAC and electrical industries. Here are a few examples:
- HVAC Technician: Install, maintain, and repair heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 6% growth in employment for HVAC mechanics and installers from 2022 to 2032. The median annual wage for HVAC mechanics and installers was $59,690 in May 2023.
- Electrician: Install and maintain electrical systems in buildings. Electricians are in high demand, with a projected 6% growth in employment from 2022 to 2032. The median annual wage for electricians was $65,200 in May 2023.
- Generator Technician: Specialize in the installation, maintenance, and repair of generators. This is a growing field due to the increasing reliance on backup power systems.
Relevant Certifications
Obtaining relevant certifications can enhance your skills and credibility in the HVAC and electrical fields. Some important certifications include:
- NATE (North American Technician Excellence): Demonstrates competency in HVAC installation, maintenance, and service.
- EPA Section 608 Certification: Required for handling refrigerants.
- OSHA Safety Training: Covers workplace safety practices.
- Electrical Certifications (e.g., Journeyman Electrician, Master Electrician): Required for performing electrical work in many jurisdictions.
Real-world example: Sarah, an HVAC apprentice, obtained her NATE certification after completing her training program. This certification helped her secure a higher-paying job and advance in her career.
Industry Trends and the Future of HVAC
The HVAC industry is constantly evolving, driven by factors such as energy efficiency, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. Some key trends include:
- Smart HVAC Systems: Integration of smart thermostats and sensors to optimize energy consumption and improve comfort.
- High-Efficiency Equipment: Development of more efficient furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Combining HVAC systems with renewable energy sources such as solar and geothermal.
- Emphasis on Indoor Air Quality: Growing awareness of the importance of indoor air quality and the use of air purifiers and filtration systems.
As the industry continues to evolve, HVAC professionals will need to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices to remain competitive. Continuous learning and professional development are essential for long-term success in this field. Consider pursuing additional training and certifications to enhance your skills and knowledge.
Conclusion
Wiring a furnace to a generator is a complex task that requires careful planning, attention to detail, and adherence to safety guidelines. By following the steps outlined in this guide and consulting with qualified professionals when needed, you can ensure a safe and reliable power backup system for your home or business. Remember that safety is always the top priority, and never hesitate to seek professional assistance if you are unsure about any aspect of the wiring process. With the right skills and knowledge, you can contribute to a safer and more resilient community.