Hvac Control Systems For Large Buildings

Large buildings, whether sprawling office complexes, bustling retail centers, or expansive industrial facilities, face unique energy challenges. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are often the biggest energy consumers, driving up operational costs and impacting environmental footprint. Fortunately, advanced HVAC control systems offer a path towards significant energy savings, improved occupant comfort, and a healthier bottom line. This article explores the various types of HVAC control systems available for large buildings, their benefits, and how to choose the right system for your needs.
Understanding HVAC Control Systems
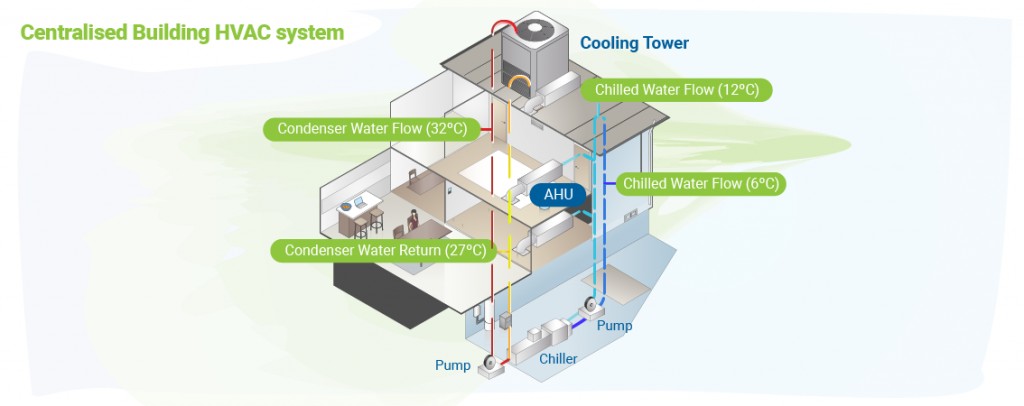
At their core, HVAC control systems manage and optimize the operation of heating, cooling, and ventilation equipment. These systems range from basic manual controls to sophisticated, automated platforms that integrate with other building systems. The goal is to maintain comfortable temperatures and adequate ventilation while minimizing energy consumption.
Types of HVAC Control Systems
Several types of HVAC control systems are available, each with varying levels of complexity and functionality:
- Traditional Thermostats: These basic controls are manually set to maintain a constant temperature. While simple and inexpensive, they lack the sophistication to adapt to changing occupancy patterns or external weather conditions, leading to energy waste.
- Programmable Thermostats: These thermostats allow users to set different temperature schedules for different times of day or days of the week. This can reduce energy consumption by lowering temperatures when the building is unoccupied. However, they rely on accurate programming and can be ineffective if schedules are not consistently followed.
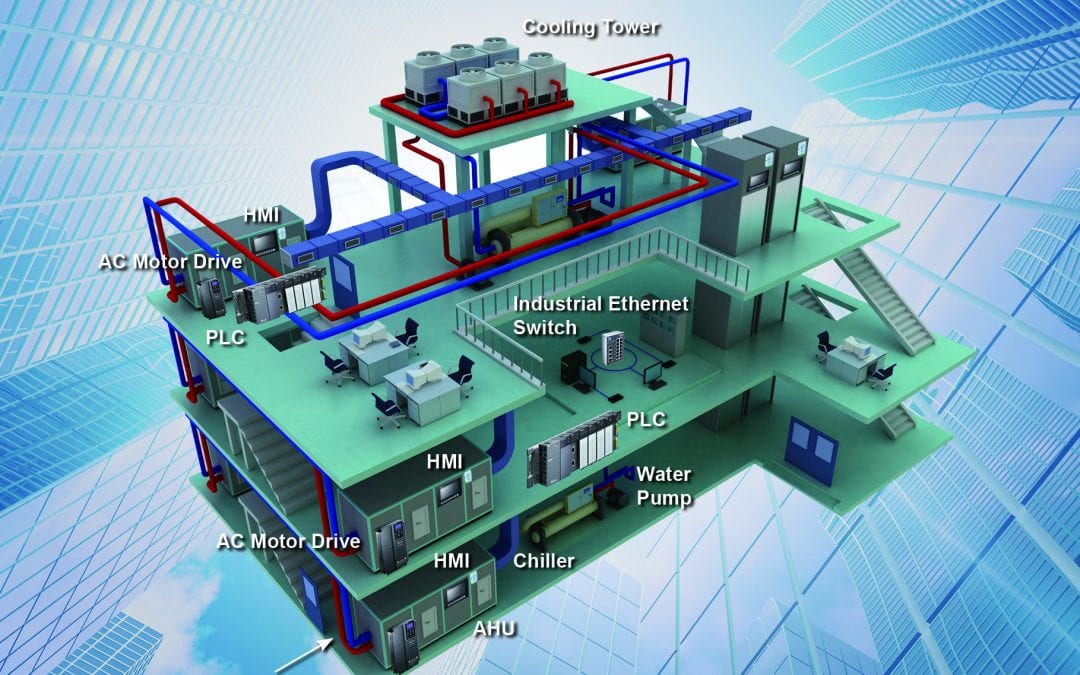
- Building Automation Systems (BAS): BAS are comprehensive control systems that integrate HVAC with other building systems like lighting, security, and fire alarms. They offer advanced control strategies, data logging, and remote monitoring capabilities.
- Direct Digital Control (DDC): A specific type of BAS, DDC systems use microprocessors to control HVAC equipment. DDC systems provide precise control, real-time monitoring, and the ability to implement sophisticated energy-saving strategies.
- Wireless HVAC Control Systems: Utilizing wireless sensors and communication protocols, these systems offer flexibility and ease of installation, particularly in existing buildings where running new wiring can be costly and disruptive.
- Smart HVAC Systems: These systems leverage advanced technologies like cloud connectivity, machine learning, and predictive analytics to optimize HVAC performance. They can learn occupancy patterns, anticipate weather changes, and adjust settings automatically to maximize energy savings and occupant comfort.
Benefits of Advanced HVAC Control Systems
Investing in an advanced HVAC control system offers numerous benefits for large buildings:
- Energy Savings: This is arguably the most significant benefit. Studies show that advanced HVAC control systems can reduce energy consumption by 15-30% or more, leading to substantial cost savings. For example, the Energy Star program offers resources and guidelines for optimizing HVAC performance and achieving significant energy reductions.
- Improved Occupant Comfort: Precise temperature control and adequate ventilation ensure a more comfortable and productive environment for building occupants.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Advanced control systems can monitor equipment performance, detect potential problems early, and schedule maintenance proactively, preventing costly breakdowns and extending equipment lifespan.
- Enhanced System Performance: Optimized control strategies ensure that HVAC equipment operates efficiently, maximizing its performance and lifespan.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Many advanced systems offer remote monitoring and control capabilities, allowing building managers to adjust settings, troubleshoot problems, and receive alerts from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Data-Driven Insights: These systems collect and analyze data on energy consumption, equipment performance, and occupant comfort, providing valuable insights that can be used to further optimize HVAC operations.
- Increased Property Value: Energy-efficient buildings are increasingly attractive to tenants and buyers, increasing property value and marketability.
- Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption contributes to a smaller carbon footprint and helps organizations meet their sustainability goals.
Key Features to Look For
When selecting an HVAC control system for a large building, consider the following key features:
- Scalability: The system should be able to accommodate the size and complexity of the building and be easily expandable as needs grow.
- Integration: The system should be able to integrate with other building systems, such as lighting, security, and fire alarms.
- User-Friendliness: The system should be easy to use and understand, with a clear and intuitive interface.
- Reporting and Analytics: The system should provide detailed reports and analytics on energy consumption, equipment performance, and occupant comfort.
- Remote Access: The system should offer remote monitoring and control capabilities.
- Security: The system should be secure and protected from unauthorized access.
- Open Standards: Systems using open communication protocols are often easier to integrate and maintain. Common protocols include BACnet and Modbus.
Integration with Smart Building Technologies
HVAC control systems can be seamlessly integrated with other smart building technologies to create a truly intelligent and energy-efficient environment. Some examples include:
- Smart Lighting: Integrating HVAC with smart lighting systems allows for coordinated energy savings. For example, when occupancy sensors detect that a room is unoccupied, both the lights and the HVAC system can be automatically turned down.
- Occupancy Sensors: These sensors detect the presence of people in a room and can adjust HVAC settings accordingly, ensuring that energy is only used when needed.
- Weather Data Integration: Integrating HVAC systems with real-time weather data allows them to anticipate changes in temperature and humidity and adjust settings proactively.
- Demand Response Programs: Participating in demand response programs allows building owners to reduce their energy consumption during peak demand periods, earning financial incentives and helping to stabilize the grid.
Calculating ROI and Incentives
The return on investment (ROI) for an HVAC control system upgrade can be significant, thanks to reduced energy costs and improved operational efficiency. To calculate the ROI, consider the following factors:
- Initial Investment: The cost of the new HVAC control system, including equipment, installation, and commissioning.
- Energy Savings: The estimated annual energy savings resulting from the upgrade. Base these estimates on historical energy consumption data and projected performance improvements.
- Maintenance Savings: The estimated annual maintenance savings resulting from the upgrade.
- Incentives and Rebates: Many utility companies and government agencies offer incentives and rebates for energy-efficient HVAC upgrades. Check with your local utility company and state energy office to see what incentives are available. The DSIRE (Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency) is a great resource for finding rebates and incentives.
For example, let's say a building owner invests $50,000 in a new HVAC control system that is projected to save $10,000 per year in energy costs and $2,000 per year in maintenance costs. The utility company offers a $5,000 rebate. The simple payback period would be:
($50,000 - $5,000) / ($10,000 + $2,000) = 3.75 years
This means the building owner would recover their investment in less than four years.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of an HVAC control system. It is essential to hire a qualified and experienced HVAC contractor to install the system. The contractor should be familiar with the specific type of system being installed and have experience working in large buildings.
Regular maintenance should be performed according to the manufacturer's recommendations. This may include cleaning sensors, calibrating controls, and inspecting wiring. A preventative maintenance plan can help to identify and address potential problems before they become major issues.
Choosing the Right HVAC Control System
Selecting the right HVAC control system for a large building requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Building Size and Complexity: Larger and more complex buildings require more sophisticated control systems.
- Occupancy Patterns: Buildings with variable occupancy patterns can benefit from systems that automatically adjust settings based on occupancy levels.
- Budget: The budget for the HVAC control system upgrade will influence the type of system that can be implemented.
- Energy Goals: The organization's energy goals will determine the level of energy savings that needs to be achieved.
- Existing Infrastructure: The existing HVAC equipment and building systems will influence the type of control system that can be easily integrated.
It is advisable to consult with an HVAC expert or energy consultant to assess your building's specific needs and recommend the most appropriate control system.
Investing in an advanced HVAC control system is a smart decision for large buildings looking to reduce energy costs, improve occupant comfort, and enhance operational efficiency. By carefully considering the various types of systems available, their benefits, and the specific needs of your building, you can select a system that delivers significant and lasting results. Remember to always look for Energy Star certified products when upgrading, as these products meet strict energy efficiency guidelines. Also consider the long-term cost savings and potential ROI when making your purchasing decision.