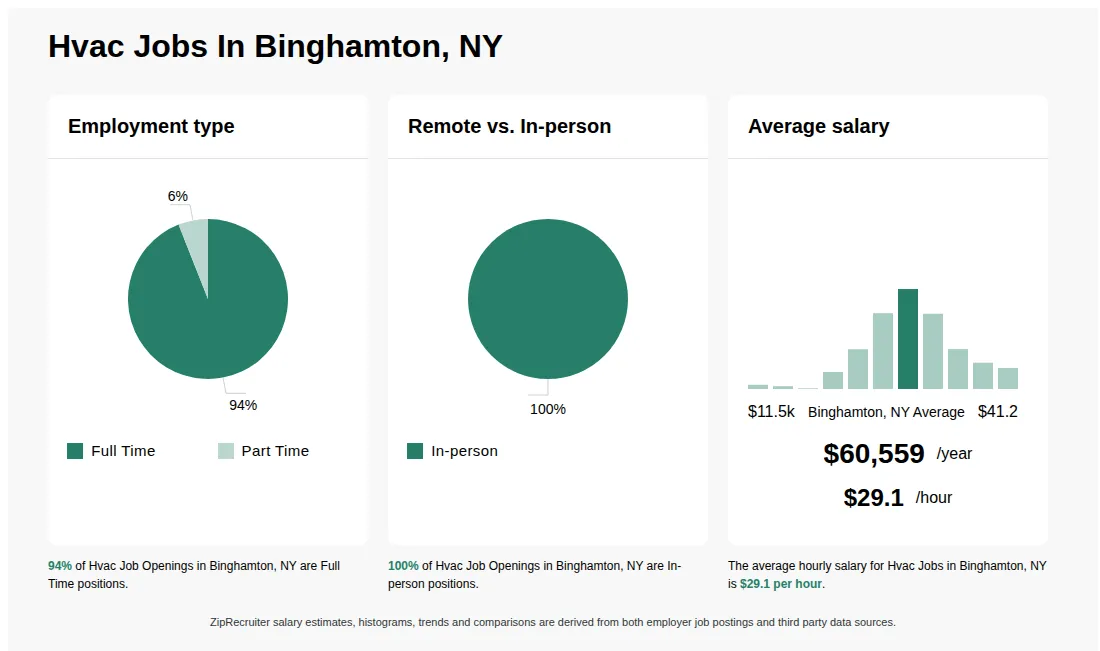
Hvac Jobs In New York Ny

New York City, a bustling metropolis of towering skyscrapers and diverse neighborhoods, presents a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape for the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry. From maintaining the climate control systems of iconic landmarks to ensuring comfortable environments in residential buildings, HVAC professionals are essential to the city's infrastructure and the well-being of its residents. This article provides a comprehensive overview of HVAC jobs in New York City, covering career paths, salary expectations, required certifications, and industry trends for students, experienced technicians, and employers.
The Demand for HVAC Professionals in NYC
The demand for skilled HVAC technicians in New York City is consistently high, driven by several factors:
- Aging Infrastructure: NYC's older building stock often requires upgrades and repairs to existing HVAC systems, creating a continuous need for maintenance and installation services.
- New Construction: Ongoing construction projects, including residential complexes, commercial buildings, and infrastructure developments, fuel the demand for HVAC professionals to install and commission new systems.
- Regulations and Energy Efficiency: Stringent energy efficiency regulations and building codes in NYC necessitate the installation of modern, energy-efficient HVAC equipment, leading to opportunities for technicians specializing in these technologies.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: NYC experiences extreme temperature variations throughout the year, placing a heavy reliance on HVAC systems for heating and cooling, thus requiring prompt maintenance and repair services.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the job outlook for HVAC mechanics and installers is projected to grow in the coming years. While specific NYC-level data can fluctuate, the general trend reflects a strong and stable demand across the metropolitan area.
HVAC Job Roles and Career Paths in NYC
The HVAC industry in NYC offers a diverse range of job roles, catering to different skill levels and career aspirations. Here are some common positions:
Entry-Level Positions
- HVAC Apprentice: Apprentices work under the supervision of experienced technicians, learning the fundamentals of HVAC systems through on-the-job training and classroom instruction. This is the most common entry point for individuals new to the field.
- HVAC Installer Helper: Helpers assist technicians with installing HVAC equipment, carrying tools, and performing basic tasks.
Mid-Level Positions
- HVAC Technician: Technicians diagnose, repair, and maintain HVAC systems, working independently or as part of a team. They possess a strong understanding of electrical, mechanical, and refrigeration principles.
- HVAC Service Technician: Service technicians specialize in troubleshooting and repairing HVAC systems, often responding to emergency calls and providing preventative maintenance.
- HVAC Installer: Installers focus on installing new HVAC systems, ensuring proper connections, and commissioning the equipment.
Advanced Positions
- HVAC Project Manager: Project managers oversee HVAC installation or renovation projects, coordinating teams, managing budgets, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- HVAC Estimator: Estimators assess project requirements and prepare cost estimates for HVAC installations or repairs.
- HVAC Design Engineer: Design engineers design HVAC systems for new construction or renovation projects, considering factors such as building size, occupancy, and energy efficiency.
- HVAC Supervisor: Supervisors lead and manage teams of HVAC technicians, providing guidance, training, and ensuring quality workmanship.
Real-world example: Maria started her career as an HVAC apprentice after completing a vocational program. She gained valuable experience working alongside seasoned technicians, eventually earning her certifications. After several years, she transitioned into a service technician role, where she excelled at diagnosing and repairing complex HVAC systems. Her dedication and technical expertise led to her promotion as a HVAC Supervisor, managing a team of technicians and overseeing large-scale projects.
HVAC Salaries in New York City
Salaries for HVAC professionals in New York City vary depending on experience, certifications, job role, and employer. Generally, NYC offers competitive compensation compared to the national average, reflecting the high cost of living and the strong demand for skilled technicians.
Here's a general salary range overview (as of late 2023 - early 2024; always check updated sources like BLS and Indeed for current data):
- HVAC Apprentice: $35,000 - $45,000 per year
- HVAC Technician: $50,000 - $75,000 per year
- HVAC Service Technician: $55,000 - $85,000 per year
- HVAC Installer: $48,000 - $70,000 per year
- HVAC Project Manager: $75,000 - $120,000+ per year
Experienced technicians with specialized skills and certifications, such as those related to energy efficiency or building automation, can command higher salaries. Overtime opportunities are also common, particularly during peak seasons.
Essential HVAC Certifications in NYC
Certifications play a crucial role in demonstrating competency and enhancing career prospects in the HVAC industry. Several certifications are highly valued in New York City:
- EPA Section 608 Certification: Required by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for technicians who handle refrigerants. There are different types of certifications based on the type of equipment serviced (Type I, Type II, Type III, and Universal). This is a non-negotiable requirement for most HVAC positions.
- NATE Certification: The North American Technician Excellence (NATE) certification is a widely recognized industry credential that demonstrates a technician's knowledge and skills in specific HVAC areas. NATE certification can significantly enhance a technician's credibility and earning potential.
- HVAC Excellence Certification: Another reputable certification program that validates HVAC technicians' skills and knowledge.
- OSHA Safety Certifications: OSHA 10-hour or 30-hour certifications are often required for construction-related HVAC jobs, demonstrating awareness of safety regulations.
- NYC Refrigeration Operating Engineer License: Required for operating and maintaining refrigeration systems exceeding a certain tonnage capacity in New York City. This requires specific experience and passing an exam administered by the city.
- Other Specialized Certifications: Depending on the specific job role, certifications related to specific equipment manufacturers, building automation systems (BAS), or energy efficiency may be beneficial.
Tip for students and apprentices: Prioritize obtaining the EPA 608 certification early in your career. It's a fundamental requirement and will open doors to numerous opportunities.
Finding HVAC Jobs in NYC
Several resources can help HVAC professionals find job opportunities in New York City:
- Online Job Boards: Websites like Indeed, LinkedIn, Glassdoor, and ZipRecruiter list numerous HVAC jobs in NYC.
- HVAC Industry Associations: Organizations like the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) and the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA) often have job boards and networking events.
- HVAC Companies' Websites: Many HVAC companies in NYC post job openings on their websites.
- Recruiting Agencies: Several recruiting agencies specialize in placing HVAC professionals in NYC.
- Networking: Attend industry events, connect with HVAC professionals on LinkedIn, and leverage your network to find job opportunities.
Industry Trends Shaping HVAC Jobs in NYC
The HVAC industry in NYC is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and sustainability initiatives. Some key trends include:
- Energy Efficiency: Growing demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems and technologies, driven by regulations and cost savings.
- Smart HVAC Systems: Increasing adoption of smart thermostats, building automation systems (BAS), and remote monitoring technologies.
- Sustainable Practices: Focus on sustainable HVAC practices, such as using environmentally friendly refrigerants and implementing energy-saving strategies.
- Indoor Air Quality: Heightened awareness of indoor air quality (IAQ) and the importance of proper ventilation and air filtration systems.
- Green Building Standards: New York City's commitment to green building standards like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is driving demand for HVAC professionals with expertise in sustainable design and construction.
Employers: Investing in training programs that focus on these emerging technologies and sustainable practices is crucial for staying competitive and attracting top talent.
Conclusion
HVAC jobs in New York City offer a rewarding and stable career path for individuals with the right skills, certifications, and dedication. The demand for qualified HVAC professionals is expected to remain strong, driven by the city's aging infrastructure, new construction projects, and commitment to energy efficiency and sustainability. By acquiring the necessary education, certifications, and experience, HVAC professionals can thrive in this dynamic and essential industry.