Most Efficient Temp For Air Conditioning

Finding the Sweet Spot: The Most Efficient Temperature for Your Air Conditioning
Balancing comfort and energy savings is a top priority for homeowners, HVAC technicians, and facility managers alike. Setting your air conditioning to the most efficient temperature can significantly reduce energy bills and extend the lifespan of your HVAC system. But what exactly is the most efficient temperature, and how do you determine the best setting for your specific needs and circumstances?
Understanding Efficiency: SEER, EER, and COP
Before diving into specific temperature recommendations, it's crucial to understand the key metrics that measure air conditioning efficiency. These ratings allow you to compare different systems and make informed decisions about your cooling needs:
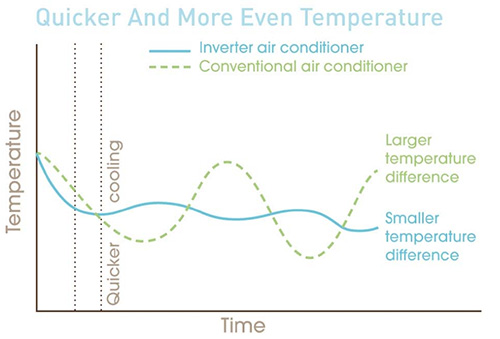
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio): This is the most common rating you'll see on air conditioning units. SEER measures the cooling output of an AC unit during a typical cooling season divided by the total electric energy input during the same period. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit. Modern AC units typically have SEER ratings ranging from 13 to 25 or higher. For example, a unit with a SEER of 18 is generally considered more efficient than a unit with a SEER of 14. Look for the Energy Star label to ensure the unit meets certain energy efficiency standards.
- EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio): EER measures the cooling output of an AC unit at a specific operating point (usually 95°F outdoor temperature and 80°F indoor temperature) divided by the electrical input. EER is useful for comparing the efficiency of units under specific, consistent conditions. A higher EER indicates better efficiency.
- COP (Coefficient of Performance): COP is typically used for heat pumps, which can both heat and cool. It represents the ratio of heating or cooling output to the electrical energy input. A higher COP indicates greater efficiency.
For homeowners, understanding these ratings is key to making informed decisions when purchasing new equipment. HVAC technicians use these ratings to properly size and install systems. Facility managers rely on these ratings to track energy consumption and identify opportunities for optimization.
The Recommended Temperature: A Balancing Act
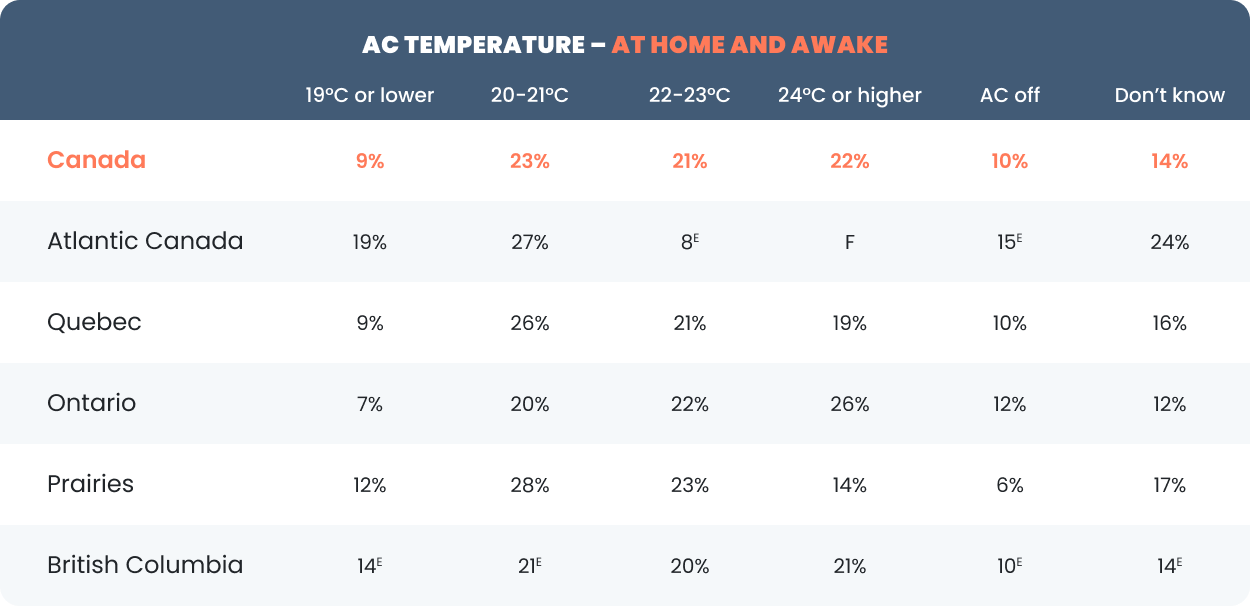
While personal preference plays a significant role, energy experts generally recommend setting your thermostat to 78°F (26°C) when you're home and awake. This temperature offers a good balance between comfort and energy savings. When you're away from home, or asleep, you can raise the thermostat to 82°F-85°F (28°C-29°C) to save even more energy. The U.S. Department of Energy recommends this approach to minimize energy consumption. Each degree you raise the thermostat can save you 1-3% on your cooling costs.
However, several factors influence the ideal temperature:
- Climate: In hotter climates, you might be tempted to set your thermostat lower. But even in these regions, 78°F is a good starting point. Consider using ceiling fans to circulate air and improve comfort without lowering the thermostat.
- Insulation: Homes with poor insulation will require more energy to maintain a consistent temperature. Upgrading insulation can significantly improve energy efficiency and allow you to set your thermostat higher without sacrificing comfort.
- Home Activity: If you engage in strenuous activities indoors, you may need to lower the thermostat for a short period. However, avoid consistently running the AC at a lower temperature, as this will significantly increase energy consumption.
- Personal Preference: Ultimately, comfort is a priority. Experiment with different temperatures to find a setting that works for you while minimizing energy waste.
Smart Thermostats: Automating Efficiency
Smart thermostats offer a convenient way to optimize your AC settings. These devices allow you to program different temperatures for different times of the day, ensuring that you're only cooling your home when necessary. Many smart thermostats also learn your habits and automatically adjust the temperature to maximize energy savings. Some models can even be controlled remotely via a smartphone app, allowing you to adjust the temperature from anywhere.
For example, a smart thermostat could be programmed to:
- Lower the temperature to 72°F an hour before you wake up.
- Raise the temperature to 78°F when you leave for work.
- Raise the temperature to 82°F during the hottest part of the afternoon.
- Lower the temperature to 72°F an hour before you return home.
This level of automation can significantly reduce energy consumption without sacrificing comfort. HVAC technicians often recommend smart thermostats as a key component of energy-efficient HVAC systems. Facility managers can use smart thermostats to monitor and control the temperature in multiple units, ensuring optimal energy use across an entire building.
Maintenance: Keeping Your System Running Efficiently
Even the most efficient AC unit will perform poorly if it's not properly maintained. Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and extending the lifespan of your system:
- Air Filter Replacement: Dirty air filters restrict airflow, forcing your AC unit to work harder and consume more energy. Replace your air filter every 1-3 months, or more frequently if you have pets or allergies.
- Coil Cleaning: The evaporator and condenser coils can become dirty over time, reducing their ability to transfer heat. Clean the coils regularly to maintain optimal efficiency. HVAC technicians typically recommend professional coil cleaning at least once a year.
- Ductwork Inspection: Leaky ductwork can waste a significant amount of energy. Inspect your ductwork for leaks and seal any cracks or holes.
- Professional Tune-Ups: Schedule annual tune-ups with a qualified HVAC technician. A technician can inspect your system, identify potential problems, and ensure that it's running at peak efficiency.
"Regular maintenance is the key to extending the lifespan of your HVAC system and maximizing energy savings." - HVAC Experts of America
Beyond Temperature: Other Ways to Improve Efficiency
Setting the right temperature is just one piece of the puzzle. Here are other strategies to improve your AC system's efficiency:
- Seal Air Leaks: Caulk windows and doors, and seal any cracks or holes in your home's exterior.
- Improve Insulation: Add insulation to your attic, walls, and floors.
- Use Fans: Ceiling fans and portable fans can help circulate air and make you feel cooler without lowering the thermostat.
- Close Curtains and Blinds: During the hottest part of the day, close curtains and blinds to block sunlight and reduce heat gain.
- Consider a Whole-House Fan: Whole-house fans can effectively cool your home at night by drawing in cool outside air and exhausting hot indoor air.
- Upgrade to a More Efficient Unit: If your AC unit is old or inefficient, consider upgrading to a newer model with a higher SEER rating.
Cost Considerations: Short-Term vs. Long-Term
While upgrading to a more efficient AC unit can be a significant upfront investment, the long-term savings can be substantial. Use an online energy calculator to estimate how much you could save each year by switching to a more efficient model. Remember to factor in installation costs, which can vary depending on the complexity of the project. In many cases, the energy savings will offset the initial cost of the upgrade over time.
Also, consider available rebates and tax incentives for energy-efficient appliances. Many utility companies offer rebates for purchasing Energy Star-certified AC units and installing smart thermostats. These incentives can further reduce the cost of upgrading your HVAC system.
Conclusion: Optimizing for Comfort and Savings
Finding the most efficient temperature for your air conditioning involves balancing comfort with energy savings. By understanding the key metrics of efficiency, adopting smart thermostat technology, and implementing regular maintenance, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption and extend the lifespan of your HVAC system. Whether you're a homeowner, HVAC technician, or facility manager, these strategies can help you optimize your cooling costs and create a more comfortable and energy-efficient environment.