P T Chart For 410a Refrigerant

Understanding the 410A Refrigerant PT Chart: A Comprehensive Guide for HVAC Systems
When it comes to the performance and efficiency of your HVAC system, understanding the properties of its refrigerant is crucial. 410A refrigerant, a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) blend, is a common choice in modern air conditioners and heat pumps. To properly diagnose issues, charge the system, and ensure optimal operation, technicians rely on a pressure-temperature (PT) chart. This guide will explain the PT chart for 410A, its importance, and how it relates to your HVAC system's performance.
What is a PT Chart?
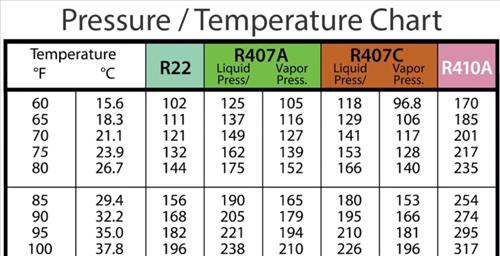
A PT chart is a table or graph that shows the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a refrigerant in a saturated state (meaning it's at a point where it can exist as both a liquid and a gas). For 410A, this chart provides specific pressure readings for corresponding temperatures. This information is critical for diagnosing problems like leaks or over/undercharging of the refrigerant, which directly impacts the cooling and heating capacity of your system.
Why is the 410A PT Chart Important?
The 410A PT chart is a vital tool for several reasons:
- Proper Charging: Ensures the correct amount of refrigerant is in the system. Overcharging or undercharging can drastically reduce efficiency and potentially damage the compressor, the heart of your HVAC system.
- Diagnostic Purposes: Helps identify potential issues such as restrictions in the refrigerant lines, compressor problems, or leaks. Abnormal pressure readings, when compared to the expected temperature, can pinpoint the problem area.
- System Performance: Optimizes the cooling and heating capacity of the system, leading to improved comfort and lower energy bills.
- Safety: Prevents potentially dangerous situations that can arise from operating a system with incorrect refrigerant levels.
Reading a 410A PT Chart
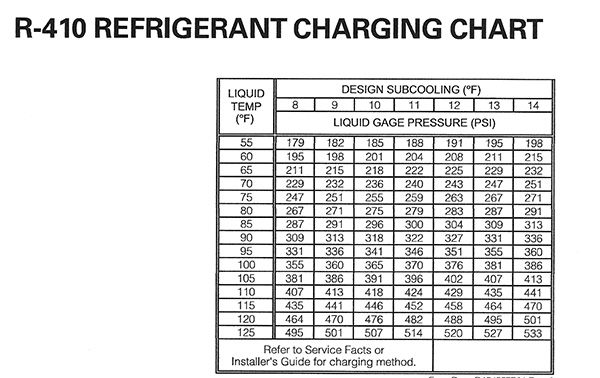
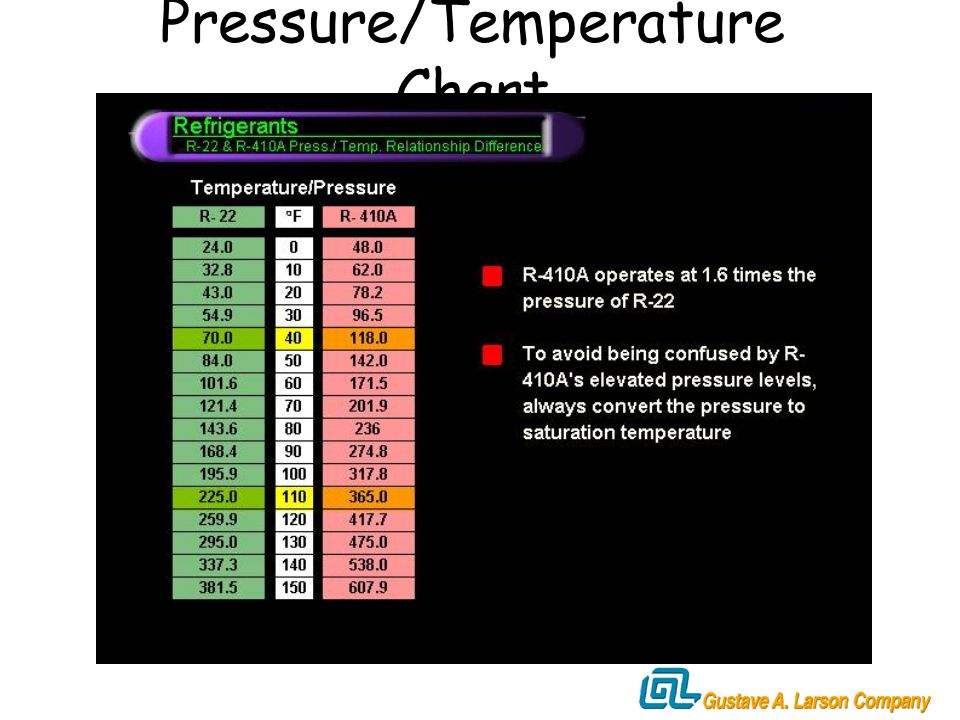
A typical 410A PT chart will list temperatures in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius, and corresponding pressures in pounds per square inch (PSI). Here's how to interpret it:
- Find the Temperature: Use a thermometer or temperature sensor to measure the temperature of the refrigerant line (usually the suction line).
- Locate the Corresponding Pressure: On the PT chart, find the temperature you measured. The chart will then show the corresponding pressure that the refrigerant *should* be at for that temperature, assuming it's in a saturated state.
- Compare Readings: Compare the pressure reading on the chart to the actual pressure reading on your system's gauges. Significant discrepancies indicate a potential problem.
Example Scenario
Let's say you measure the temperature of the suction line to be 60°F. Consulting a 410A PT chart, you find that the corresponding pressure should be around 118 PSI. If your gauge reads significantly lower, say 90 PSI, it could indicate a refrigerant leak or undercharge. Conversely, a much higher reading could suggest overcharging or a restriction in the system.
Common HVAC Issues Diagnosed with a PT Chart
The 410A PT chart is used to diagnose a variety of common HVAC problems:
- Refrigerant Leaks: Low pressure readings, coupled with a low temperature, strongly suggest a refrigerant leak. Finding and repairing these leaks is crucial for both efficiency and environmental reasons.
- Compressor Issues: Abnormal pressure readings, either high or low, can indicate a failing compressor. Compressors are expensive to replace, so early detection is key.
- Restrictions in Refrigerant Lines: Blockages or restrictions in the refrigerant lines can cause significant pressure drops. The PT chart helps identify these restrictions.
- Non-Condensables in the System: Air or other non-condensable gases in the refrigerant lines can cause high pressure readings. The PT chart helps identify their presence.
Choosing an HVAC System with 410A Refrigerant
While 410A is a common refrigerant, it is being phased out due to environmental concerns. Future HVAC systems will likely use refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP), such as R-32 or R-454B. When selecting a new HVAC system, consider the refrigerant type and its environmental impact. While 410A systems are still available, understand that they may become less common in the future, potentially impacting long-term serviceability.
Here's a look at some popular HVAC brands and models (using 410A where applicable, but note the trend towards alternatives):
Carrier
Pros: High efficiency, innovative technology, reliable performance.
Cons: Can be more expensive than other brands.
Example Model: Carrier Infinity Series (check refrigerant specifications for current models).
Ratings: AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) up to 98.5% for furnaces; SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) up to 26 for air conditioners; HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) up to 13 for heat pumps.
Trane
Pros: Durable construction, efficient operation, good warranty coverage.
Cons: Can be noisy compared to some competitors.
Example Model: Trane XV20i (check refrigerant specifications for current models).
Ratings: AFUE up to 97%; SEER up to 22; HSPF up to 10.
Lennox
Pros: Wide range of models, quiet operation, high efficiency options.
Cons: Installation costs can be higher.
Example Model: Lennox SL280V (check refrigerant specifications for current models).
Ratings: AFUE up to 99%; SEER up to 28; HSPF up to 12.
Goodman
Pros: More affordable than other brands, simple design, reliable operation.
Cons: May not have as many advanced features.
Example Model: Goodman GSX16 (check refrigerant specifications for current models).
Ratings: AFUE up to 96%; SEER up to 16; HSPF up to 9.
Warranties and Maintenance
A solid warranty is essential for any HVAC system. Pay close attention to the terms and conditions, including what is covered and for how long. Regular maintenance is also crucial for extending the life of your system and maintaining its efficiency. This includes:
- Annual Inspections: A qualified HVAC technician should inspect your system at least once a year.
- Filter Changes: Replace air filters regularly (typically every 1-3 months).
- Coil Cleaning: Keep the evaporator and condenser coils clean.
- Refrigerant Level Checks: Have the refrigerant level checked periodically and addressed if needed. Understanding how the 410A PT Chart works will help you discuss this service intelligently with your HVAC technician.
The Future of Refrigerants
As environmental regulations evolve, HVAC manufacturers are transitioning to refrigerants with lower GWP. Be aware of these changes and consider the long-term implications for your HVAC system. While 410A systems will likely be serviceable for many years to come, future systems will almost certainly use more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Conclusion
Understanding the 410A refrigerant PT chart is essential for ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of your HVAC system. It's a crucial tool for technicians diagnosing problems and optimizing performance. While the HVAC industry is moving towards newer refrigerants with lower environmental impact, knowledge of 410A remains important for servicing existing systems. By understanding the concepts discussed in this guide, you can be a more informed homeowner or real estate investor, making better decisions about your heating and cooling needs. Remember to always consult a qualified HVAC professional for any service or repairs related to your refrigerant system.