Parts Of An Air Conditioner System

Understanding the inner workings of your air conditioner is crucial for maximizing its efficiency, minimizing energy consumption, and ultimately, lowering your energy bills. Whether you're a homeowner aiming for a smaller carbon footprint, a business seeking to upgrade to a more eco-friendly system, a smart home enthusiast integrating advanced controls, or an HVAC contractor providing sustainable solutions, this guide breaks down the essential components of an air conditioner system and how they contribute to efficient cooling.
The Core Components of an Air Conditioning System
At its most basic, an air conditioner operates on the principle of heat transfer, moving heat from inside your home to the outside. This process relies on several key components working in harmony.
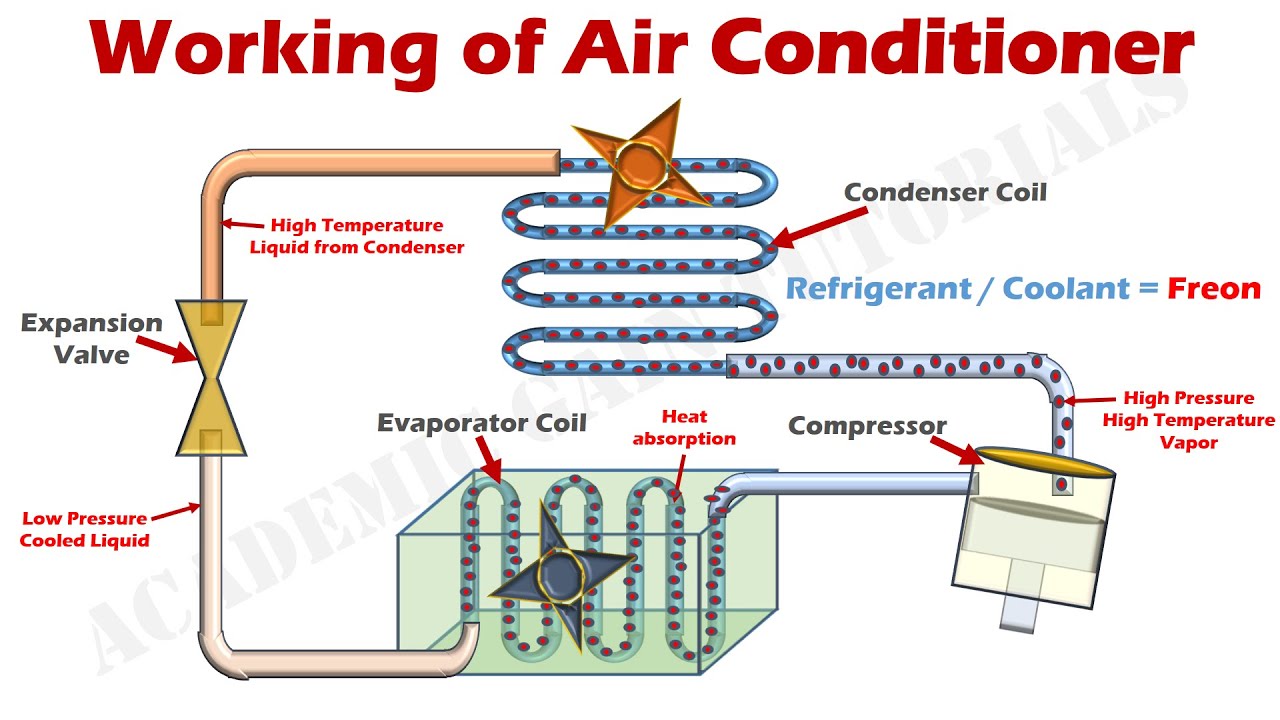
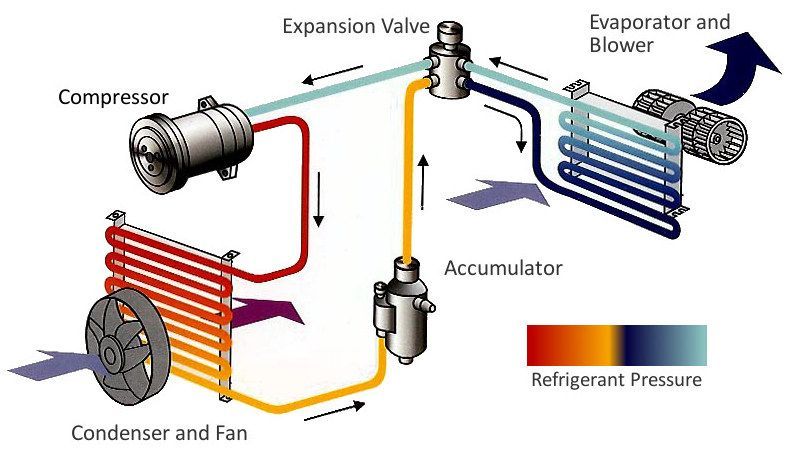
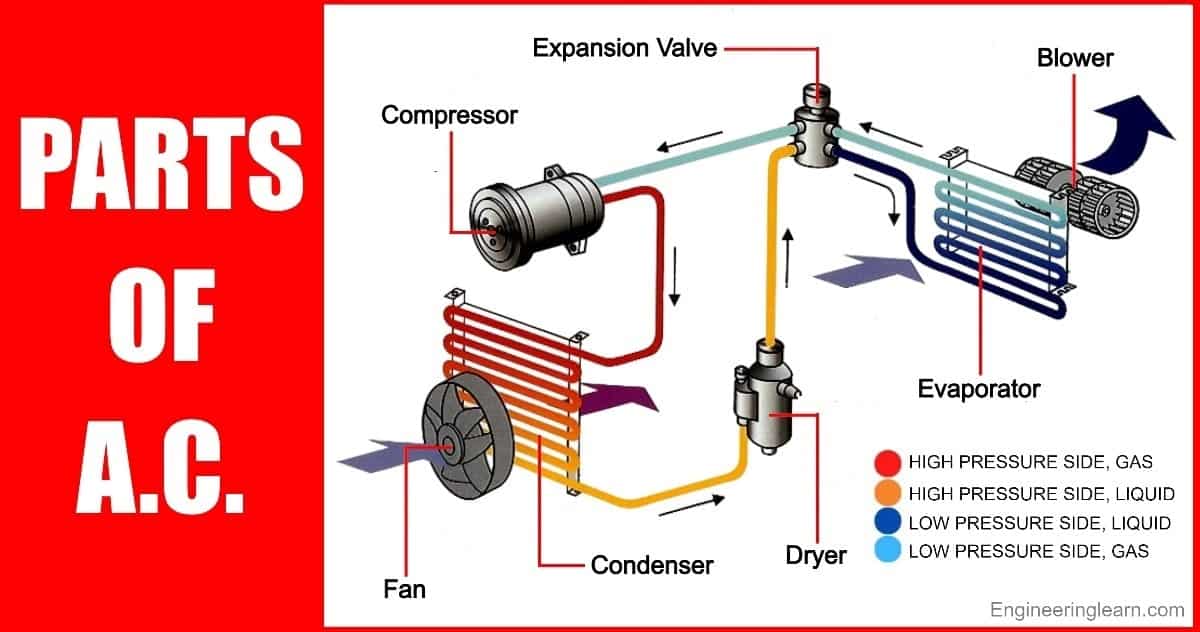
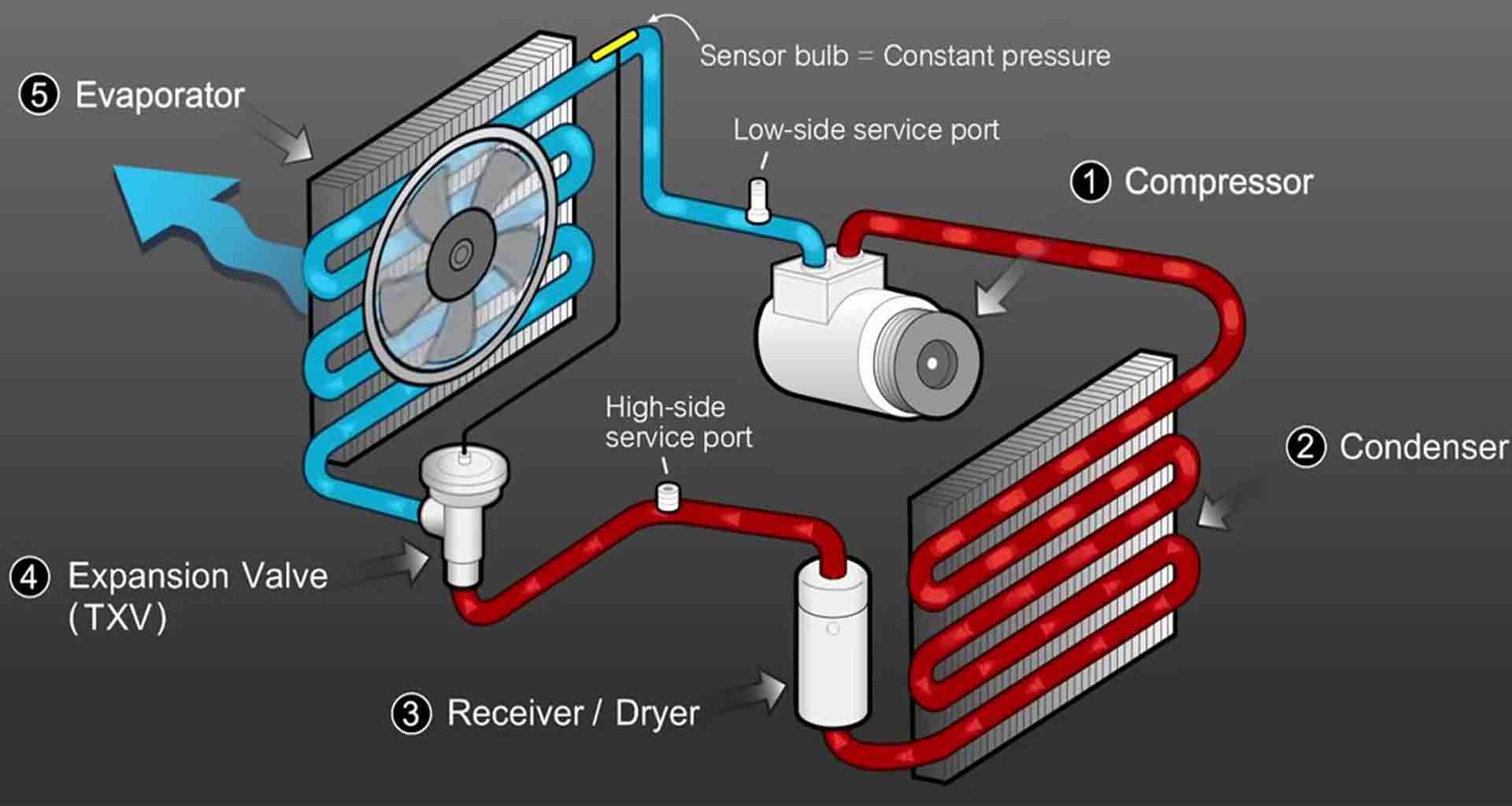
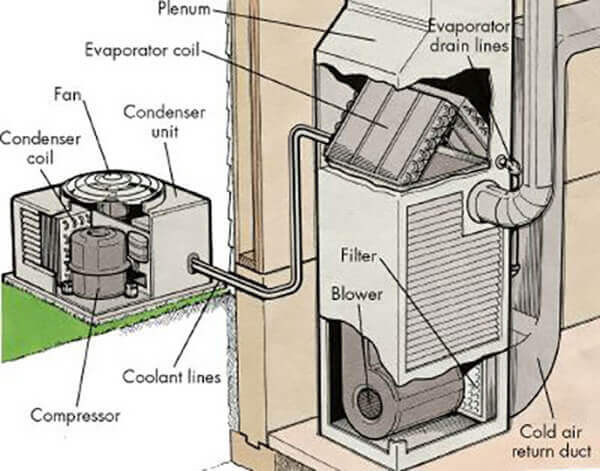
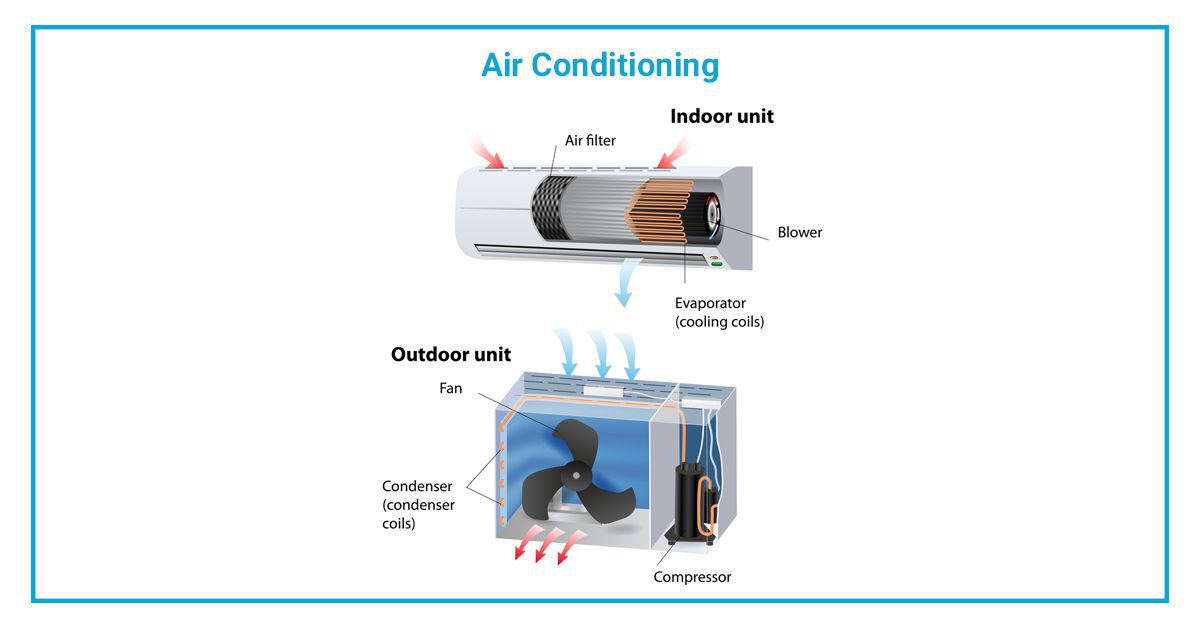
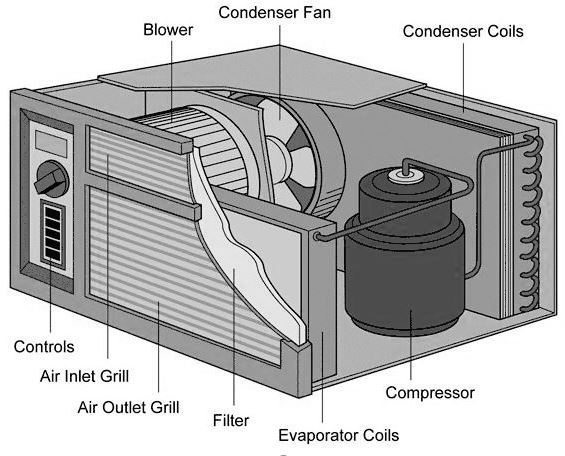
1. The Compressor: The Heart of the System
The compressor is arguably the most vital component. It's responsible for circulating the refrigerant, a special fluid that absorbs and releases heat, throughout the system. Think of it as the heart pumping blood through your body. The compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, preparing it to release heat in the condenser.
Energy Efficiency Considerations: Compressors consume a significant portion of the AC's energy. Newer, high-efficiency models often feature variable-speed technology. Variable-speed compressors, also known as inverter compressors, adjust their speed based on the cooling demand, using less energy during periods of lower demand compared to single-speed compressors that operate at full capacity regardless of the cooling load. According to Energy Star, upgrading to a high-efficiency AC with a variable-speed compressor can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%.
2. The Condenser: Releasing the Heat
Located outside your home, the condenser is where the high-pressure, hot refrigerant releases its heat to the outside air. The condenser consists of a coil (similar to a radiator in a car) and a fan. As the refrigerant flows through the coil, the fan blows air across it, dissipating the heat. The refrigerant then cools and condenses into a liquid.
Efficiency and Maintenance: A dirty condenser coil hinders heat transfer, forcing the compressor to work harder and consume more energy. Regularly cleaning the condenser coil, either yourself or by a professional, is crucial for maintaining optimal efficiency. Consider installing your outdoor condenser unit in a shaded area, as direct sunlight can increase its operating temperature and reduce its efficiency.
3. The Evaporator: Absorbing the Heat
The evaporator, situated inside your air handler, is where the cold, liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air. As warm air from your home passes over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant absorbs the heat, causing it to evaporate into a gas. The cooled air is then circulated back into your home.
Importance of Airflow: Proper airflow across the evaporator coil is essential for efficient cooling. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, reducing the evaporator's ability to absorb heat. Regularly replacing your air filter is a simple yet crucial step in maintaining your AC's efficiency. Consider using a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter for improved air quality, especially if you have allergies or respiratory issues.
4. The Expansion Valve (or Metering Device): Controlling Refrigerant Flow
The expansion valve, also known as a metering device, regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, allowing it to expand and cool down as it enters the evaporator coil.
Types of Expansion Valves: There are several types of expansion valves, including thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs) and capillary tubes. TXVs are more efficient as they adjust the refrigerant flow based on the cooling demand, while capillary tubes provide a fixed flow rate. Upgrading to a system with a TXV can improve overall efficiency.
5. Refrigerant: The Heat Transfer Medium
Refrigerant is the lifeblood of your air conditioning system. It's a special fluid that absorbs and releases heat as it cycles through the system. Older AC systems often used R-22 refrigerant, which is being phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties. Modern systems use more environmentally friendly refrigerants like R-410A.
Refrigerant Leaks: A refrigerant leak can significantly reduce your AC's efficiency and lead to costly repairs. If you suspect a leak, contact a qualified HVAC technician to locate and repair the leak. Regularly inspecting the refrigerant lines and connections can help prevent leaks.
6. Air Handler: Circulating the Cooled Air
The air handler contains the evaporator coil and a blower fan that circulates the cooled air throughout your home. It's typically located inside your home, often in an attic, basement, or closet.
Air Handler Maintenance: Ensure the air handler is properly insulated to prevent heat gain. Regularly inspect the blower fan and motor for dust and debris, and clean as needed. A well-maintained air handler contributes to efficient air circulation and consistent cooling.
Beyond the Basics: Smart HVAC Integration and Efficiency
Modern HVAC systems offer advanced features that can further enhance energy efficiency and comfort. Integrating your AC with smart home technology can provide greater control and optimization.
Smart Thermostats: Intelligent Temperature Control
Smart thermostats learn your heating and cooling preferences and automatically adjust the temperature based on your schedule and occupancy. They can be controlled remotely via a smartphone app, allowing you to adjust the temperature even when you're away from home. Many smart thermostats also provide energy usage reports, helping you identify areas where you can save energy.
ROI and Rebates: The initial investment in a smart thermostat is often offset by the energy savings it provides. Many utility companies offer rebates for installing smart thermostats, further reducing the cost. According to a study by Nest, their smart thermostat saves users an average of 10-12% on heating bills and 15% on cooling bills.
Zoning Systems: Targeted Cooling
Zoning systems divide your home into different zones, allowing you to control the temperature in each zone independently. This is particularly useful for homes with different heating and cooling needs in different areas. For example, you can cool the bedrooms at night while keeping the living areas warmer.
Benefits of Zoning: Zoning systems improve comfort and reduce energy waste by only cooling the areas that need it. They can be integrated with smart thermostats for even greater control and efficiency. The Department of Energy estimates that zoning systems can save homeowners up to 30% on their energy bills.
Sensors: Real-Time Data and Optimization
Integrating sensors into your HVAC system can provide real-time data on temperature, humidity, and occupancy. This data can be used to optimize the system's performance and ensure that it's only cooling when and where it's needed.
Applications of Sensors: Sensors can be used to detect when windows are open or closed, automatically adjusting the AC to prevent energy waste. They can also be used to monitor the temperature in different rooms and adjust the airflow accordingly. Advanced sensors can even detect air leaks and identify areas where insulation needs to be improved.
Maintenance for Optimal Efficiency
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring that your air conditioning system operates efficiently and reliably. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and costly repairs.
Regular Air Filter Replacement
As mentioned earlier, replacing your air filter regularly is one of the simplest and most effective ways to maintain your AC's efficiency. Dirty air filters restrict airflow, forcing the system to work harder and consume more energy. The frequency of filter replacement depends on the type of filter and the amount of dust and debris in your home, but a good rule of thumb is to replace it every one to three months.
Coil Cleaning
Keep the condenser and evaporator coils clean to ensure efficient heat transfer. You can clean the condenser coil yourself using a garden hose and a soft brush, but it's best to have a professional clean the evaporator coil to avoid damaging the delicate fins.
Professional HVAC Tune-Ups
Schedule regular tune-ups with a qualified HVAC technician. During a tune-up, the technician will inspect the system, clean the coils, check the refrigerant levels, and lubricate moving parts. This helps ensure that the system is operating at peak efficiency and can identify potential problems before they become major issues. Many HVAC contractors offer maintenance plans that include regular tune-ups at a discounted rate.
Government Guidelines and Rebates
The Energy Star program provides guidelines for energy-efficient appliances, including air conditioners. Look for Energy Star-certified AC units when purchasing a new system. These units meet strict energy efficiency standards and can save you money on your energy bills. Many utility companies and government agencies offer rebates for purchasing Energy Star-certified appliances and installing energy-efficient HVAC systems. Check with your local utility company and the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) for available rebates in your area.
Conclusion
Understanding the different components of your air conditioning system, embracing smart HVAC integration, and prioritizing regular maintenance are key steps to lowering energy costs and creating a more sustainable home or business. By investing in energy-efficient equipment, implementing smart controls, and following proper maintenance procedures, you can enjoy a comfortable indoor environment while minimizing your environmental impact and saving money on your energy bills. Don't underestimate the power of knowledge in transforming your approach to HVAC – a well-informed decision today leads to a greener and more cost-effective tomorrow.