Parts Of Central Air Conditioning System

Understanding Your Central Air Conditioning System: A Guide to Efficiency and Savings
Central air conditioning is a cornerstone of modern comfort, but understanding its components is crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing energy costs. Whether you're a homeowner looking to lower your bills, a business aiming for sustainable operations, or an HVAC contractor seeking to provide energy-efficient solutions, this guide will break down the essential parts of a central AC system and how they contribute to overall performance.
The Core Components
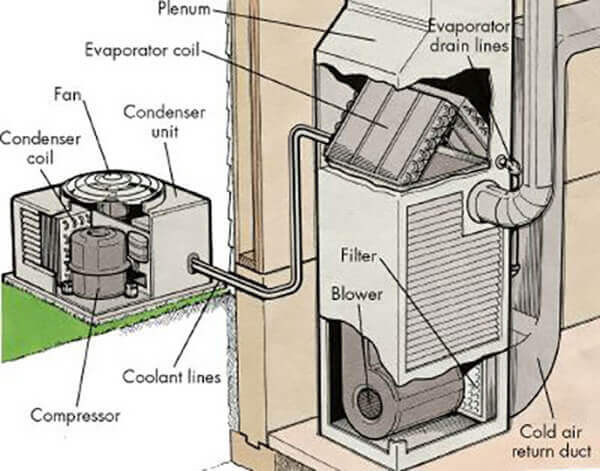
A central AC system isn't a single unit, but rather a collection of interconnected parts working in harmony to cool your indoor environment. Here’s a breakdown of the key players:
1. The Compressor: The Heart of the System
The compressor is arguably the most vital component. Located in the outdoor unit, it's the pump that circulates refrigerant throughout the system. It increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, turning it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas. A failing compressor often signals significant repair costs, and is one of the most expensive parts to replace. Upgrading to a more efficient compressor, like a scroll compressor, can significantly improve your system's Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating.
2. The Condenser: Releasing Heat to the Outside World
The condenser, also housed in the outdoor unit, is responsible for releasing the heat absorbed from inside your home. The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor flows through the condenser coils, where a fan blows air across them. This process cools the refrigerant, turning it into a high-pressure liquid. Regular cleaning of the condenser coils is essential for efficient operation; dirty coils impede heat transfer and force the compressor to work harder, increasing energy consumption. A study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) found that dirty condenser coils can reduce AC efficiency by up to 30%.
3. The Evaporator: Absorbing Heat from Inside
The evaporator, located inside your air handler or furnace, is where the cooling magic happens. The high-pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser flows through the evaporator coils, where it expands and evaporates, absorbing heat from the indoor air. A fan blows air across the cold evaporator coils, cooling the air and circulating it through your ductwork. A clogged or dirty evaporator coil can restrict airflow, reduce cooling capacity, and even cause the system to freeze up. Regular filter changes are crucial to prevent dust and debris from accumulating on the evaporator coil.
4. The Expansion Valve (or Metering Device): Regulating Refrigerant Flow
The expansion valve, also known as a metering device, controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, allowing it to expand and evaporate in the evaporator coils. Different types of expansion valves exist, including thermostatic expansion valves (TXVs) and fixed orifice devices. TXVs are generally more efficient as they automatically adjust refrigerant flow based on cooling demand, optimizing performance. Upgrading to a TXV can improve system efficiency and cooling capacity.
5. Refrigerant: The Lifeblood of the System
Refrigerant is the working fluid that circulates through the AC system, absorbing and releasing heat. Older systems often used R-22 refrigerant, which is being phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties. Modern systems use refrigerants like R-410A, which are more environmentally friendly. If your system uses R-22, consider upgrading to a newer system that uses a more sustainable refrigerant. Regulations surrounding refrigerants are constantly evolving, so staying informed is key.
6. Air Ducts: Delivering Cool Air
Air ducts are the network of channels that distribute cooled air throughout your home. Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can waste a significant amount of energy, as cooled air escapes into unconditioned spaces. According to the Department of Energy (DOE), duct leakage can account for up to 30% of energy loss in a central AC system. Sealing and insulating your ducts is a cost-effective way to improve energy efficiency. Consider having a professional perform a duct leakage test to identify and address any leaks.
7. Air Handler (or Furnace): Moving Air
The air handler, often part of your furnace system, houses the blower fan that circulates air through the evaporator coil and ductwork. The blower fan's speed and efficiency play a significant role in overall system performance. Variable-speed blowers offer superior comfort and energy savings compared to single-speed blowers, as they can adjust airflow based on cooling demand. This results in more consistent temperatures and reduced energy consumption. Many modern air handlers also include advanced filtration systems to improve indoor air quality.
8. Thermostat: The Brains of the Operation
The thermostat is the control center of your AC system. It senses the indoor temperature and signals the system to turn on or off to maintain the desired temperature. Programmable thermostats allow you to set different temperatures for different times of the day, reducing energy consumption when you're away or asleep. Smart thermostats take this a step further, learning your preferences and automatically adjusting the temperature based on your schedule and even external factors like weather conditions. Integration with smart home systems allows for remote control and advanced energy management features. Energy Star certified smart thermostats can save you up to 8% on your energy bills annually.
Smart HVAC Integration: Taking Control of Your Comfort and Savings
Integrating your central AC system with smart home technology opens up a world of possibilities for energy savings and enhanced comfort. Smart thermostats, sensors, and even smart vents can work together to optimize your system's performance. For example:
- Zoned Cooling: Smart vents allow you to control the airflow to individual rooms, directing cooling only to the areas where it's needed. This eliminates wasted energy cooling unoccupied spaces.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Smart thermostats allow you to monitor and control your AC system from anywhere using your smartphone or tablet. You can adjust the temperature, set schedules, and even receive alerts if there's a problem with your system.
- Predictive Maintenance: Some smart HVAC systems can monitor system performance and detect potential problems before they become major issues. This allows for proactive maintenance, preventing costly repairs and extending the lifespan of your system.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Pairing your smart HVAC system with solar panels can further reduce your energy costs and environmental impact. The smart system can prioritize using solar energy to power your AC system, reducing your reliance on the grid.
Maintenance Matters: Keeping Your System Running Efficiently
Regular maintenance is essential for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of your central AC system. Here are some key maintenance tasks:
- Change Air Filters Regularly: Dirty air filters restrict airflow, forcing the system to work harder and reducing efficiency. Check your air filter monthly and replace it as needed, typically every 1-3 months.
- Clean Condenser Coils: Dirty condenser coils impede heat transfer, reducing efficiency. Clean the coils at least once a year, preferably in the spring before the cooling season begins.
- Inspect and Seal Ducts: Leaky ducts waste energy and reduce cooling capacity. Have your ducts inspected and sealed by a professional to ensure optimal performance.
- Schedule Regular Maintenance: Have your system professionally inspected and tuned up at least once a year. A qualified HVAC technician can identify and address potential problems before they become major issues.
Energy Efficiency Incentives and Rebates
Many utility companies and government agencies offer incentives and rebates for upgrading to energy-efficient HVAC equipment. Energy Star certified systems often qualify for these incentives, which can significantly reduce the upfront cost of upgrading your system. Check with your local utility company and state energy office to learn about available incentives in your area. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) also provides tax credits and rebates for energy-efficient home improvements, including HVAC upgrades.
Calculating ROI: The Long-Term Benefits of Efficiency
While upgrading to a more efficient AC system may require an initial investment, the long-term savings can be substantial. By reducing your energy consumption, you can lower your monthly utility bills and reduce your carbon footprint. To calculate the Return on Investment (ROI) of an HVAC upgrade, consider the following factors:
- Initial Cost: The cost of the new system, including installation.
- Energy Savings: The estimated reduction in your energy consumption, based on the SEER rating of the new system.
- Utility Rates: Your current energy rates.
- Rebates and Incentives: Any rebates or incentives you may be eligible for.
- Lifespan: The expected lifespan of the new system.
By factoring in these variables, you can determine how long it will take for the energy savings to offset the initial cost of the upgrade. In many cases, energy-efficient HVAC systems pay for themselves within a few years.
Understanding the parts of your central air conditioning system is the first step towards optimizing its performance and saving money on your energy bills. By embracing smart technology, prioritizing regular maintenance, and taking advantage of available incentives, you can create a comfortable and energy-efficient home or business.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-central-air-conditioners-1152645_V2-390c6f1f6ca14b4ebc59426f226a78a8.png)