Piping Diagram For Hot Water Boiler

Imagine waking up on a chilly morning, ready for a hot shower, only to be greeted by a stream of icy water. A malfunctioning hot water boiler is a common household headache, but often, the problem isn't as daunting as it seems. This guide will walk you through basic troubleshooting steps, empowering you to identify and potentially resolve the issue yourself, while emphasizing safety and knowing when to call in a professional.
Understanding Your Hot Water Boiler and Its Piping Diagram
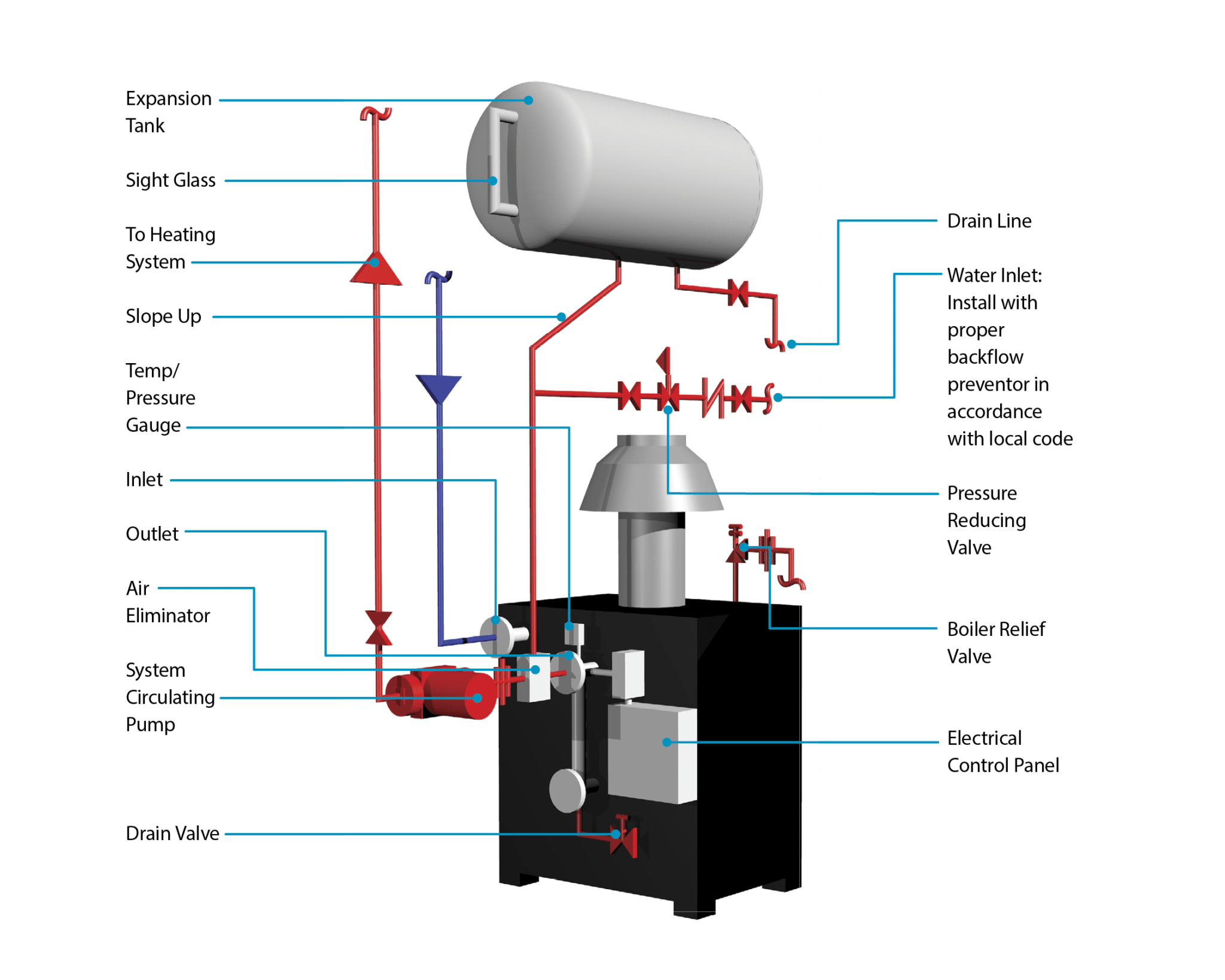
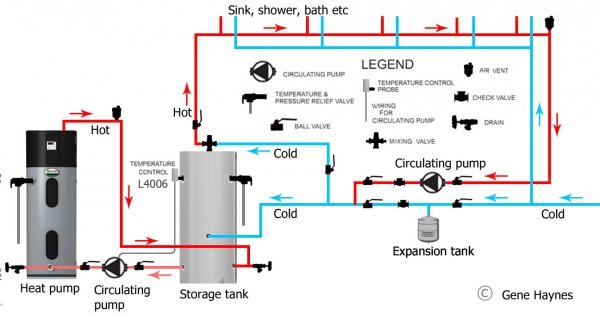
Before diving into troubleshooting, it's crucial to understand the basic components of your hot water boiler system and how they interact. A piping diagram is essentially a roadmap of your boiler, showing how water flows through it. It illustrates the connections between the boiler, cold water inlet, hot water outlet, expansion tank, pressure relief valve, circulator pump (if applicable), and other vital components.
Refer to your boiler's manual to find its specific piping diagram. This diagram will be invaluable during the troubleshooting process.
Key Components and Their Functions:
- Boiler: The core of the system, heating the water.
- Cold Water Inlet: Supplies cold water to the boiler.
- Hot Water Outlet: Delivers heated water to your plumbing fixtures.
- Expansion Tank: Accommodates the expansion of water as it heats, preventing pressure buildup.
- Pressure Relief Valve (PRV): A safety device that releases pressure if it exceeds a safe level.
- Circulator Pump (if applicable): Used in some systems to circulate hot water through the plumbing, ensuring faster hot water delivery.
- Drain Valve: Used to drain the boiler for maintenance or repairs.
- Temperature and Pressure Gauge: Displays the temperature and pressure within the boiler.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Follow these steps in a systematic manner to identify the cause of your hot water woes. Always prioritize safety and remember that working with electricity, gas, or complex mechanical components requires expertise.
Step 1: The Obvious - Check the Power Supply
Sometimes the simplest solutions are the most overlooked. Start with these basic checks:
- Check the Circuit Breaker: Locate the circuit breaker dedicated to the hot water boiler (refer to your electrical panel). If it's tripped (in the 'off' or middle position), flip it fully to the 'off' position and then back to the 'on' position.
- Check the Power Switch: Some boilers have a dedicated power switch on the unit itself. Ensure it is in the 'on' position.
- Check the Power Cord: If the boiler uses a power cord, ensure it is securely plugged into the outlet.
Safety First: Before working with any electrical components, ensure your hands are dry and you are standing on a dry surface. If you are unsure about electrical safety, call a qualified electrician.
Step 2: Examine the Boiler Settings
Incorrect settings can lead to inadequate hot water or no hot water at all.
- Temperature Setting: Check the thermostat on the boiler. Is it set to a reasonable temperature? A setting between 120°F (49°C) and 140°F (60°C) is generally recommended. Lower settings conserve energy, but higher settings may be necessary depending on your needs.
- Pilot Light (for Gas Boilers): If you have a gas boiler, check if the pilot light is lit. If not, carefully follow the manufacturer's instructions for relighting it. This usually involves turning a gas control knob to the 'pilot' position, pressing and holding a button to release gas, and simultaneously using a lighter or igniter to ignite the pilot flame.
- Vacation Mode: Some boilers have a 'vacation mode' which lowers the water temperature to conserve energy when you are away. Ensure this mode is disabled if you are home.
Gas Safety: If you smell gas, immediately leave the area and call your gas company or the fire department from a safe location. Do not attempt to relight the pilot light if you smell gas.
Step 3: Inspect the Pressure Relief Valve (PRV)
The PRV is a crucial safety device. If it's constantly leaking, it indicates a problem.
- Check for Leaks: Examine the PRV for any signs of water leakage. A small drip occasionally is normal, but a continuous leak indicates a problem.
- Pressure Reading: Look at the temperature and pressure gauge on the boiler. Is the pressure exceeding the recommended level (typically indicated on the gauge)? If so, the PRV might be activating to relieve excess pressure.
- Temporary Relief: (Caution: hot water may be released) Carefully lift the lever on the PRV manually to flush out any sediment that might be obstructing the valve. Release the lever quickly. If the leaking stops, the problem may have been a minor obstruction. If it continues to leak, the PRV may need replacement.
Safety First: Hot water can scald. Exercise extreme caution when working near the PRV.
Step 4: Examine the Expansion Tank
The expansion tank is designed to accommodate the expansion of water as it heats. A faulty expansion tank can lead to pressure problems and PRV leaks.
- Check for Waterlogging: Tap on the side of the expansion tank. It should sound hollow on the top and solid on the bottom. If it sounds solid all the way up, it may be waterlogged, meaning the air bladder inside has failed.
- Check Air Pressure: Locate the Schrader valve (similar to a tire valve) on the expansion tank. Remove the cap and use a tire pressure gauge to check the air pressure. The pressure should typically match the static water pressure in your plumbing system (usually around 12-15 PSI). If the pressure is low or non-existent, the tank may need to be recharged or replaced.
Professional Assistance: Recharging or replacing an expansion tank requires proper tools and knowledge of plumbing systems. It's best left to a qualified plumber.
Step 5: Check for Leaks in the Piping
Leaks can reduce the efficiency of your boiler and potentially cause water damage.
- Visually Inspect: Carefully examine all the pipes and fittings connected to the boiler for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. Pay close attention to joints and connections.
- Dampness or Staining: Look for dampness or staining around pipes, which can indicate slow leaks.
Small Leaks: Minor leaks at pipe joints can sometimes be temporarily fixed with plumbing tape or pipe sealant. However, for persistent or significant leaks, it's crucial to contact a plumber for professional repair.
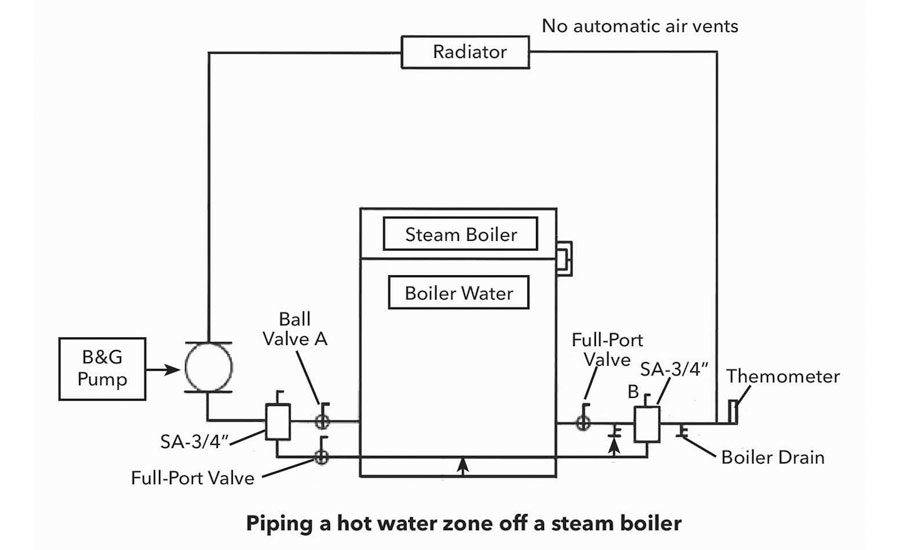
Step 6: Bleeding Air from the System (If Applicable)
Air trapped in the hot water system can cause noise, reduced heating efficiency, and uneven hot water distribution. If you have radiators or baseboard heaters, you may need to bleed them.
- Locate Bleeder Valves: Find the bleeder valves on your radiators or baseboard heaters. They are usually small valves located near the top of the unit.
- Prepare a Container: Have a container (e.g., a small bowl or cup) and a rag ready to catch any water that is released.
- Open the Bleeder Valve: Slowly open the bleeder valve using a bleeder key or a small screwdriver. You should hear air hissing out.
- Close the Valve: Once water starts to flow out steadily without any air, close the bleeder valve tightly.
- Repeat: Repeat this process for each radiator or baseboard heater in your system.
Caution: The water released from the bleeder valves may be hot. Be careful not to burn yourself.
Step 7: Checking the Circulator Pump (If Applicable)
If your system uses a circulator pump to circulate hot water, a malfunctioning pump can lead to no hot water or inconsistent hot water delivery.
- Listen for Noise: Put your ear close to the pump and listen for any unusual noises, such as grinding, humming, or rattling.
- Check for Vibration: Feel the pump to see if it is vibrating excessively.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the pump for any signs of leaks.
Professional Assistance: Replacing a circulator pump involves electrical and plumbing work and should be done by a qualified technician.
When to Call a Professional
While these troubleshooting steps can help you identify and resolve common hot water boiler problems, there are situations where it's essential to call a qualified professional:
- Gas Leaks: If you smell gas, evacuate the area immediately and call your gas company or the fire department.
- Electrical Problems: If you are uncomfortable working with electricity or suspect a serious electrical issue, call a qualified electrician.
- Complex Repairs: If the problem involves complex mechanical components, such as the burner, gas valve, or electronic control board, it's best to leave the repair to a qualified technician.
- Persistent Leaks: If you have persistent or significant leaks, contact a plumber for professional repair.
- Lack of Experience: If you are unsure about any step in the troubleshooting process, it's always better to err on the side of caution and call a professional.
- Boiler Age: If your boiler is old and frequently experiencing problems, it may be more cost-effective to replace it with a new, more efficient model.
Remember: Your safety is paramount. Don't hesitate to call a professional if you are unsure about anything.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance can help prevent hot water boiler problems and extend the life of your system.
- Annual Inspection: Schedule an annual inspection by a qualified technician. They can identify potential problems and perform necessary maintenance.
- Flush the Boiler: Periodically flush the boiler to remove sediment buildup. This can improve efficiency and prevent corrosion. Refer to your boiler's manual for instructions.
- Check the PRV and Expansion Tank: Regularly check the PRV and expansion tank for leaks or signs of failure.
- Insulate Pipes: Insulate hot water pipes to reduce heat loss and improve efficiency.
By following these troubleshooting steps and preventive maintenance tips, you can keep your hot water boiler running smoothly and enjoy a reliable supply of hot water for years to come.