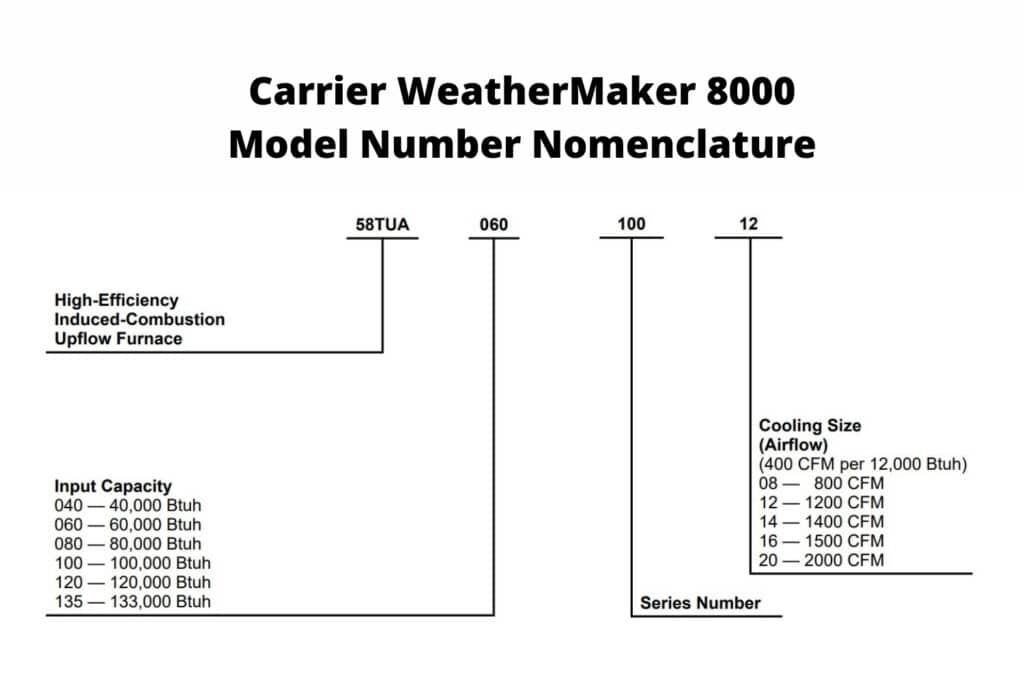
Reading Carrier Model Numbers
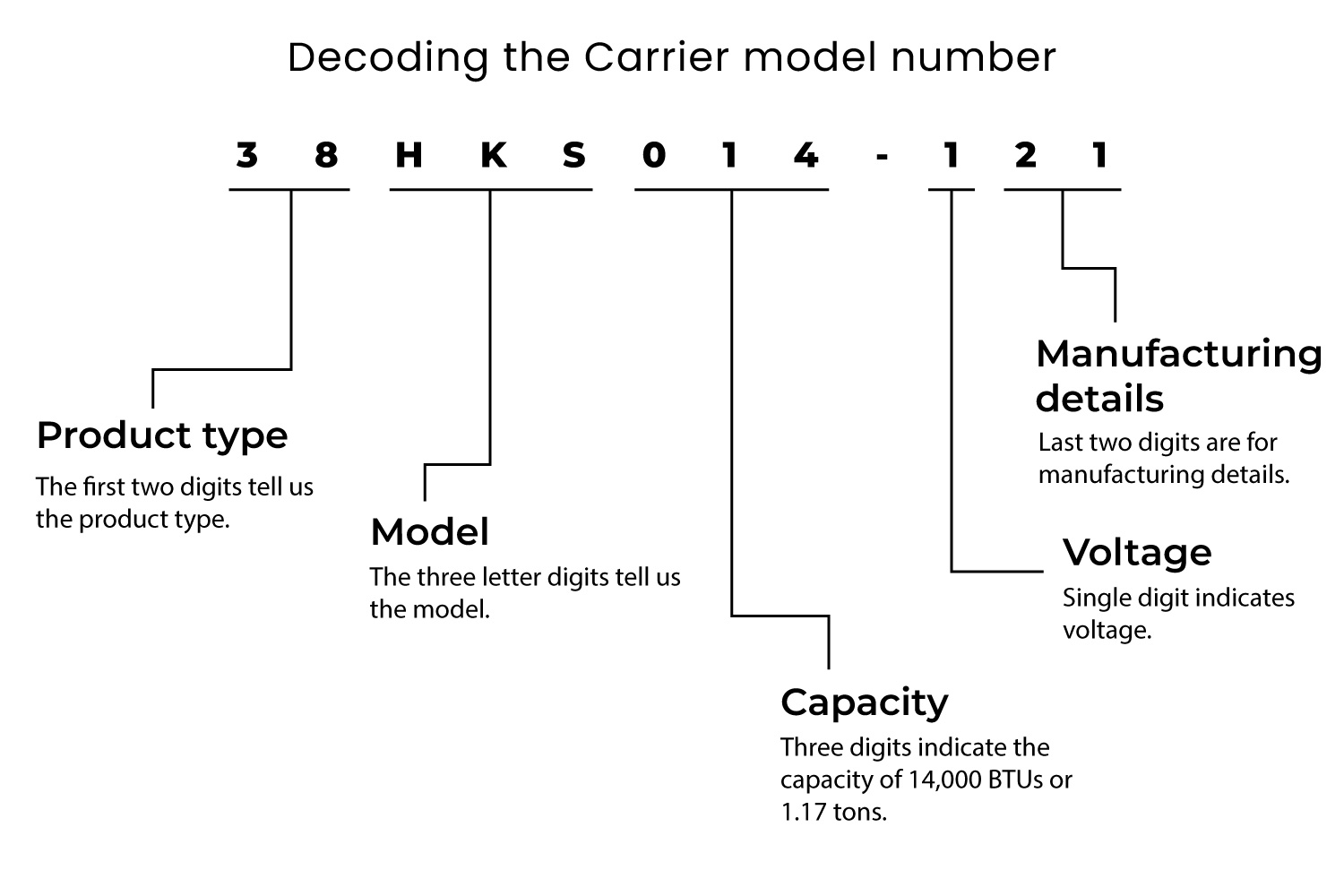
Understanding the model number on your Carrier air conditioner or furnace can unlock a wealth of information about its specifications, features, and performance. Deciphering this code isn't as daunting as it might seem. This guide will break down the components of a typical Carrier model number, empowering you to make informed decisions when comparing units, troubleshooting issues, or simply understanding your home's HVAC system.
Understanding the Basics
Carrier model numbers are typically a string of letters and numbers. Each segment of this string represents a specific attribute of the unit. While the exact format can vary depending on the type of equipment (air conditioner, furnace, heat pump, etc.) and its age, there are common elements you can learn to identify. Let’s explore these elements.
Common Elements in Carrier Model Numbers
Here are some of the key segments you'll typically find in a Carrier model number, along with explanations of what they mean:
1. Unit Type/Family: The initial letters often designate the type of unit. For example:
- FA: Furnace
- CA: Air Conditioner
- CH: Heat Pump
- FB: Fan Coil
2. Efficiency Rating: This section often indicates the unit's efficiency. It's frequently expressed using numbers or letters that correlate to a standard efficiency rating like SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) for air conditioners and heat pumps, or AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) for furnaces. Higher numbers generally mean greater efficiency and lower energy bills. Remember that while a higher efficiency rating might mean a higher initial cost, the long-term savings on energy bills can make it a worthwhile investment.
3. Series/Model Designator: Following the efficiency rating, you will usually find a series of numbers or letters that further define the model. This segment can indicate the unit's specific features, performance characteristics, and technological advancements. Think of it as the model's "personality."
4. Cooling Capacity (Air Conditioners/Heat Pumps): For cooling units, this section usually denotes the cooling capacity in British Thermal Units per hour (BTU/h), divided by 1,000. For example, "024" would indicate a 24,000 BTU/h unit, which is a 2-ton system. A 36,000 BTU/h system is a 3-ton system, and so on.
5. Heating Capacity (Furnaces/Heat Pumps): For furnaces, this section indicates the heating capacity, also in BTU/h, and often divided by 1,000. It signifies the amount of heat the furnace can produce per hour.
6. Voltage: This often specifies the voltage requirements of the unit (e.g., 115, 208/230, 460). It's critical to ensure that the unit's voltage requirements match your home's electrical system. Mismatched voltage can damage the unit or even create a fire hazard.
7. Features/Variations: The last part of the model number might indicate specific features or variations of the model. This could include things like:
- Variable speed blower motor
- Two-stage operation
- Specific control options
- Specific design variations
Decoding Example Carrier Model Numbers
Let's break down a few hypothetical Carrier model numbers to illustrate how these segments work together:
Example 1: CA16NA024000A
- CA: Indicates this is an Air Conditioner.
- 16: Likely indicates a SEER rating of 16, representing a higher efficiency unit.
- NA: Could denote a specific series within Carrier's air conditioner lineup, maybe a Comfort series.
- 024: Specifies a 24,000 BTU/h cooling capacity (2 tons).
- 000: Might represent a standard voltage and feature set.
- A: Could indicate a specific revision or design variation.
Example 2: FA80N060360
- FA: Indicates this is a Furnace.
- 80: Likely indicates an AFUE rating of 80%, which is a standard efficiency furnace.
- N: Could denote a particular series or type of burner used.
- 060: Specifies a 60,000 BTU/h heating capacity.
- 360: Might relate to the physical size or blower motor type of the furnace.
Example 3: CH14NB030000
- CH: Indicates this is a Heat Pump.
- 14: Likely indicates a SEER rating of 14.
- NB: Could specify a particular series or features of the heat pump.
- 030: Specifies a 30,000 BTU/h cooling capacity (2.5 tons).
- 000: Likely refers to a standard voltage and feature set.
Where to Find the Model Number
The model number is typically located on the unit's nameplate. The nameplate is usually a metallic or plastic sticker affixed to the exterior of the unit. Here's where you can typically find it:
- Air Conditioners (Outdoor Unit): On the side or back of the outdoor condenser unit.
- Furnaces: Inside the furnace cabinet, often on the door or side panel. You may need to remove an access panel to view it. Always turn off the power to the furnace before opening any access panels. Safety first!
- Heat Pumps (Outdoor Unit): Similar to air conditioners, on the side or back of the outdoor unit.
- Fan Coils: Inside the unit's cabinet, often on the door or side panel.
Why Understanding Model Numbers Matters
Knowing how to read a Carrier model number can be beneficial in several ways:
- Equipment Identification: Accurately identifying your unit for replacement parts or service.
- Performance Evaluation: Understanding the unit's efficiency and capacity to determine if it's meeting your heating and cooling needs.
- Comparison Shopping: Comparing different models based on their features and specifications.
- Troubleshooting: Providing the model number to a technician can help them diagnose problems more quickly.
- Warranty Information: You'll need the model number when registering your unit for warranty coverage and for any subsequent warranty claims.
Efficiency Ratings: SEER and AFUE
Let’s delve a little deeper into the efficiency ratings commonly found in Carrier model numbers:
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio)
SEER measures the cooling efficiency of air conditioners and heat pumps. It represents the total cooling output of the unit during a typical cooling season, divided by the total electrical energy input during the same period. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit. The minimum SEER rating currently mandated by the U.S. Department of Energy is 14 in most regions.
Think of SEER as miles per gallon for your car, but for your air conditioner. A higher SEER means it takes less electricity to cool your home.
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency)
AFUE measures the heating efficiency of furnaces. It represents the percentage of fuel that is converted into usable heat. The higher the AFUE, the more efficient the furnace. For example, an 80% AFUE furnace converts 80% of the fuel it consumes into heat, while the remaining 20% is lost, typically through the flue. High-efficiency furnaces can have AFUE ratings of 90% or higher.
Just like with SEER, a higher AFUE means lower energy bills during the heating season.
Variable Speed and Two-Stage Systems
Some Carrier model numbers might indicate whether the unit has variable speed or two-stage operation. These features can significantly improve comfort and energy efficiency.
Variable Speed
Variable speed motors in air conditioners, heat pumps, and furnaces can adjust their speed based on the cooling or heating demand. This allows for more precise temperature control, quieter operation, and improved dehumidification. Variable speed systems can run at lower speeds for longer periods, providing more consistent comfort and reducing energy consumption.
Two-Stage
Two-stage systems have two levels of operation: high and low. In milder weather, the unit can operate in the low stage, which uses less energy and provides quieter operation. In extreme weather, the unit can switch to the high stage to provide maximum heating or cooling. Two-stage systems offer a balance of comfort and efficiency.
Important Considerations
While understanding Carrier model numbers is helpful, it's essential to remember that it's just one piece of the puzzle. When selecting a new HVAC system, it's crucial to consider factors such as:
- Your Home's Size and Insulation: A properly sized unit is essential for optimal performance. An undersized unit won't be able to adequately heat or cool your home, while an oversized unit can lead to short cycling and poor efficiency.
- Climate: The climate you live in will influence the type of system that's best suited for your needs.
- Budget: Consider both the initial cost of the unit and the long-term operating costs.
- Professional Installation: Proper installation is crucial for ensuring that your HVAC system operates efficiently and reliably. Always hire a qualified HVAC contractor to install your new system.
Seeking Expert Advice
Deciphering Carrier model numbers is a good starting point, but ultimately, choosing the right HVAC system for your home is a complex decision. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional is highly recommended. They can assess your specific needs, recommend the appropriate equipment, and ensure proper installation.
By understanding the basics of Carrier model numbers and seeking expert advice, you can make informed decisions that will keep your home comfortable and energy-efficient for years to come.