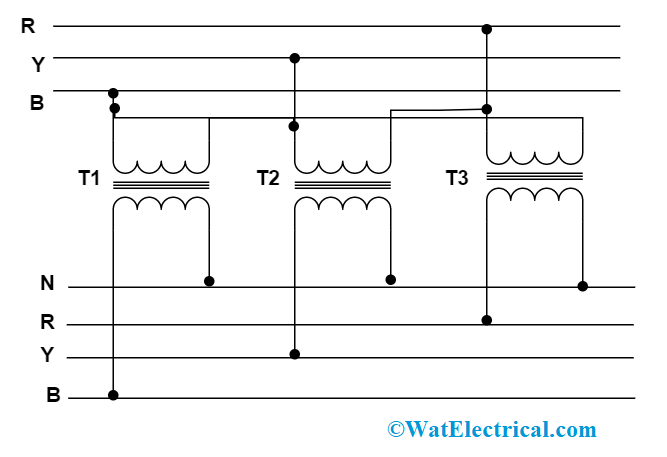
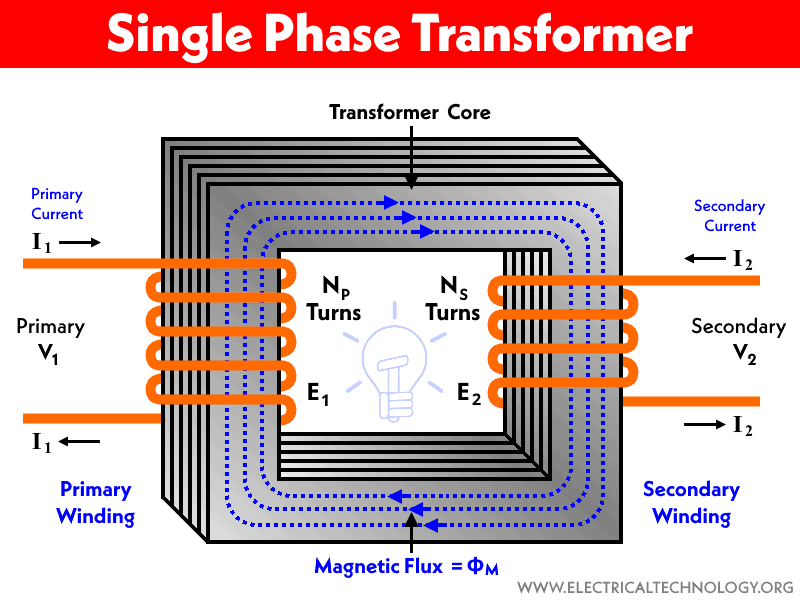
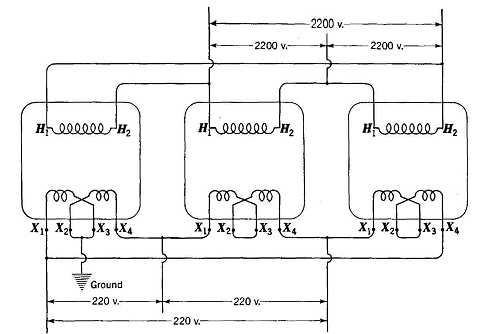
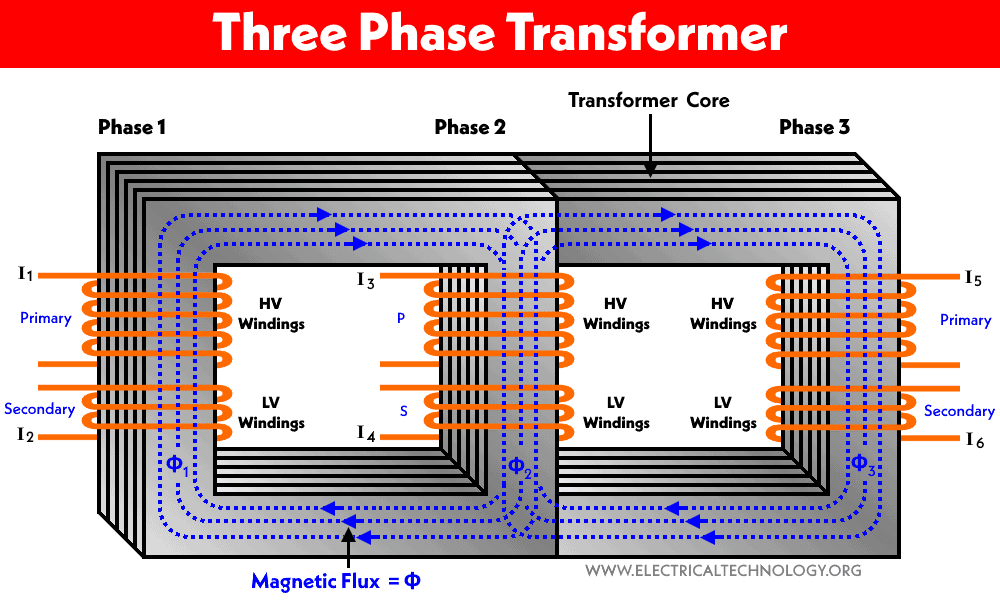
Single Phase To 3 Phase Transformer
Many homeowners, especially those with larger HVAC systems or specialized equipment, sometimes encounter a need for 3-phase power. While residential power is typically single-phase, some appliances, particularly older or more powerful HVAC units, require the consistent power delivery of a 3-phase system. This is where a single-phase to 3-phase transformer comes into play. Let's dive into what these transformers are, how they work, potential issues, and when you absolutely need to call a qualified electrician or HVAC technician.
Understanding Single-Phase and 3-Phase Power
Before we delve into transformers, it's crucial to understand the difference between the two types of electrical power. Single-phase power delivers electricity in a single, fluctuating wave. This is suitable for most household appliances like lights, refrigerators, and smaller air conditioners. 3-phase power, on the other hand, delivers electricity in three separate waves, offset from each other. This provides a smoother, more consistent power delivery, making it ideal for heavy-duty equipment that requires constant torque and efficiency, such as larger HVAC compressors, motors, and industrial machinery.
What is a Single-Phase to 3-Phase Transformer?
A single-phase to 3-phase transformer (also known as a phase converter) takes the standard single-phase power available in most homes and converts it into 3-phase power. It essentially synthesizes the missing phases, allowing you to run 3-phase equipment on a single-phase supply. These transformers come in various sizes and configurations, depending on the power requirements of the 3-phase equipment they are intended to serve.
How Does It Work?
The transformation process involves using capacitors and inductors to shift the phase angles of the single-phase power, effectively creating the three separate phases. The transformer doesn't actually "create" more power; it redistributes the existing power to mimic a 3-phase system. Different types of phase converters exist, including:
- Rotary Phase Converters: These use a rotating motor-generator to generate the 3-phase power. They are generally more robust and can handle heavier loads.
- Static Phase Converters: These use capacitors to shift the phase angles. They are simpler and less expensive but often have limitations in terms of load capacity and starting torque.
- Electronic Phase Converters (also known as Solid-State Phase Converters): These use sophisticated electronic components to synthesize the 3-phase power. They offer better efficiency and control but are typically more expensive.
Identifying the Need for a 3-Phase Transformer
How do you know if you need a single-phase to 3-phase transformer? Here are a few telltale signs:
- Your HVAC equipment specifically requires 3-phase power. This information will be clearly indicated on the equipment's nameplate.
- You are experiencing frequent motor failures in your HVAC system. This could be due to the motor struggling to start or operate efficiently on single-phase power.
- Your utility company is unable to provide 3-phase service to your location, but you need to run 3-phase equipment.
- You're retrofitting an older home with modern HVAC systems that require 3-phase power.
DIY Considerations (With Strong Warnings!)
While some basic electrical tasks can be safely tackled by homeowners, working with single-phase to 3-phase transformers is generally NOT a DIY project. The voltages and currents involved are extremely dangerous, and improper wiring can lead to severe electric shock, fire hazards, and damage to your equipment. That being said, here are some things a homeowner *might* consider (but always with extreme caution and only if *absolutely* comfortable and knowledgeable):
- Visual Inspection: Check for any obvious signs of damage to the transformer, such as burnt wires, cracked casings, or leaking fluids.
- Checking Connections: Ensure that all connections are tight and secure. Loose connections can cause overheating and arcing. Turn off the power at the breaker before inspecting connections!
- Voltage Testing (Advanced): If you have experience with a multimeter and understand electrical safety procedures, you can test the input and output voltages of the transformer. This can help determine if the transformer is functioning correctly.
- Cleaning: Keep the transformer clean and free of dust and debris. This can help prevent overheating.
WARNING: Working with electrical systems is inherently dangerous. If you are not comfortable working with electricity, or if you have any doubts about your abilities, DO NOT attempt to diagnose or repair a single-phase to 3-phase transformer yourself. Contact a qualified electrician or HVAC technician. Incorrectly installed or repaired transformers can cause serious injury, death, and property damage.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
Even with proper installation, single-phase to 3-phase transformers can experience problems. Here are some common issues:
- Overheating: This can be caused by overloading the transformer, poor ventilation, or loose connections.
- Voltage Imbalance: This occurs when the voltage on each of the three phases is not equal. This can damage connected equipment.
- Phase Loss: This occurs when one of the three phases is lost. This can cause motors to overheat and fail.
- Transformer Failure: This can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, overloading, and voltage surges.
- Excessive Noise: A humming or buzzing sound could indicate a loose core or other internal problems.
Troubleshooting Steps (Use Extreme Caution!):
- Check the Breaker: Ensure that the breaker supplying power to the transformer is not tripped.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for any loose or damaged wires.
- Measure Voltage (Advanced): Use a multimeter to measure the voltage on each phase. If there is a significant voltage imbalance or phase loss, the transformer may be faulty.
- Check for Overload: Ensure that the load connected to the transformer is not exceeding its capacity.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: If you hear any unusual noises, such as humming, buzzing, or crackling, the transformer may be damaged.
Remember: These are only basic troubleshooting steps. More complex problems require the expertise of a qualified electrician or HVAC technician.
When to Call a Professional
There are several situations where you should always call a professional:
- You are not comfortable working with electricity.
- You suspect that the transformer is damaged.
- You are experiencing frequent problems with the transformer.
- You need to install a new transformer.
- You are unsure how to troubleshoot the problem.
A qualified electrician or HVAC technician will have the knowledge, experience, and tools to safely and effectively diagnose and repair single-phase to 3-phase transformer problems. They can also ensure that the transformer is properly sized and installed for your specific application.
Estimating Repair Costs
The cost of repairing or replacing a single-phase to 3-phase transformer can vary depending on several factors, including:
- The size of the transformer. Larger transformers are generally more expensive to repair or replace.
- The type of transformer. Electronic phase converters are typically more expensive than rotary or static phase converters.
- The complexity of the problem. Simple repairs, such as replacing a wire, will be less expensive than more complex repairs, such as replacing a faulty winding.
- The labor rates in your area. Labor rates can vary significantly depending on your location.
Here's a general estimate (these are broad ranges and should not be considered a firm quote):
- Simple Repairs (e.g., replacing a wire, tightening connections): $100 - $300
- More Complex Repairs (e.g., replacing a capacitor, repairing a winding): $300 - $800
- Transformer Replacement (Small): $500 - $1500 (including labor)
- Transformer Replacement (Large): $1500 - $5000+ (including labor)
Important: These are just estimates. It's always best to get a quote from a qualified electrician or HVAC technician before proceeding with any repairs or replacements. Be sure to get multiple quotes to ensure you are getting a fair price.
Preventative Maintenance
To extend the life of your single-phase to 3-phase transformer and prevent costly repairs, consider these preventative maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Visually inspect the transformer for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or burnt wires.
- Keep it Clean: Keep the transformer clean and free of dust and debris.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Make sure the transformer has adequate ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not overload the transformer beyond its rated capacity.
- Monitor Voltage: Periodically check the voltage on each phase to ensure that it is balanced.
Conclusion
Single-phase to 3-phase transformers are essential components for running 3-phase equipment in residential settings. While some basic troubleshooting steps can be performed by homeowners, it's crucial to understand the risks involved and to call a qualified professional for any complex repairs or installations. By understanding the basics of these transformers, you can better identify potential problems and ensure the safe and efficient operation of your HVAC system.