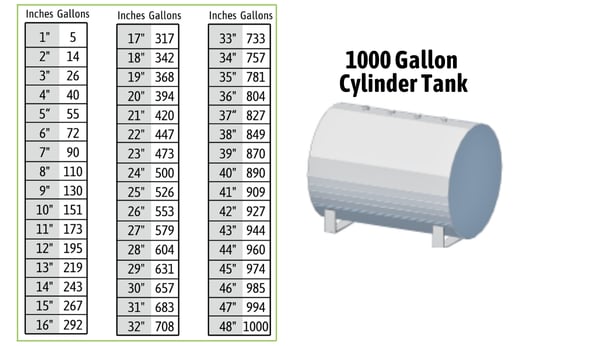
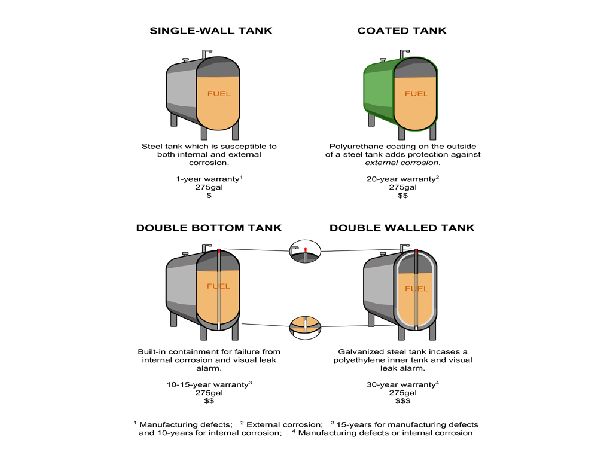
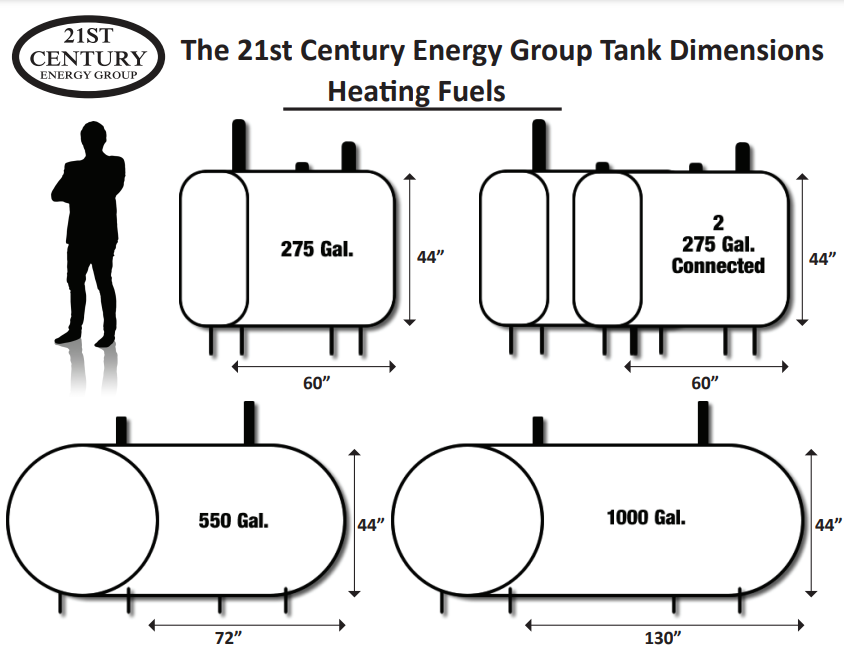
Size Of Oil Tanks For Home Heating

One of the most common issues homeowners face, especially those new to oil heating, revolves around the size of their oil tank. It's not just about fitting in the space; it's about adequately supplying your home with heat without constant worry about running dry. A too-small tank leads to frequent, inconvenient, and potentially costly refills, while an excessively large tank can represent unnecessary upfront expense and potentially degrade the oil over time. Let's explore how to troubleshoot and understand if your tank is the right size for your needs.
Step 1: Identifying the Problem - Are You Running Out Too Quickly?
The first step is to determine if you genuinely have a tank size issue or if the problem lies elsewhere. Here's a methodical approach:
Track Your Oil Consumption
Keep a detailed record of your oil deliveries. Note the date, quantity delivered (in gallons/liters), and the date your tank gauge hits a specific low point (e.g., 1/4 full). This data is crucial for calculating your average consumption.
Use a simple spreadsheet or even a notebook. The more precise your data, the more accurate your analysis will be.
Consider the Season and Weather
Your oil consumption will naturally fluctuate with the seasons. Colder months will demand significantly more oil than warmer months. Note the average outdoor temperature during the periods you're tracking. A particularly harsh winter will skew your consumption upwards, while a mild one will skew it downwards.
Compare your consumption from year to year, if possible, to account for seasonal variations. Compare heating degree days from year to year. Heating degree days are a measure of how cold it has been over a period of time relative to a base temperature, usually 65 degrees Fahrenheit.
Assess Your Home's Insulation
A poorly insulated home will lose heat faster, forcing your furnace to work harder and consume more oil. Check for drafts around windows and doors, and ensure your attic and walls are adequately insulated. These are key factors impacting your oil consumption, regardless of tank size.
Check for Leaks (Visually and Olfactorily)
Carefully inspect your tank, supply lines, and furnace for any signs of oil leaks. Look for stains, drips, or a strong oily odor. Even a small leak can waste a significant amount of oil over time. If you suspect a leak, shut off the furnace immediately and proceed with caution!
Step 2: Calculating Your Oil Consumption Rate
Now that you've gathered data, it's time to calculate your average oil consumption rate. This will help you determine if your tank is adequately sized.
Calculate Gallons/Liters Used Per Day/Week
Using your delivery records, calculate the number of gallons/liters you used between each delivery. Then, divide that number by the number of days/weeks between those deliveries to get your average daily/weekly consumption rate.
Example: You received 200 gallons on October 1st, and the tank reached 1/4 full on November 1st (31 days). Your average daily consumption is 200 gallons / 31 days = 6.45 gallons per day.
Account for Varying Temperatures
Ideally, calculate your consumption rate for periods with similar average temperatures. This will provide a more accurate picture of your normal consumption.
You might have one consumption rate for November-December and another for January-February when temperatures are typically colder.
Consider the Size of Your Home
The square footage of your home directly impacts how much oil you'll consume. Larger homes naturally require more heat. Multiply your average daily consumption by the number of square feet in your home for a general sense of consumption per square foot.
This is just a rough comparison tool. Other factors, like insulation and window efficiency, play a significant role.
Step 3: Determining the Ideal Tank Size
Once you know your average consumption rate, you can estimate the appropriate tank size.
Calculate Your Peak Consumption Period
Identify the period of the year when you consume the most oil (usually the coldest months). Use your consumption records to determine your peak daily/weekly consumption rate.
Factor in Delivery Lead Time
Consider the time it takes for your oil company to deliver oil after you place an order. This "lead time" is crucial. You need enough oil in your tank to last until the next delivery.
Typical lead times range from 1-3 days, but it's best to confirm with your local oil company.
Account for a Safety Margin
Never let your tank run completely empty! This can cause sediment to clog your fuel lines and damage your furnace. Always maintain a safety margin of at least 1/4 of the tank's capacity. This also provides a buffer in case of unexpected cold snaps or delivery delays.
Estimate the Minimum Tank Size
Multiply your peak daily consumption by the delivery lead time (in days) and then add your safety margin. This gives you an estimate of the minimum tank size you need.
Example: Your peak daily consumption is 8 gallons, your delivery lead time is 2 days, and you want a 1/4 tank safety margin on a 275-gallon tank (68.75 gallons). 8 gallons/day * 2 days + 68.75 gallons = 84.75 gallons. You'll never let your tank run below 84.75 gallons.
Consider Future Needs
Think about any potential changes in your heating needs. Are you planning to add an addition to your home? Will more family members be living with you? These factors will increase your oil consumption.
Err on the side of caution and choose a slightly larger tank if you anticipate increased demand in the future.
Step 4: DIY Troubleshooting and Safe Solutions
Before jumping to replacing your tank, try these DIY solutions to address potential issues impacting your oil consumption:
Improve Insulation
Seal drafts around windows and doors with weather stripping or caulk. Add insulation to your attic and walls. These simple steps can significantly reduce heat loss and lower your oil consumption.
Adjust Thermostat Settings
Lower your thermostat a few degrees, especially when you're away from home or asleep. Consider using a programmable thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures throughout the day.
Regular Furnace Maintenance
Change your furnace filter regularly (every 1-3 months) to ensure proper airflow. A dirty filter restricts airflow, making your furnace work harder and consume more oil. Inspect and clean the burner assembly, as soot and carbon buildup can impact efficiency.
Bleed Your Radiators
If you have radiators, bleed them periodically to remove trapped air. Air in the system reduces heating efficiency. You'll need a radiator key, turn the valve to allow the air to escape. Once water starts to drip out, the air is out and you can close the valve.
Check and Seal Ductwork
If you have forced-air heating, inspect your ductwork for leaks. Seal any leaks with duct tape or mastic sealant. Leaky ducts can waste a significant amount of heat.
When to Call a Professional
While DIY solutions can address some issues, certain problems require professional intervention. Never attempt repairs on your oil tank or furnace unless you are qualified and comfortable doing so.
Suspected Leaks
If you suspect an oil leak, immediately contact a qualified HVAC technician. Oil leaks are hazardous and require professional cleanup.
Furnace Malfunctions
If your furnace is making unusual noises, producing smoke, or not heating properly, call a qualified HVAC technician. Do not attempt to diagnose or repair complex furnace problems yourself.
Tank Replacement
Replacing an oil tank is a complex and potentially dangerous task that requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Always hire a licensed and insured contractor to replace your oil tank. They will ensure proper disposal of the old tank and safe installation of the new one.
If consumption is inexplicably high after DIY efforts
If you've tried all the DIY solutions and your oil consumption remains abnormally high, consult with a qualified HVAC technician. They can perform a thorough inspection of your heating system and identify any underlying problems that are contributing to excessive oil consumption.
Conclusion
Understanding your oil consumption and choosing the right tank size is crucial for efficient and cost-effective home heating. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can diagnose potential problems, implement simple DIY solutions, and determine when professional assistance is necessary. Remember, safety is paramount. When in doubt, always consult with a qualified HVAC technician.