Sporlan Thermostatic Expansion Valve Selection Chart
The Sporlan thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) selection chart is an indispensable tool for HVAC/R professionals. Properly selecting a TXV is crucial for ensuring optimal system performance, energy efficiency, and equipment longevity. This guide provides a comprehensive, yet accessible, overview of how to use Sporlan TXV selection charts effectively.
Understanding Thermostatic Expansion Valves (TXVs)
Before diving into the selection chart, it's essential to understand the function of a TXV. Think of a TXV as the gatekeeper controlling the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil. Refrigerant, often described as the "blood" of your AC system, is the substance that carries heat from inside your building to the outside.
The TXV's primary job is to maintain a specific level of superheat at the evaporator outlet. Superheat is the temperature of the refrigerant vapor above its saturation temperature (the temperature at which it boils) at a given pressure. Maintaining proper superheat ensures that all the refrigerant has completely boiled into vapor *before* it reaches the compressor. Liquid refrigerant entering the compressor can cause catastrophic damage.
In simple terms, the TXV monitors the temperature of the refrigerant leaving the evaporator coil. If the temperature is too low (indicating insufficient superheat), the valve restricts the flow of refrigerant. Conversely, if the temperature is too high (indicating excessive superheat), the valve opens up to allow more refrigerant to flow.
Why Proper TXV Selection is Critical
Selecting the wrong TXV can lead to a host of problems:
* Poor System Performance: An undersized valve restricts refrigerant flow, leading to reduced cooling capacity and inefficient operation. An oversized valve can flood the evaporator, potentially damaging the compressor. * Compressor Damage: Liquid refrigerant entering the compressor (known as "liquid slugging") can cause severe damage to internal components. * Inefficient Energy Consumption: An improperly sized TXV forces the system to work harder, resulting in higher energy bills. * System Instability: Fluctuating superheat levels can cause erratic system operation and temperature swings. * Reduced Equipment Lifespan: Consistent strain on the system due to an improperly sized TXV can shorten the lifespan of various components.Deciphering the Sporlan TXV Selection Chart
Sporlan TXV selection charts are typically organized to simplify the selection process. However, understanding the different sections and parameters is vital.
1. Refrigerant Type
The first step is to identify the refrigerant used in your system (e.g., R-410A, R-22, R-134a). TXVs are designed to work with specific refrigerants, and using the wrong valve can lead to significant performance issues. The selection chart will be divided into sections based on the refrigerant type.
2. Valve Series
Sporlan offers various TXV series, each designed for specific applications and capacity ranges. Common series include:
- Type A: General purpose, often used in smaller refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- Type B: Similar to Type A but may have different body styles or features.
- Type C: Higher capacity valves, suitable for larger systems.
- Type E: Designed for close control applications.
- Type G: Typically used in medium temperature refrigeration applications.
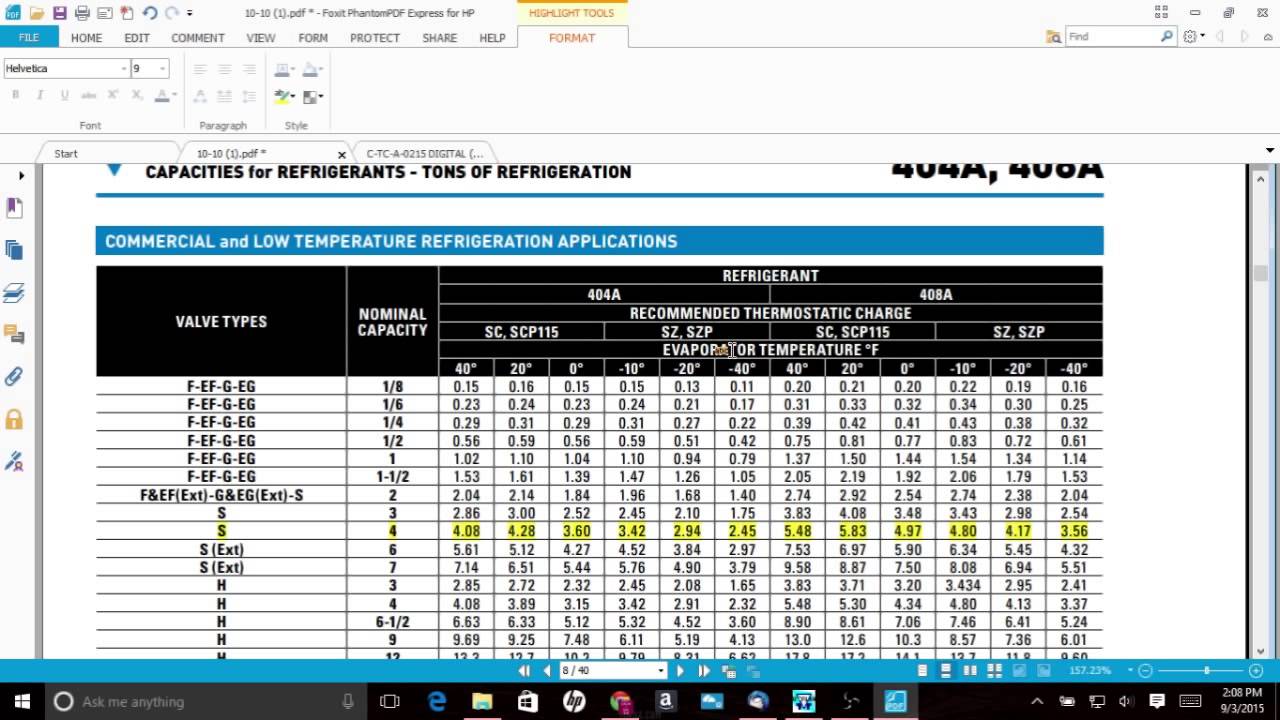
3. Evaporator Capacity (Tons or kW)
The evaporator capacity, measured in tons of refrigeration (TR) or kilowatts (kW), indicates the amount of heat the evaporator coil can remove per unit of time. This is a critical parameter for TXV selection. The selection chart will display capacity ranges for each valve model at various operating conditions.
4. Evaporating Temperature
The evaporating temperature is the temperature at which the refrigerant boils inside the evaporator coil. This temperature depends on the desired space temperature and the refrigerant used. The selection chart will often list capacity ratings at different evaporating temperatures.
5. Liquid Temperature
The liquid temperature is the temperature of the liquid refrigerant entering the TXV. This temperature is affected by the condenser performance and the length of the liquid line. The selection chart might have adjustments or correction factors for different liquid temperatures.
6. Pressure Drop Across the Valve
The pressure drop across the valve is the difference between the inlet pressure and the outlet pressure of the valve. This pressure drop affects the valve's capacity. The selection chart might include corrections for different pressure drops.
7. Superheat Setting
The superheat setting is the desired superheat at the evaporator outlet. This setting determines how much the valve will open or close in response to changes in superheat. Sporlan TXVs often have adjustable superheat settings, allowing for fine-tuning of system performance.
8. MOP (Maximum Operating Pressure)
Some TXVs have a MOP (Maximum Operating Pressure). This refers to the maximum pressure that the valve can withstand before it starts to throttle back refrigerant flow, preventing excessive pressure in the evaporator. Selecting a valve with the appropriate MOP is crucial for system safety.
Using the Sporlan TXV Selection Chart: A Step-by-Step Example
Let's walk through an example of how to use a Sporlan TXV selection chart:
- Identify the Refrigerant: Suppose your system uses R-410A refrigerant. You will need to look at the section of the chart that specifically covers R-410A valves.
- Determine the Evaporator Capacity: Assume your evaporator has a capacity of 5 tons (TR).
- Determine the Evaporating Temperature: Let's say the desired evaporating temperature is 40°F.
- Determine the Liquid Temperature: Assume the liquid temperature entering the TXV is 100°F.
- Locate the Correct Table: Find the table in the chart for R-410A valves. Look for a section or column that corresponds to an evaporating temperature of 40°F.
- Find the Capacity Range: Within that column, look for a valve model that has a capacity rating of approximately 5 TR at a liquid temperature of 100°F.
- Consider Adjustments: The chart may have correction factors for liquid temperature or pressure drop. Apply these factors if necessary to refine your selection. For example, if your liquid temperature is significantly different from the chart's standard conditions, you may need to choose a slightly larger or smaller valve.
- Check the MOP (if applicable): If your system requires a valve with a MOP, ensure that the selected valve's MOP rating is appropriate for your system's operating pressures.
- Select the Valve: Once you have considered all the factors, choose the Sporlan TXV model that best matches your system's requirements.
Tips for Accurate TXV Selection
To ensure accurate TXV selection, keep the following tips in mind:
* Consult the Manufacturer's Literature: Always refer to the latest version of the Sporlan TXV selection chart and technical documentation. These resources contain the most up-to-date information and detailed specifications. * Accurate Data: Obtain accurate data on system parameters, such as refrigerant type, evaporator capacity, evaporating temperature, and liquid temperature. Inaccurate data will lead to incorrect valve selection. * Consider System Load Variations: Consider how the system load might vary over time. If the load fluctuates significantly, you may need to choose a valve with a wider capacity range or a valve with adjustable superheat settings. * Factor in Line Losses: Account for pressure drops in the liquid line and suction line. These pressure drops can affect the valve's capacity and performance. * Consult with Experts: If you are unsure about any aspect of TXV selection, consult with a qualified HVAC/R engineer or Sporlan technical support. * Verify Superheat After Installation: After installing the TXV, verify the superheat at the evaporator outlet to ensure that the valve is operating correctly. Adjust the superheat setting if necessary. * Consider the Application: Different applications (e.g., refrigeration, air conditioning, heat pumps) may require different TXV characteristics. Choose a valve that is specifically designed for your application. * Document your Selection: Keep a record of the TXV model number, system parameters, and any adjustments you made during the selection process. This documentation will be helpful for future maintenance and troubleshooting.Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can lead to incorrect TXV selection. Avoid these pitfalls:
* Ignoring Refrigerant Type: Using a TXV designed for the wrong refrigerant is a critical error that can damage the system. * Overlooking Capacity: Selecting a valve with insufficient or excessive capacity will result in poor system performance. * Neglecting Liquid Temperature: Failing to account for liquid temperature can lead to inaccurate capacity ratings. * Ignoring Pressure Drop: Ignoring the pressure drop across the valve can affect its performance. * Assuming All Valves Are Interchangeable: Different TXV models have different characteristics and are not always interchangeable. * Failing to Verify Superheat: Not verifying superheat after installation can lead to undetected problems.Conclusion
Selecting the correct Sporlan TXV is essential for achieving optimal performance, energy efficiency, and reliability in HVAC/R systems. By understanding the key parameters, using the selection chart correctly, and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure that your system operates at its best. Remember to always consult the manufacturer's literature and seek expert advice when needed. Proper TXV selection is a vital step towards a well-functioning and long-lasting HVAC/R system.