Trane Serial Number Guide
Understanding the manufacturing date and specifications of HVAC equipment is crucial for accurate diagnostics, maintenance, and parts replacement. For Trane units, deciphering the serial number is the key to unlocking this information. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of Trane serial numbers, its use, and information that can be gathered, along with career insights for HVAC professionals.
Decoding Trane Serial Numbers
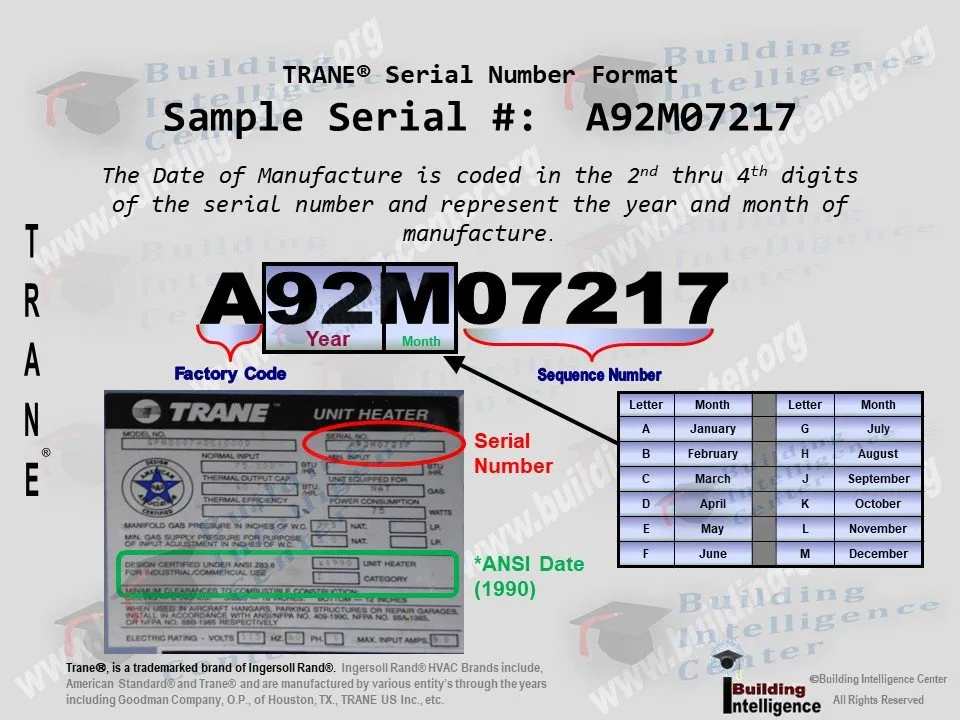
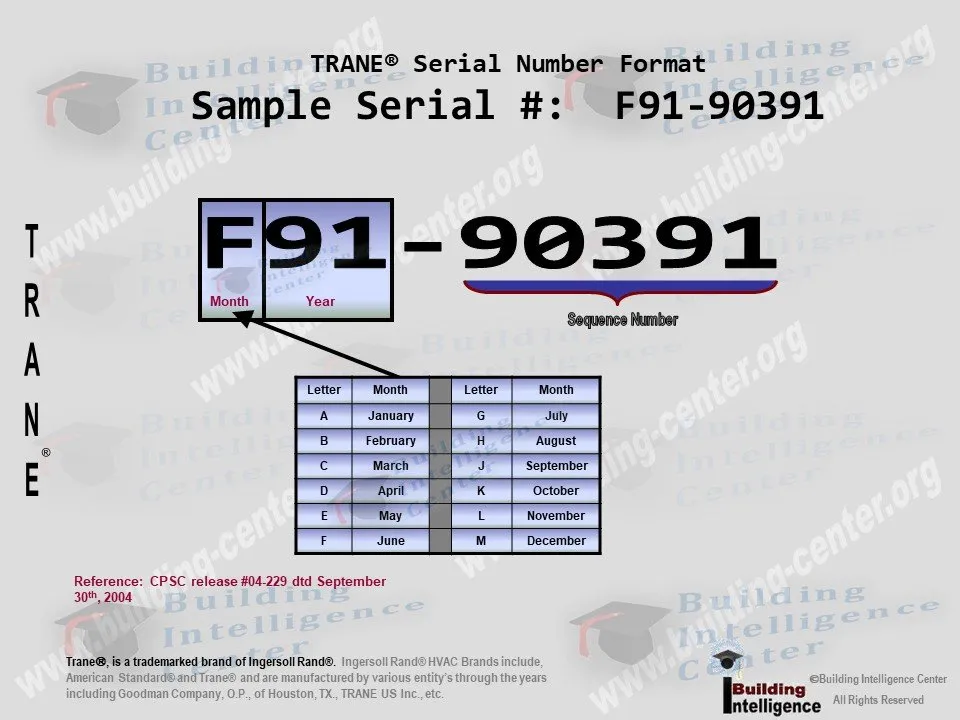
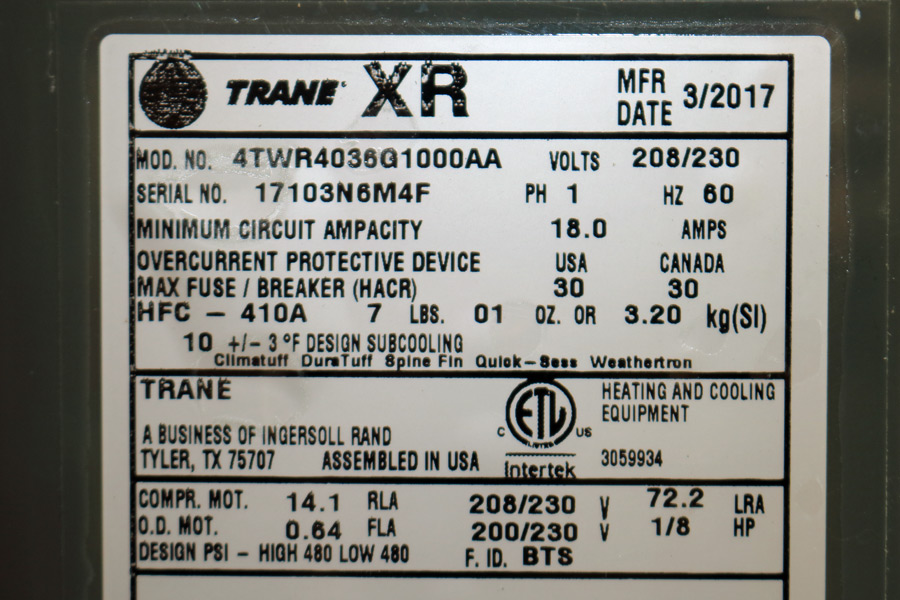
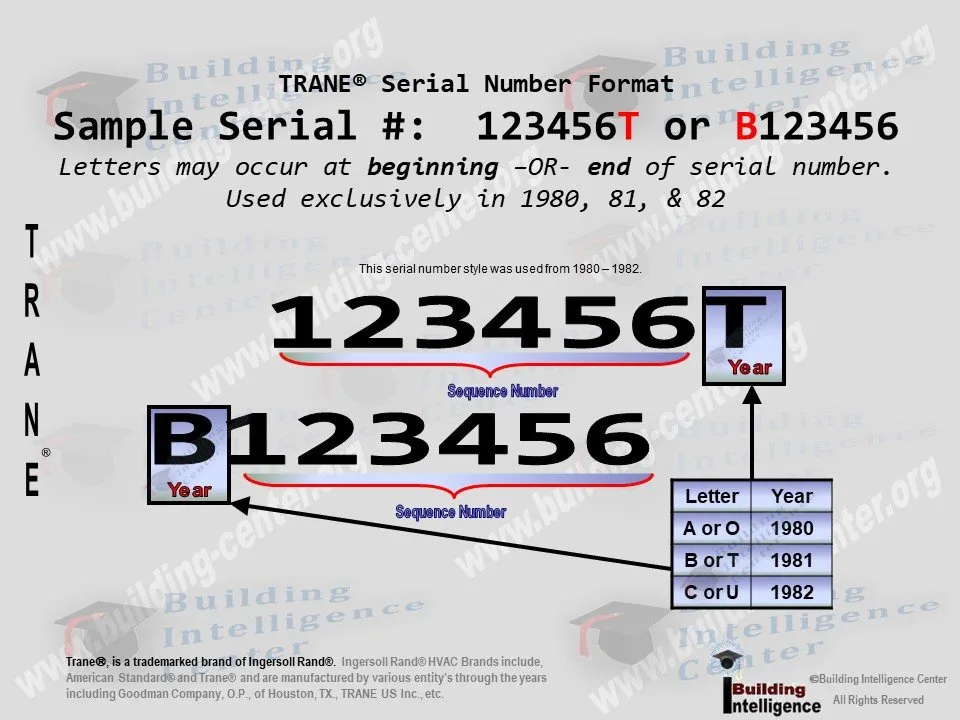
Trane serial numbers are typically found on the unit's nameplate, often located on the exterior of the equipment. While the exact format can vary depending on the year of manufacture and product type (e.g., air conditioner, furnace, heat pump), the underlying principle remains consistent: specific characters or groups of characters convey specific information. Here's a general framework for understanding a Trane serial number:
Typical Structure: A Trane serial number usually consists of 10 alphanumeric characters.
Key Components:
- Manufacturing Date: Often embedded within the first few characters. Trane typically uses a combination of letters and numbers to indicate the month and year of manufacture. Understanding Trane's date coding system is crucial, and resources are available online to help you translate these codes.
- Manufacturing Location: Some serial numbers incorporate codes identifying the plant where the unit was manufactured.
- Sequential Production Number: The remaining characters usually represent a sequential number, indicating the order in which the unit was produced at that particular plant during that specific time frame.
Example: While specific examples can vary, a serial number might look something like: "2345ABCD67". Note that these codes vary widely by product line and year. Consulting manufacturer documentation or using online Trane serial number lookup tools will provide the most accurate interpretation.
Accessing Trane's Documentation
Trane provides documentation and resources to aid in identifying and understanding its equipment. Consult Trane's official website or contact their customer support for specific serial number decoding guides related to the unit in question. Also, many HVAC distributors have Trane-specific expertise and can offer support. Always prioritize using official sources over third-party interpretations.
Why Understanding Serial Numbers Matters
Knowing how to decipher a Trane serial number is vital for several reasons:
- Accurate Parts Replacement: Ensures you order and install the correct replacement parts, preventing equipment damage and ensuring optimal performance.
- Warranty Validation: Manufacturers use serial numbers to track warranty periods. Knowing the manufacturing date is essential for determining if a unit is still under warranty.
- Troubleshooting: The serial number can help access specific technical documentation, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting guides related to the unit.
- Equipment History: Provides insight into the unit's age and potential maintenance history, which can inform repair strategies and replacement decisions.
HVAC Career Paths and the Importance of Technical Skills
The HVAC industry is experiencing strong growth, driven by factors such as increasing construction activity, climate change, and growing demand for energy-efficient systems. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of HVAC mechanics and installers is projected to grow 6% from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations. Approximately 41,600 openings for HVAC mechanics and installers are projected each year, on average, over the decade.
Entry-level positions typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, along with vocational training or an apprenticeship. However, advanced roles, such as HVAC technicians, service managers, and design engineers, often require further education, certifications, and specialized skills.
Career Examples:
- HVAC Technician: Installs, maintains, and repairs heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Average salary: $50,000 - $70,000 per year. Strong understanding of electrical systems, refrigeration principles, and troubleshooting techniques is essential.
- HVAC Installer: Specializes in installing new HVAC systems. Requires knowledge of building codes, ductwork design, and equipment specifications. Average salary: $45,000 - $65,000 per year.
- HVAC Service Manager: Oversees a team of technicians, manages service schedules, and ensures customer satisfaction. Requires strong leadership, communication, and organizational skills. Average salary: $60,000 - $90,000 per year.
- HVAC Design Engineer: Designs and develops HVAC systems for buildings and industrial facilities. Requires a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and a strong understanding of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and building science. Average salary: $70,000 - $100,000+ per year.
The Role of Certifications
Certifications play a significant role in career advancement and earning potential in the HVAC industry. Some of the most recognized certifications include:
- NATE (North American Technician Excellence): Demonstrates competency in specific HVAC areas, such as installation, service, and maintenance. NATE certification enhances credibility and improves job prospects.
- EPA Section 608 Certification: Required by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for technicians who handle refrigerants. This certification ensures compliance with environmental regulations and proper handling of refrigerants.
- HVAC Excellence: Another widely recognized certification program that assesses technical skills and knowledge in HVAC.
Continuing Education: The HVAC industry is constantly evolving with new technologies and regulations. Ongoing training and education are essential for staying up-to-date and maintaining a competitive edge. Employers value technicians who demonstrate a commitment to professional development.
The Employer's Perspective: Hiring and Training
Employers in the HVAC industry are constantly seeking skilled and qualified technicians. When hiring, employers prioritize candidates with:
- Technical Skills: A strong understanding of HVAC systems, troubleshooting techniques, and repair procedures.
- Certifications: NATE, EPA 608, and other industry-recognized certifications.
- Experience: Hands-on experience in installation, maintenance, and repair.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to diagnose and resolve complex HVAC issues.
- Customer Service Skills: The ability to communicate effectively with customers and provide excellent service.
Investing in Training: Many employers invest in training programs to develop the skills of their employees. These programs may include:
- On-the-Job Training: Providing hands-on experience under the supervision of experienced technicians.
- Apprenticeship Programs: Structured training programs that combine classroom instruction with on-the-job training.
- Vendor Training: Training programs offered by HVAC equipment manufacturers, such as Trane.
By investing in training, employers can ensure that their workforce has the skills needed to meet the demands of the industry and provide high-quality service to their customers.
The Future of HVAC: Technology and Innovation
The HVAC industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements. Some of the key trends shaping the future of HVAC include:
- Smart HVAC Systems: The integration of sensors, controls, and internet connectivity to optimize energy efficiency, improve comfort, and enable remote monitoring and control.
- Energy-Efficient Technologies: The development of more energy-efficient equipment, such as variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems, heat pumps, and geothermal systems.
- Green Refrigerants: The transition to refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP) to reduce environmental impact.
- Building Automation Systems (BAS): The use of sophisticated control systems to manage and optimize building energy performance.
These technological advancements are creating new opportunities for HVAC professionals with the skills and knowledge to work with these advanced systems.
Conclusion
Understanding Trane serial numbers is a fundamental skill for HVAC professionals. Combine this skill with professional certifications and ongoing education to unlock a successful and rewarding career in this growing industry. By staying up-to-date on the latest technologies and trends, HVAC professionals can continue to provide valuable services and contribute to a more sustainable future.