Venting Requirements For High Efficiency Furnace
High-Efficiency Furnace Venting: A Comprehensive Guide for HVAC Professionals
The shift towards high-efficiency furnaces has revolutionized the HVAC industry, offering homeowners significant energy savings and environmental benefits. However, proper venting is crucial for these systems to operate safely and efficiently. This article provides a detailed overview of venting requirements for high-efficiency furnaces, covering essential regulations, materials, installation practices, and career opportunities in this specialized field.
Understanding High-Efficiency Furnaces
Unlike traditional furnaces, high-efficiency models (often designated as 90%+ AFUE – Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) extract more heat from combustion gases. This process cools the exhaust to the point where water vapor condenses. This condensation necessitates a different venting approach compared to conventional furnaces. Because the exhaust gases are cooler, they have less buoyancy and are more corrosive, demanding specialized venting materials and installation techniques.
Venting Requirements: Codes and Regulations
Compliance with local and national codes is paramount when installing or servicing high-efficiency furnace venting systems. The International Fuel Gas Code (IFGC) is a widely adopted standard that outlines specific requirements for venting. These requirements address:
- Material Compatibility: Approved materials include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride), and polypropylene. These materials are resistant to the corrosive effects of the acidic condensate. Using improper materials, such as standard metal vent pipes, can lead to rapid deterioration and dangerous carbon monoxide leaks.
- Vent Sizing: Proper vent sizing is crucial for maintaining adequate airflow and preventing condensation buildup. Undersized vents can restrict airflow, leading to furnace inefficiency and potential safety hazards. Oversized vents can allow the exhaust gases to cool excessively, increasing condensation and corrosion. Vent sizing charts, provided by furnace manufacturers and referenced in the IFGC, must be consulted.
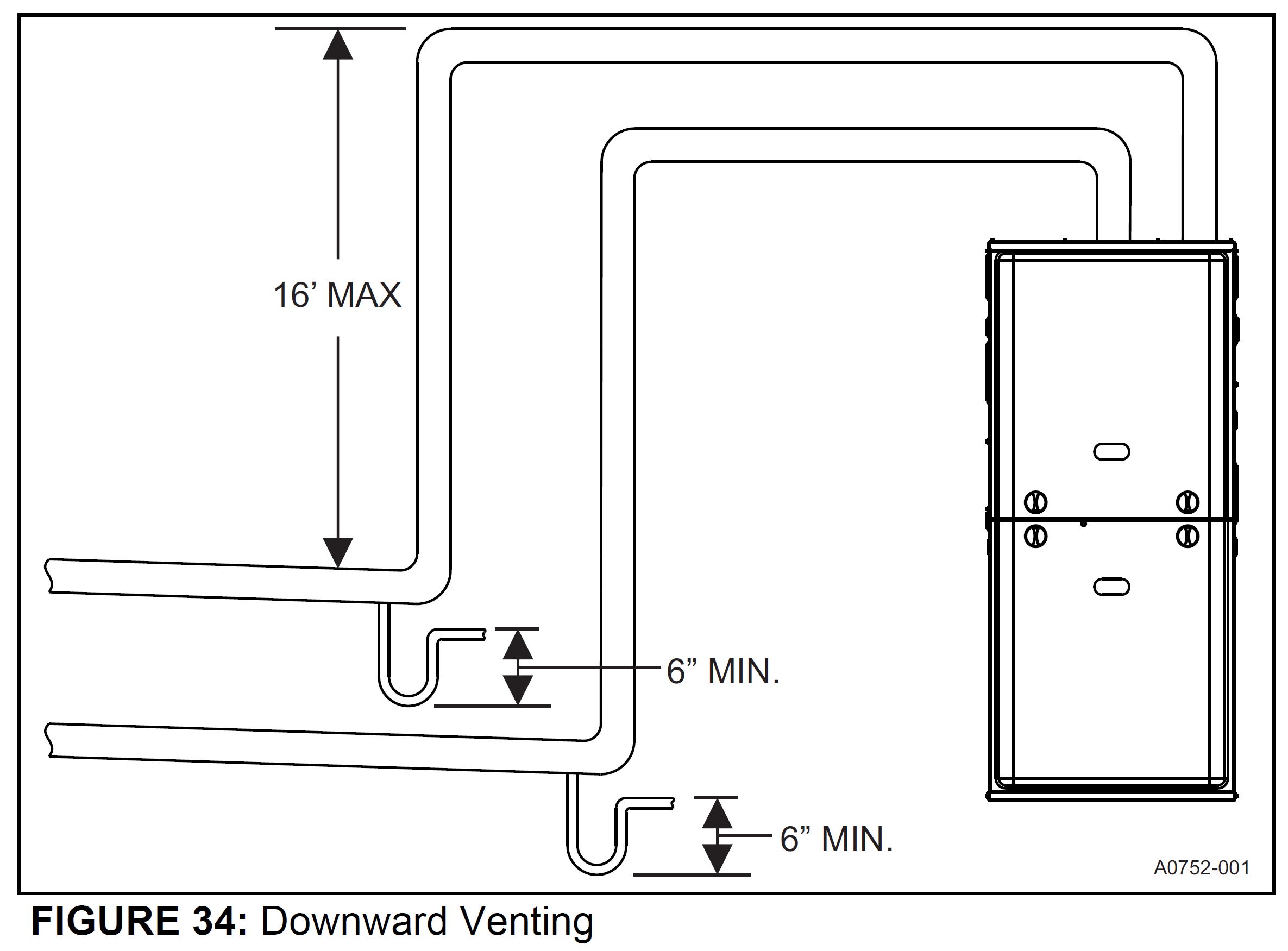
- Slope and Support: Vent pipes must be properly sloped to allow condensate to drain back into the furnace. Adequate support is also essential to prevent sagging or damage to the venting system. Typically, a downward slope of at least ¼ inch per foot is required. Supports should be placed at appropriate intervals, as specified by the vent manufacturer.
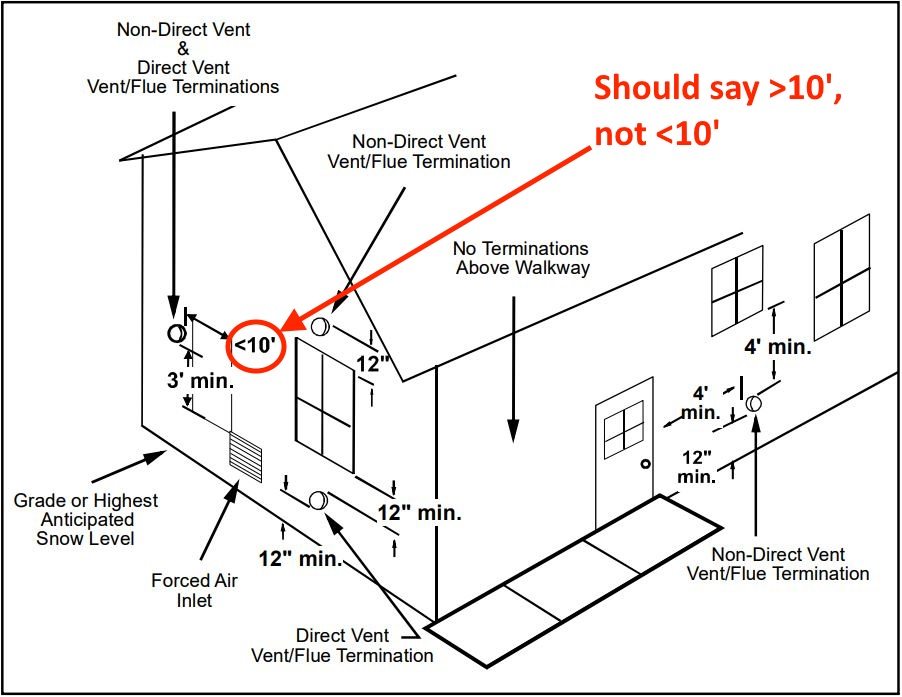
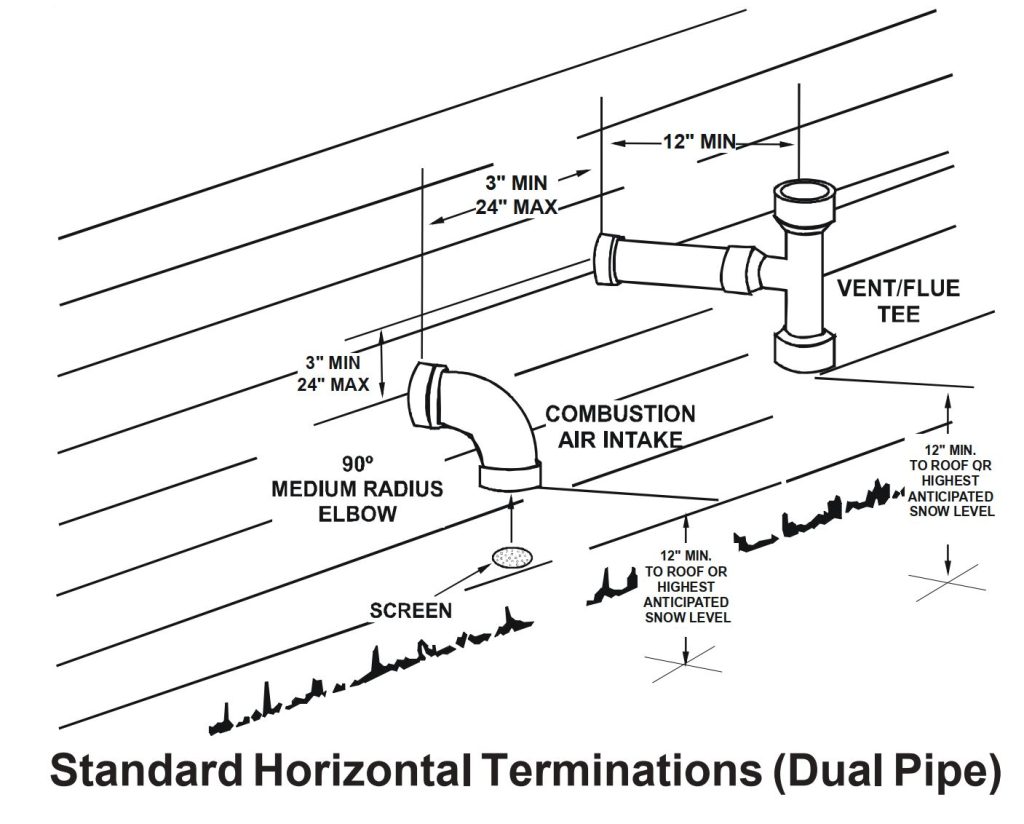
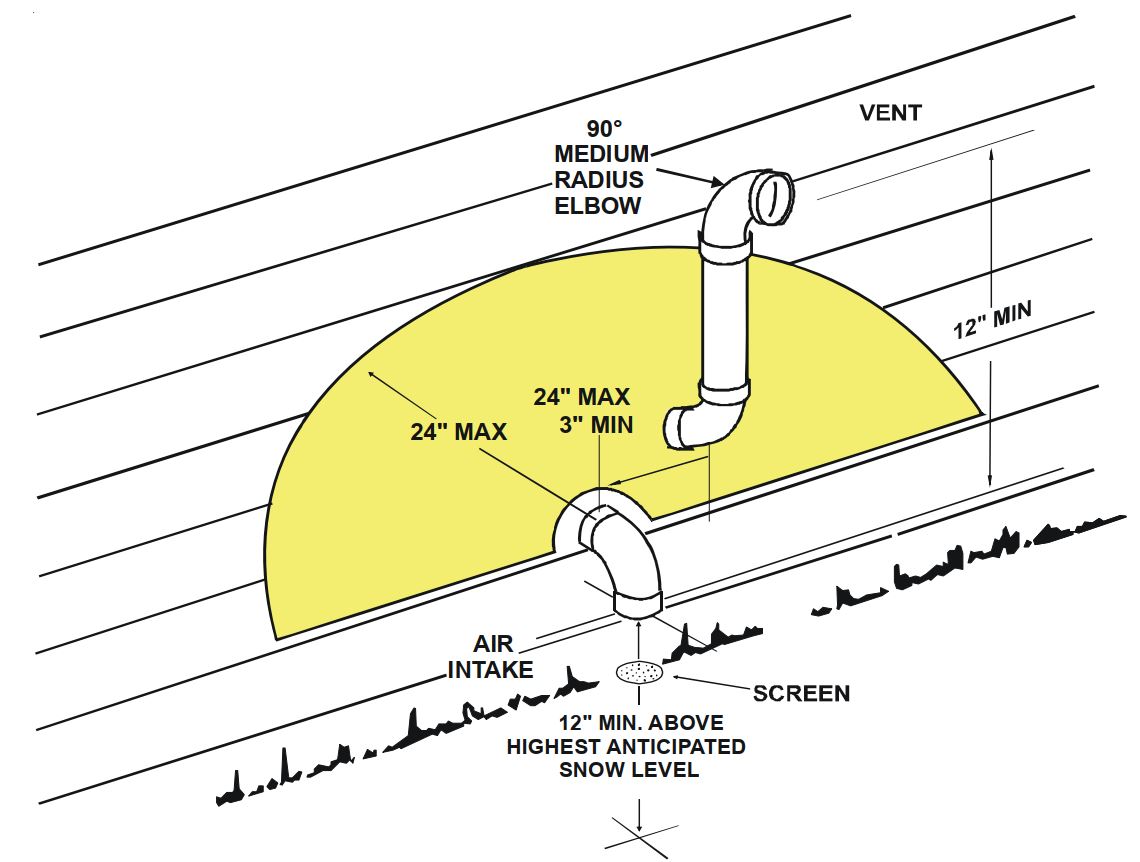
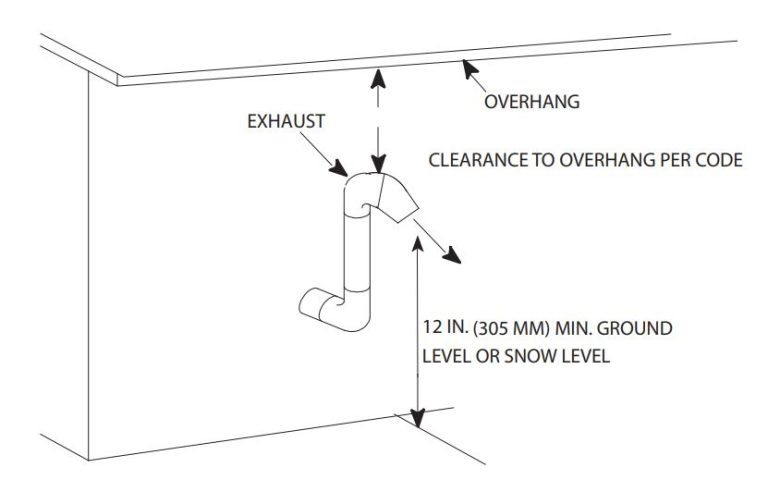
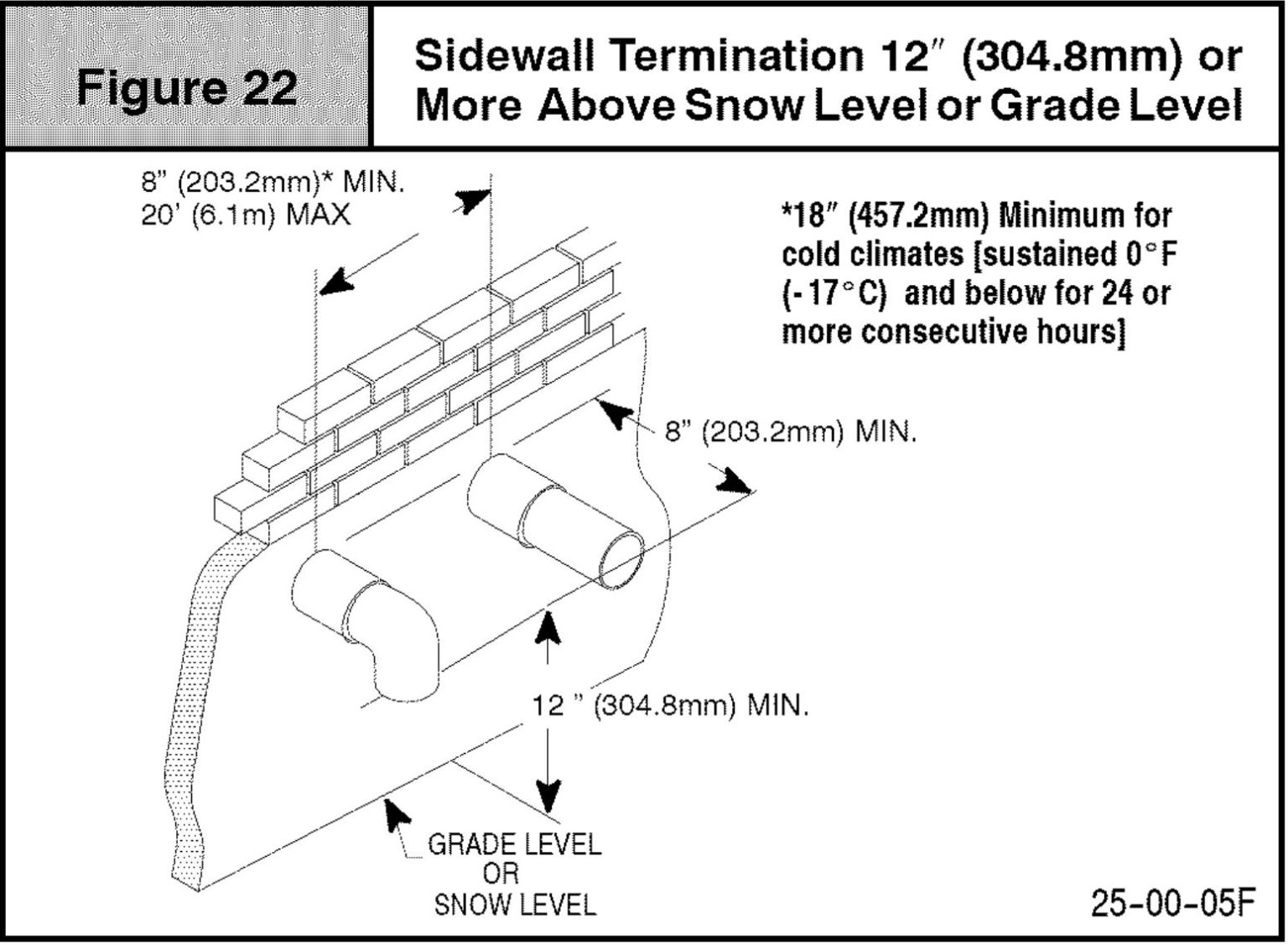
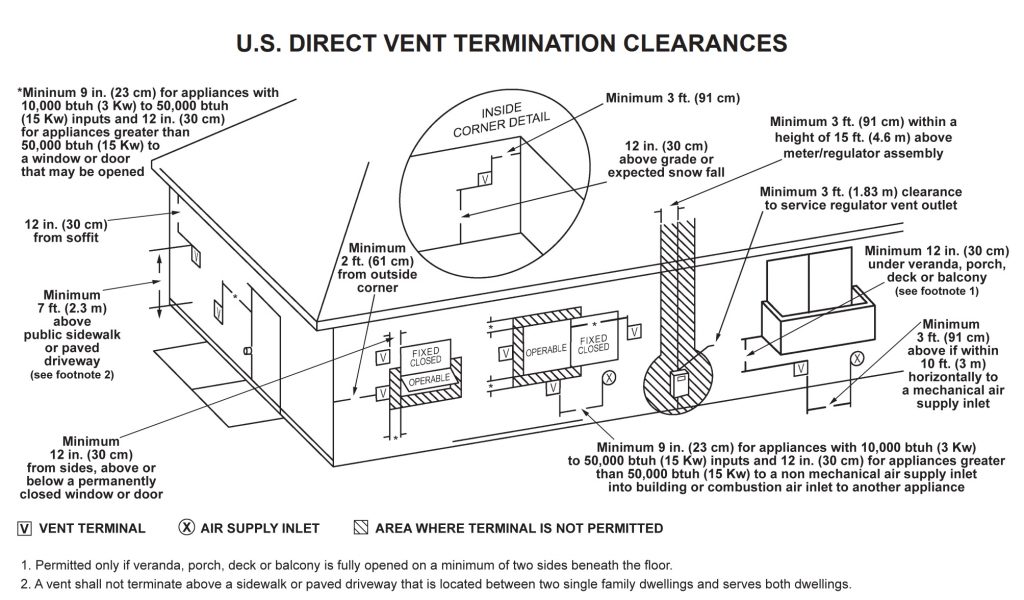
- Termination Requirements: Vent termination points must be located away from windows, doors, and air intakes to prevent exhaust gases from re-entering the building. The IFGC specifies minimum distances from these openings. Terminations should also be designed to prevent snow or debris from blocking the vent.
- Condensate Drainage: High-efficiency furnaces produce significant amounts of condensate, which must be properly drained away from the furnace. Condensate drains must be properly sized and routed to an approved drainage location. Freeze protection measures, such as heat tape, may be necessary in colder climates.
Materials Used in High-Efficiency Venting
Selecting the correct venting material is essential for the longevity and safety of the system. Here's a breakdown of commonly used materials:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A cost-effective and widely used material for venting high-efficiency furnaces. PVC is resistant to corrosion from acidic condensate but has a lower temperature rating compared to CPVC.
- CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride): Offers higher temperature resistance than PVC, making it suitable for furnaces with higher exhaust gas temperatures. CPVC is also more resistant to certain chemicals.
- Polypropylene: An increasingly popular option due to its excellent chemical resistance and high-temperature rating. Polypropylene venting systems are often used in condensing boilers and other high-temperature applications.
Important Note: Always refer to the furnace manufacturer's instructions for approved venting materials. Mixing and matching different venting materials is generally not permitted and can compromise the integrity of the system.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is critical for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of a high-efficiency furnace venting system. Here are some key best practices:
- Follow Manufacturer's Instructions: Always adhere to the furnace manufacturer's installation instructions. These instructions provide specific guidelines for vent sizing, material selection, and termination requirements.
- Use Approved Fittings and Sealants: Use only fittings and sealants that are specifically designed for the selected venting material. Ensure that all connections are properly sealed to prevent leaks.
- Inspect for Leaks: After installation, thoroughly inspect the venting system for leaks using a leak detection solution or electronic leak detector. Address any leaks immediately.
- Combustion Analysis: Perform a combustion analysis to verify that the furnace is operating efficiently and safely. This test measures the levels of carbon monoxide, oxygen, and other gases in the exhaust stream.
- Proper Support: Securely support the venting system to prevent sagging or damage. Follow the vent manufacturer's recommendations for support spacing.
Career Paths in High-Efficiency Furnace Installation and Service
The demand for skilled HVAC technicians specializing in high-efficiency furnace installation and service is growing. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the job outlook for HVAC technicians is projected to grow 6 percent from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations. About 38,000 openings for HVAC mechanics and installers are projected each year, on average, over the decade. The median annual wage for HVAC mechanics and installers was $59,620 in May 2023.
Several career paths are available for individuals interested in this field:
- HVAC Technician: Install, maintain, and repair heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, including high-efficiency furnaces.
- HVAC Installer: Specialize in the installation of new HVAC systems, including high-efficiency furnaces and their associated venting systems.
- HVAC Service Technician: Focus on the maintenance and repair of existing HVAC systems, including troubleshooting venting issues and performing combustion analysis.
- HVAC Sales Engineer: Design and sell HVAC systems to commercial and residential clients, requiring a thorough understanding of high-efficiency furnace technology and venting requirements.
Certifications and Training
Earning relevant certifications can significantly enhance your career prospects in the HVAC industry. Some popular certifications include:
- NATE (North American Technician Excellence): This is a leading certification for HVAC technicians, demonstrating competency in specific areas such as gas heating. NATE certification is highly valued by employers.
- EPA Section 608 Certification: Required for technicians who handle refrigerants. Although not directly related to venting, it's a fundamental certification for HVAC professionals.
- Manufacturer-Specific Training: Many furnace manufacturers offer training programs on their specific products, including installation and venting procedures. Completing these programs can enhance your expertise and marketability.
Formal training programs, such as apprenticeships and vocational schools, provide a solid foundation in HVAC fundamentals and specialized skills related to high-efficiency furnace venting. Look for programs accredited by organizations like HVAC Excellence.
The Role of Employers
Employers play a crucial role in ensuring that their technicians are properly trained and equipped to handle high-efficiency furnace venting. This includes:
- Providing Ongoing Training: Offer regular training sessions on new technologies, code updates, and best practices.
- Investing in Proper Equipment: Equip technicians with the necessary tools and equipment for installing and servicing venting systems, including combustion analyzers and leak detectors.
- Promoting Certification: Encourage technicians to pursue relevant certifications, such as NATE and EPA 608.
- Prioritizing Safety: Emphasize the importance of safety procedures and provide adequate safety equipment.
Employers can also attract and retain top talent by offering competitive salaries and benefits. According to industry surveys, HVAC technicians with specialized skills in high-efficiency systems and venting can command higher salaries. A skilled and certified HVAC technician working on high-efficiency furnaces and venting can expect to earn between $50,000 and $80,000 annually, with experienced specialists potentially exceeding this range.
The Future of High-Efficiency Venting
The HVAC industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and regulations emerging regularly. Staying up-to-date on the latest trends in high-efficiency furnace venting is essential for success. Some key trends to watch include:
- Smart Venting Systems: Advanced venting systems that incorporate sensors and controls to optimize airflow and prevent condensation.
- Improved Venting Materials: Ongoing research and development of new venting materials with enhanced durability, temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- Stricter Energy Efficiency Standards: As energy efficiency standards become more stringent, the demand for high-efficiency furnaces and proper venting will continue to grow.
By investing in training, certifications, and the latest technologies, HVAC professionals can position themselves for success in this dynamic and rewarding field. With the increased focus on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, the demand for expertise in high-efficiency furnace venting will only continue to rise, creating ample opportunities for skilled and knowledgeable technicians. A career in HVAC, especially with a focus on high-efficiency systems, offers stability, good earning potential, and the satisfaction of contributing to a more sustainable future.
"The future of HVAC is intertwined with energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. Mastering high-efficiency furnace venting is a critical skill for any aspiring HVAC professional."